Advance in application of dermoscopy for onychomycosis diagnosis
Xiao Liu and Zhi-Yuan Yao*
Department of Dermatology and Venereology,China-Japan Friendship Clinical Medical College of Peking University,Beijing 100029,China.
Introduction
Onychomycosis refers to all kinds of fungal infections of nail plate and nail bed,including those caused by dermatophytes,non-dermatophytes,and Candida species[1].Onychomycosis is the most common nail disease in adults,accounting for 10%-30%of all infectious diseases,and 50%of all nail disorders[2-5].The most common tests used to diagnose onychomycosis are direct microscopic examination,mycological culture,histopathologic examination,and polymerase chain reaction-based tests[2,6].Because of the special structure of the sampling area,patients often experience pain during nail abrasion for the collection of samples.Furthermore,the sensitivity of onychomycosis diagnosis is not satisfied.
Dermoscopy is a novel,noninvasive examination technique that links clinical dermatology and histopathology by enabling the observation of the epidermis,dermal papilla,and deep dermis,which cannot be seen by the naked eye.The principle of dermoscopy is to eliminate reflected lightviathe use of polarizing photography.Dermoscopy is widely used for the diagnosis of melanocytic and nonmelanocytic lesions,and inflammatory and infectious diseases,including nail diseases[7-8].
In the diagnosis of onychomycosis,dermoscopy is an effective assistant method that is noninvasive,and can help improve the diagnostic sensitivity because that dermoscopy can enable the visualization of not only nail plate,but also nail folds,nail matrix,nail bed,and the fine structure and vessels of the free margin of the nail[9].The whole nail can be seen only at 10×magnification,but the observation data and accuracy is improved with the increase in magnification from 20×to 70×[10].Because of the curvature and hardness of the nails,it is difficult to use dermoscopy to closely observe the nail surface.Lesions of the nail plate surface can be directly observed using a dermoscope without medium;however,the evaluation of nail pigmentation,nail separation,and the distal nail margin requires the use of gel as an interface[11].
Onychomycosis characteristics in dermoscopy
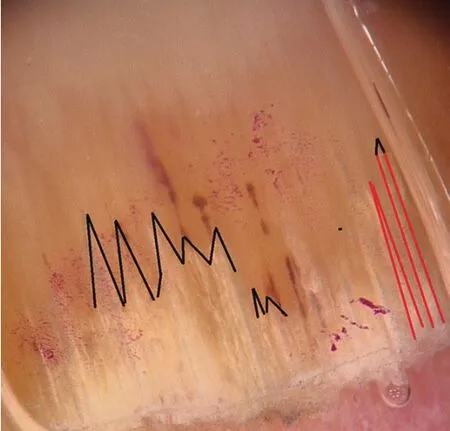
Figure 1 The black lines represent the jagged proximal edge with spikes,the red lines represent the longitudinal striae.
The four dermoscopic characteristics specific to onychomycosis are a jagged proximal edge with spikes,longitudinal striae,a ruin appearance,and longitudinal ridges along the nail bed(Figure 1),and it has identified by Jesus-Silvaet al.in 2015[12].The spiked characteristic refers to the jagged edge of the proximal nail;the longitudinal striae characteristic indicates invasive growth of dermatophytes along the nail plate toward the nail lunula;the linear edged characteristic describes a lesion with a smooth linear edge;the distal irregular characteristic shows comminution of thickened nail plate[12-13].
The incidence of each feature varies in different subtypes of onychomycosis.Some characteristics,such as the spiked characteristic and the longitudinal striae characteristic,are specific for the diagnosis of onychomycosis.The characteristic of onychomycosis is a ruin appearance with longitudinal ridges along the nail bed,longitudinal striae,and a jagged edge of the proximal nail[14].
It is difficult to diagnose fungal melanonychia(FM),as FM has a similar presentation to melanonychia caused by other factors.A retrospective study showed that FM has several characteristics in dermoscopy.The commonest characteristic seen in FM is multicolored(defined as the presence of more than two colors),of which yellow is the commonest.The second top characteristic in FM is longitudinal and nonlongitudinal homogenous.White or yellow streaks,subungual hyperkeratosis,and a reverse triangular characteristic can also be seen in FM[15].A previous case report described the characteristics of FM as subungual hyperkeratosis,a distally wider homogeneous brown-black pigmented band,and wide yellow streaks with a focal reddish hue[16].However,more reports are needed to support and further clarify the dermoscopic pattern of FM.
