Bullous Pemphigoid: Readability, Quality, and Treatments of Online Health Resources
Dear Editor,
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune blistering disease that disproportionately affects the elderly,1a population in which limited health literacy is a known barrier to health outcomes.The 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy survey found that among patients older than 65,59%had“basic”or“below basic”literacy,and only 3%were “proficient.”2Despite increased utilization of the internet to seek health information,including among the elderly,3the accessibility of online BP resources remain unknown.Herein,we examine the readability and quality of online resources on BP.
“Bullous pemphigoid” was searched on Google, Yahoo,and Bing on February 5, 2020. The first 50 results from each site were evaluated. Sites that were duplicates, blogs,subscription-based,intendedforphysicians,orunrelatedtoBP were excluded. Readability was assessed using six validated readability scales(Flesch Reading Ease,Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level, Gunning-Fog Index, SMOG Index, Coleman-Liau Index, Automated Readability). Quality was assessed with JAMA Benchmark and Discern Instrument. Two reviewers independently used the modified Discern Instrument4;discrepancies within two points were averaged,and discrepancies greater than two points were discussed to consensus.Articles authored by dermatologists were compared to those by non-dermatologists, and differences between average readability and Discern score were assessed using t-test.Individual treatments discussed on each site were tabulated.
Of 150 websites reviewed, 24 met inclusion criteria(Table 1).The averagegrade level was 11.9(range6.7–15.3),exceeding the 6thgrade level recommended by American Medical Association. The majority (21/24, 87.5%) of websites were rated as “fair” or less than “fair” using the Discern Instrument. The resources with the highest quality per Discern Instrument (patient info, 55.5 and National Organization for Rare Disorders, 54) had average grade levels of 9.8 and 13.3, respectively. Only a third of the websites met all four criteria of the JAMA Benchmark.In comparing articles written by dermatologists versus nondermatologists,there was no significant difference in average grade level (12 vs. 12, P=0.87) or quality of content per Discern score(41 vs.40,P=0.88).
The most commonly discussed treatments included systemic steroids (95.8% of websites), topical steroids(87.5%),steroid-sparing traditional immunosuppressants(83.3%),and oral antibiotics(79.2%).Biologics(41.7%)and oral nicotinamide (29.2%) were less frequently discussed. Only four websites comprehensively discussed all main treatment modalities for BP, including topical steroids, systemic steroids, oral nicotinamide, oral antibiotics, steroid-sparing traditional immunosuppressants,and biologics. More recent treatment developments were not included: omalizumab was discussed in 8.3% of the websites despite increasing evidence for its efficacy.5
Online health resources for BP fail to meet recommended reading levels.Quality of websites were variable:nearly half did not cite authorship and only a sixth comprehensively discussed treatment modalities. The difficult readability of online BP resources has been similarly identified in readability studies on other dermatologic topics.6Notably,although a prior study examining epidermolysis bullosa online resources reported dermatologist-created resources to be less readable,7our study found no difference in readability or quality of online BP resources authored by dermatologists versus non-dermatologists. However, the average dermatologist-authored BP article still required a 12thgrade reading level. BP disproportionately affects the elderly, a population in which health literacy has been identified as a barrier to improved health outcomes.Given the prevalence of BP in the elderly, internet access and utilization may already be limited in this patient population.Inappropriately high readability levels of online resources can further pose a secondary barrier to health information access.Even for patients with proficient health literacy,the majority of sites do not discuss all treatment modalities.
Our data highlights the difficult readability and limited quality of online BP resources,which represent significant impediments to care. Improving online BP resources will increase patients’ access to and understanding of healthinformation.Dermatologists should take an active role in vetting online resources for their patients and when contributing to online content,should prioritize readability and accessibility.
