Vertebral Hemangioma 椎體海綿狀血管瘤
Key Facts
Definition: Benign vertebral body vascular tumor.
Classic imaging appearance: Hypodense lesion (CT) with coarse, verticallyoriented trabeculae; hyperintense (MRI) on both T1WI and T2WI.
Most common spinal axis tumor: (1) Incidental lesion identified on imaging performed for unrelated reasons.(2) Rarer presentation (clinical or radiographic) is “aggressive hemangioma”.
Radiographic diagnostic criteria are lesion growth, bone destruction, vertebral collapse, absence of fat in lesion, and active vascular component.
May extend epidurally and cause cord compression.
CT Findings
Best imaging clue: Well-circumscribed, hypodense lesion with coarse vertical trabeculae (“white polka dots”) on axial CT.
Hypodense lesion centered in vertebral body.
Sparse, thickened trabeculae surrounded by hypodense fat.
“Spotted” appearance on axial images.
Aggressive lesions show avid contrast enhancement.
MR Findings
Typical “benign” (fatty stroma) hemangioma: (1) T1WI--hyperintense, with avid contrast enhancement.(2) T2WI--hyperintense.(3) Occasional radiographically benign lesions are isointense or hypointense on T1WI, and difficult to distinguish from metastases.
“Aggressive”(“malignant”) hemangioma: (1)T1WI--isointense to hypointense,with avid contrast enhancement.(2) T2WI--hyperintense.(3) Pathologic fracture or epidural extension common.(4) Clinically aggressive hemangiomas are usually radiographically aggressive as well.
Other Modality Findings
Plain film: Vertebral body lesion with coarse vertical trabeculae resembling corduroy.
Angiography: Normal to hypervascular stain; aggressive lesions stain vividly.
Imaging Recommendations
Both CT and MR can permit a specific diagnosis.MR best demonstratesaggressive characteristics.Sagittal and axial T1WI images most useful to characterize composition.Axial T2WI and enhanced T1WI best for characterizing epidural extent and cord compromise (aggressive lesions).Axial bone algorithm CT is most useful for characteristic features that distinguish hemangioma from metastatic lesion.
Angiography unnecessary unless embolization is being considered.
醫(yī)學(xué)詞匯注釋與簡(jiǎn)要講解
vertebral 椎體的
hemangioma 血管瘤
trabeculae 骨小梁
vertebral collapse 椎體塌陷
epidural 硬膜外的
polka dot 圓點(diǎn)、波點(diǎn)
sparse 稀疏的
stroma 基質(zhì)
pedicles 椎弓根
STIR sequence 短TI反轉(zhuǎn)恢復(fù)序列(壓脂)
Stromata= stroma 基質(zhì)
myelopathy 脊髓病變
radiculopathy 神經(jīng)根病
vertebroplasty 椎體成形術(shù)