Onychomycosis subtypes under dermoscope
Onychomycosis has following five subtypes:distal and lateral subungual onychomycosis(DLSO),total dystrophic onychomycosis(TDO),superficial white onychomycosis(SWO),proximal and lateral subungual onychomycosis(PSO),and endonyx onychomycosis(EO).
DLSO is the commonest subtype of onychomycosis.DLSO always presents with thickening of the distal and lateral regions of the nail,and a rugged and damaged nail plate surface.Under dermoscopy,there are several patterns that are present simultaneously only in DLSO.First,there is an onycholytic area with a jagged proximal edge with spikes.A spike is a white longitudinal indentation that points to the proximal nail fold,which corresponds with the proximal progression of the fungi[9,17-18];this characteristic is best identified under 20×magnification(Figure 2A).Second,there are longitudinal striae with irregular matted pigmentation of different colors(changing from white to yellow,orange,and brown),which are best visualized under 40×magnification(Figure 2B).Third,there may be black spots and balls in DLSO;however,these features are not specific,as subungual hemorrhage can present with the same pattern.
A retrospective study found that the specificities of the spiked pattern and longitudinal striae pattern in identifying DLSO were both 100%,while the sensitivities of the two patterns were 100%and 86.5%,respectively[17].A case-control study showed that the presence of a jagged proximal edge with spikes was 100%sensitive for the diagnosis of DLSO,while the sensitivity of longitudinal striae was 82.5%[19].Another study reported that longitudinal striae and jagged proximal edges were seen in all 60(100%)cases of DLSO[20].
In TDO,the whole surface of the nail plate is completely destroyed,with nail thickening,grayish yellow or taupe,and crumbling and exfoliation.All four patterns can be seen in TDO;however,the commonest pattern is the distal irregular pattern(Figure 2C).A study of 178 patients with onychomycosis showed that the distal irregular pattern was present in 67 patients,of which 41(61.76%)were clinically compatible with TDO[13].TDO was also diagnosed in 56.41%of those with skipped pattern,44.68%of those with the longitudinal striae pattern,and 58.8%of those with a linear edged pattern[13].