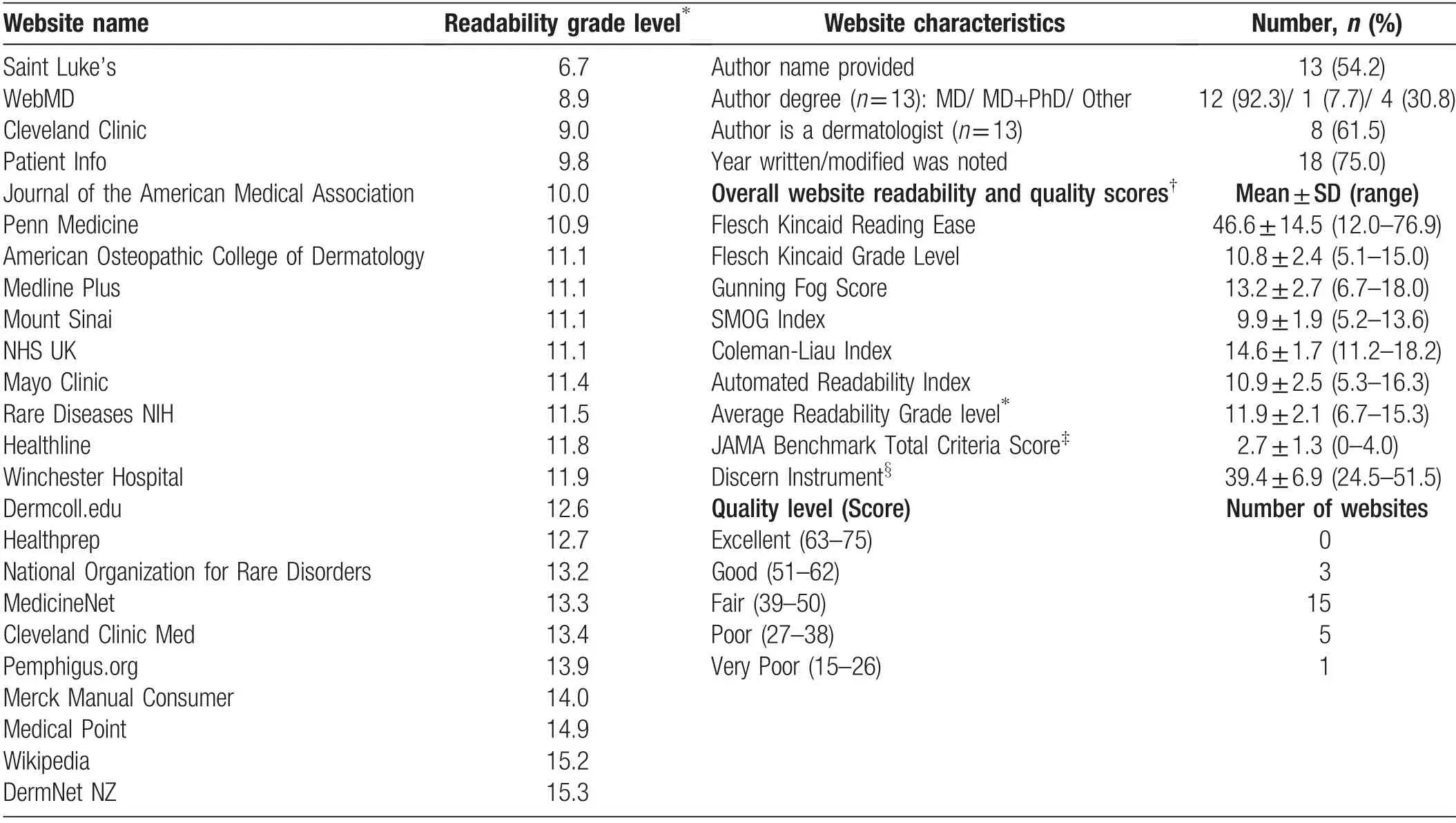
Table 1 Most searched bullous pemphigoid educational website characteristics (n=24).
Terri Shih
David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA
Natalie Villa
Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH 03766, USA
Jennifer L. Hsiao?
Department of Dermatology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90007, USA
Vivian Y. Shi
Dermatology of Dermatology, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR 72205, USA
?Corresponding author:Email:j.hsiao.publications@gmail.com
- 國際皮膚性病學(xué)雜志的其它文章
- Nail Changes as the Initial Sign of Psoriasis:A Case Report
- Tale of Two Alopecias: Alopecia Areata and Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia Occurring in the Same Patient
- Cutaneous Manifestations and Treatment Advances of Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma
- Bowen’s Disease on the Left Fifth Finger Successfully Treated with Photodynamic Therapy: A Case Report
- Concurrence of Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma in A Patient with Generalized Actinic Keratosis: A Case Report
- Nail Psoriasis: Treatment Options and Management Strategies in Special Patient Populations