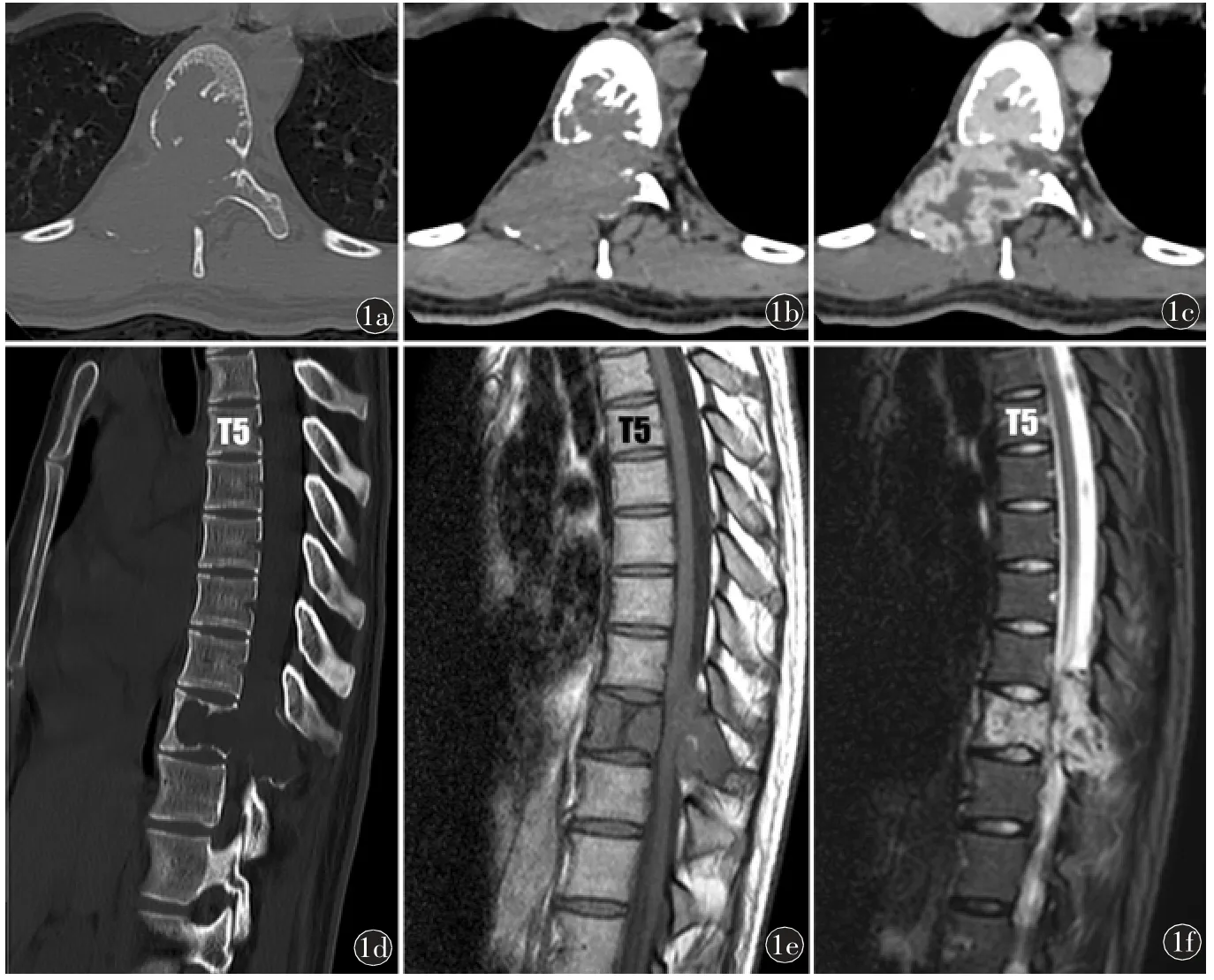
Fig 1 Typical (aggressive) hemangioma: a)~c)Axial CT shows a well-circumscribed T10 vertebral lesion with sparse, thickened trabeculae, destructive expansion into the epidural space and strong enhancement.d)Sagittal CT reconstruction.e)T1WI and f)T2WI show an iso-hyperintense T10 vertebral lesion with epidural expansion.
Differential Diagnosis
Vertebral metastases: (1) Characteristically extends into pedicles.(2) Hypointense on T1WI,hypointense to hyperintense(to marrow)on T2WI.(3)T1WI sequence helps distinguish from benign hemangioma.(4) May be difficult to distinguish from “vascular” or“agressive” hemangioma on CT.
Focal Fatty Marrow: (1) Incidental rounded focus of marrow fat that is conspicuous on MRI.(2)STIR sequence will show marked lesion hypointensity.(3)Hemangiomas typically retain some high signal due to vascular components.
Pathology
General Path Comments: (1) Slow growing; (2) Capillary, cavernous or venous origin; (3) Cavernous hemangiomas most common.
Epidemiology: (1) Common 10%-12% of adult population.(2) 25%-30%multiple; particularly in thoracic spine.(3) Peak incidence fourth to sixth decades.(4) Benign lesions M = F; aggressive lesions slightly more commonin women.
Gross Pathologic-Surgical Features: (1) Vast majority confined to vertebral body proper.(2) May be small or occupy entire vertebral body.(3) Uncommonly involve posterior elements/pedicles (10%-15%).(4) Thoracic lesions are more often aggressive than at other locations.
Microscopic Features: (1) Benign lesions show mature, thin-walled, endothelium-lined capillary and cavernous sinuses interspersed among sparse,osseous trabeculae and fatty stromata.(2) Aggressive lesions contain less fat and more vascular stromata.
Clinical Issues
Presentation: (1) Benign hemangiomas are incidentally discovered.(2) Symptomatic (aggressive) hemangiomas present with intense, localized spinal pain,myelopathy and/or radiculopathy from osseous expansion, pathologic fracture, and/or epidural extension.
Treatment: (1) Benign (fatty) hemangiomas--no treatment necessary.(2)Aggressive hemangiomas--first-line therapy is vertebroplasty in conjunction with embolization and surgery as needed.
Prognosis: (1) Benign (fatty) hemangiomas--incidental lesions, excellent prognosis.(2) Aggressive vascular hemangiomas--variable depending on size of lesion, degree of epidural extension, and presence/absence of cord compression.