SWO usually has some adherent and irregular white patches on the surface of nail plate.Under dermoscopy,SWO is mainly characterized by the presence of irregular,white-to-yellow colored,opaque,friable spots(Figure 2D).This feature must be distinguished from leukonychia.However,there are few reports of SWO in the literature.
PSO is an uncommon subtype of onychomycosis.The main symptoms of PSO are thickening of the nail,and a rugged and damaged appearance of the nail lunula and nail root.Dermoscopy reveals a white pigmentation at the nail lunula[21].Till now,no study has yet summarized the dermoscopic characteristics of PSO.
EO is rare in China.The lesion in EO is limited to the nail plate,and does not invade under the nail plate.The nail plate becomes white or gray-white,without obvious thickening,atrophy,or inflammation.The dermoscopic models of EO need further clarification.
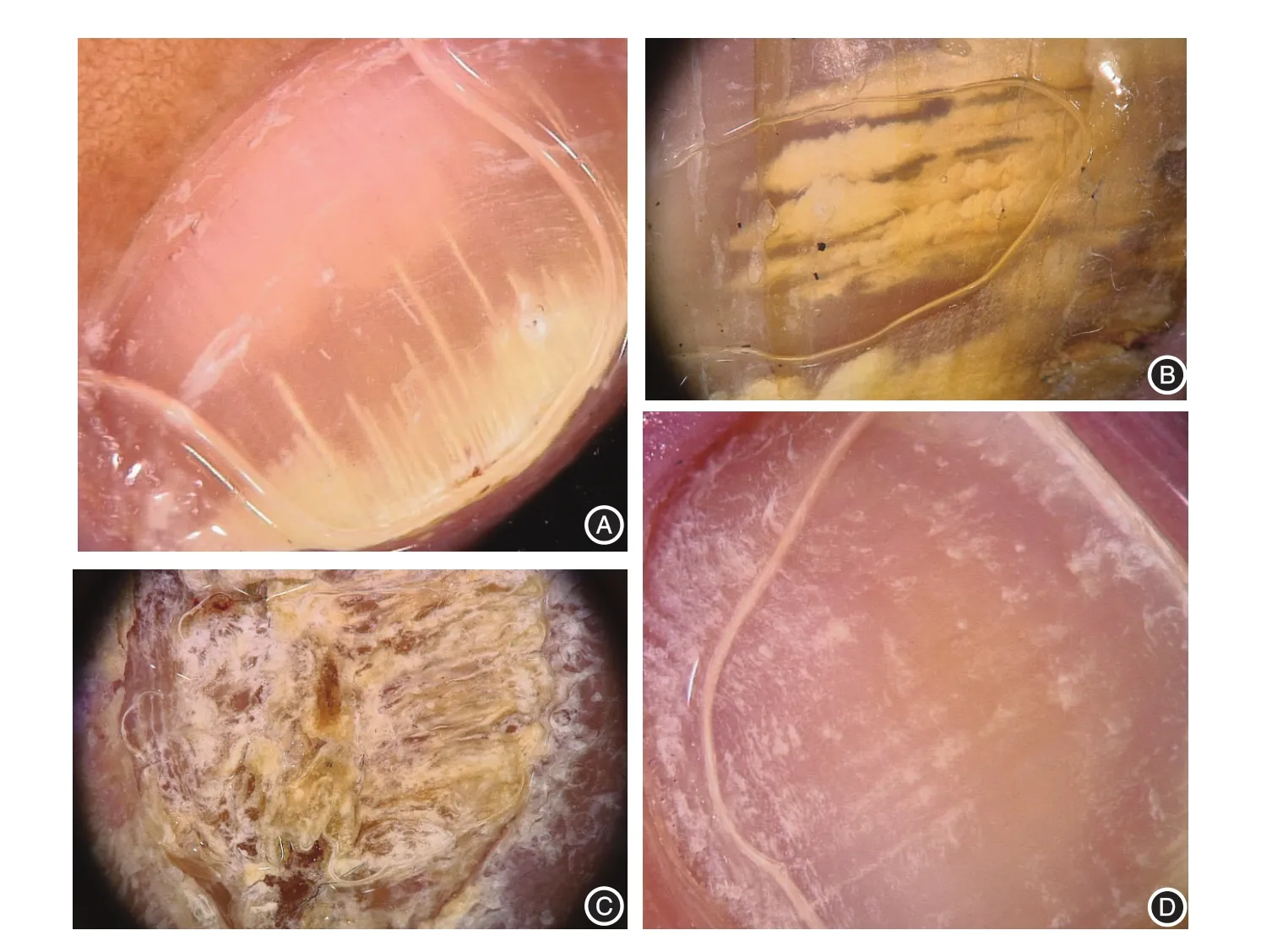
Figure 2 Dermoscopic characteristics of onychomycosis subtypes.A and B:distal and lateral subungual onychomycosis(DLSO)subtype.A:Jagged proximal edge with spikes on the onycholytic area,and longitudinal striae(20×magnification).B:Longitudinal striae with irregular,matted,yellow colored pigmentation(40×magnification).C:Total dystrophic onychomycosis(TDO)subtype.A ruin appearance can be seen in total dystrophic onychomycosis.D:Superficial white onychomycosis(SWO)subtype.White,opaque,friable spots can be seen in superficial white onychomycosis.
Dermoscopy in the differential diagnosis of onychomycosis
Due to the special structure of the nail region,it is difficult to accurately diagnose nail disease by visual observation alone.Therefore,dermoscopy is being increasingly applied in the differential diagnosis of onychomycosis such as longitudinal melanonychia(nevus of the nail matrix and nail melanoma),inflammatory onychosis(nail psoriasis and lichen planus),and dystrophic onychosis.
Longitudinal melanonychia
Dermoscopy can be used to distinguish benign and malignant longitudinal melanonychia from onychomycosis.Benign lesions(such as nevus of the nail matrix)tend to mainly present with longitudinal brown parallel lines with regular widths and inter-spaces,plus pigmentation in the nail cuticle(Figure 3A).
In contrast,the presence of melanoma is suggested when the widths and interspaces of these longitudinal lines become irregular or the parallel structures are interrupted;the Hutchinson phenomenon is also a common dermo-scopic feature of nail mela-noma.
Inflammatory onychosis
In cases of nail psoriasis(Figure 3B),dermoscopy of the nail bed is very helpful in patients with fingernail onycholysis,as it enables the visualization of the erythematous border surrounding the distal edge of the detachment.The commonest features of nail psoriasis include longi-tudinal fusiform and serpentine-like hemorrhages,pitting,distal onycholysis,and salmon patches,while dilated capillaries can also be seen on the nail bed[10].The first reported novel dermoscopic sign of nail psoriasis was the “pseudo-fiber sign”,which is defined as the presence of red and black filamentous structures located along the cuticle or underneath the distal free edge on the hyponychium or exposed areas where the nail plate has detached[22].
In nail lichen planus,there are longitudinal fissures of the nail plate,trachyonychia,anonychia,and newly formed nail plate.The newly formed nail plate is located close to the proximal nail fold,and can be seen during early monitoring of the treatment response[23].Capillaroscopic changes are not seen in lichen planus,and this can be used to distinguish lichen planus from psoriasis of the nail.
Dystrophic onychosis
In dystrophic onycholysis,the nail detachment areas have smooth linear edges(Figure 3C and 3D).
Dermoscopy in nail sampling
The determination of fungal etiology is the gold standard for the diagnosis of onychomycosis.The most common diagnostic tests are direct microscopic examination and mycological culture,which have respective sensitivities of 72%-80%and 20%-53%[18].One cause of decreased diagnostic sensitivity is the improper selection of sample materials.
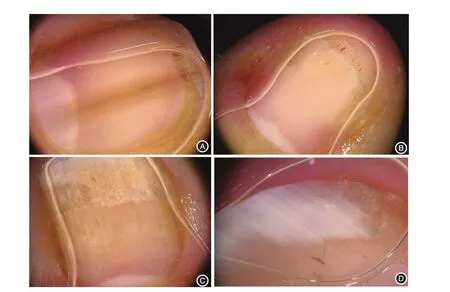
Figure 3 Dermoscopy in the diagnosis of onychomycosis.A:Longitudinal brown parallel lines with regular widths and interspaces can be seen in the nevus of the nail matrix.B:Dilated capillaris on the nail bed and“pseudo-fiber sign”.C and D:Smooth linear edges of the nail detachment area can be seen in onycholysis.
In recent years,it has been found that samples by dermoscope for diagnostic testing can improve the sensitivity of direct microscopic examination and mycological culture,because dermoscope-guided nail abrasion enables the clinician to obtain better quality mycological samples[24].A study that described the dermoscopic characteristics, direct microscopic characteristics,and mycological culture and pathology results of 502 cases reported that all of these tests detected mycelium in samples obtained from“damaged”subungual keratosis,and that dermoscopy revealed a longitudinal jagged proximal edge with spikes from distal to proximal[25].The advantage of dermoscope-guided nail sampling can effectively improve the sensitivity of fungal microscopy and culture for accurativity of diagnosis of onychomycosis.
Conclusion
With the progression of research,the application of dermoscopy in onychomycosis is expanding.The dermoscopic characteristics specific to onychomycosis are summarized as a jagged proximal edge with spikes,longitudinal striae,a ruin appearance,and longitudinal ridges along the nail bed.In particular,the presence of a jagged proximal edge and longitudinal striae are 100%specific for the diagnosis of DLSO.The use of dermoscopy can effectively improve the sensitivity of fungal microscopy and culture.However,at present,dermoscopy has limitations in the diagnosis of onychomycosis.Most studies have concentrated on DLSO,while some have focused on the other subtypes of onychomycosis.Studies with a large sample size are needed to further clarify the dermatological features of onychomycosis,especially in rare subtypes,and to further clarify the relationship between these dermoscopic characteristics,clinical manifestations,and mycological examination findings.In summary,the use of dermoscopy can effectively improve the accuracy and sensitivity of onychomycosis diagnosis,and can reduce the need for invasive diagnostic surgery.Dermoscopy may become the first step in the diagnosis of onychomycosis,especially in DLSO.
- 國際皮膚性病學(xué)雜志的其它文章
- Paraneoplastic pemphigus comorbid with cardiac cancer and duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumors:a rare case report
- Reactive perforating collagenosis
- Sun?protection knowledge and strategies of Chinese dermatologists:a nation?wide,questionnaire?based survey
- Initial presentation of acute myeloid leukemia in a patient with cutaneous myeloid sarcoma
- Persistent papules with adult?onset Still’s disease:a case report
- Primary vulvar melanoma in a 27?year?old pregnant woman:a case report and literature review

