Current Situations, Evolution Trend, and Improvement Measures of Soil Organic Matter in Cultivated Land of Northeast China
Dan SONG
Liaoning Agricultural Development Service Center, Shenyang 110034, China
Abstract The data of cultivated land quality monitoring sites, and the current situations and evolution trend of soil organic matter in cultivated land in Northeast China were analyzed. Then, the causes for low organic matter content were discussed. Finally, it came up with pertinent soil improvement recommendations, including actively promoting the quality protection technology model of cultivated land such as straw returning in accordance with local conditions, expanding organic fertilizer sources and increasing application of organic fertilizers, implementing reasonable crop rotation, planting green manure crops such as legumes, and realizing the combination of land use and land cultivation, establishing a reasonable fertilization system, combining organic and inorganic fertilizers with scientific fertilization, increasing fertilizer efficiency and reducing the application of chemical fertilizers, increasing financial investment and promoting the integration of funds related to cultivated land protection.
Key words Northeastern region of China, Monitoring site, Soil organic matter, Improvement measures
1 Introduction
Northeastern region of China includes Heilongjiang Province, Jilin Province, Liaoning Province (except Chaoyang City) and the Daxing’an Mountain Range area in the northeastern part of Inner Mongolia. The total cultivated land area of northeastern region is about 22 million ha, accounting for 18.24% of China’s total cultivated land area. In this region, the planting system is one crop a year, and vast land, fertile soil and suitable climate provide unique conditions for grain production. This region has always been China’s most important grain production base and is reputed as "China’s largest strategic reserve base for commodity grains". The region mainly includes four secondary agricultural areas, namely, Liaoning Plain hilly agriculture and forest area, Songnen Plain and Sanjiang Plain agricultural area, Changbai Mountain forestry and agricultural area, and Xing’an Mountains forest area. The main soil types of cultivated land are black soil, chernozem, dark brown soil, brown soil,etc.Cultivated land in this region has high quality, and the intermediate and high level cultivated land accounts for more than 94% of the total cultivated land area. The main obstacle factors include soil erosion, soil desertification, acidification, salinization and poor soil nutrients,etc.This part of the cultivated land has low soil fertility and water retention capacity and poor drainage, and is vulnerable to drought and flood disasters.
2 General situation of monitoring sites in northeastern region
In 2018, there were 168 cultivated land monitoring sites in the northeastern region. Specifically, there were 39 monitoring sites in Liaoning Plain hilly agriculture and forest area, accounting for 23.2% of the total monitoring sites in the northeastern region; 105 monitoring sites in Songnen Plain and Sanjiang Plain agricultural area, accounting for 62.5%; 15 monitoring sites in Changbai Mountain forestry and agricultural area, accounting for 8.9%, 9 monitoring sites in Xing’an Mountains forest area, accounting for 5.4% (Table 1).
In accordance with the Standards for Classification Indicators for Quality Monitoring of Cultivated Land in Nine Agricultural Regions and Provincial Levels in China (for Trial Implementation) issued and distributed by Cultivated Land Quality Monitoring and Protection Center, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China[1], the classification standards of main indicators for quality monitoring of cultivated land in northeastern region are shown in Table 2.
3 Current situation and evolution trend of soil organic matter in cultivated land
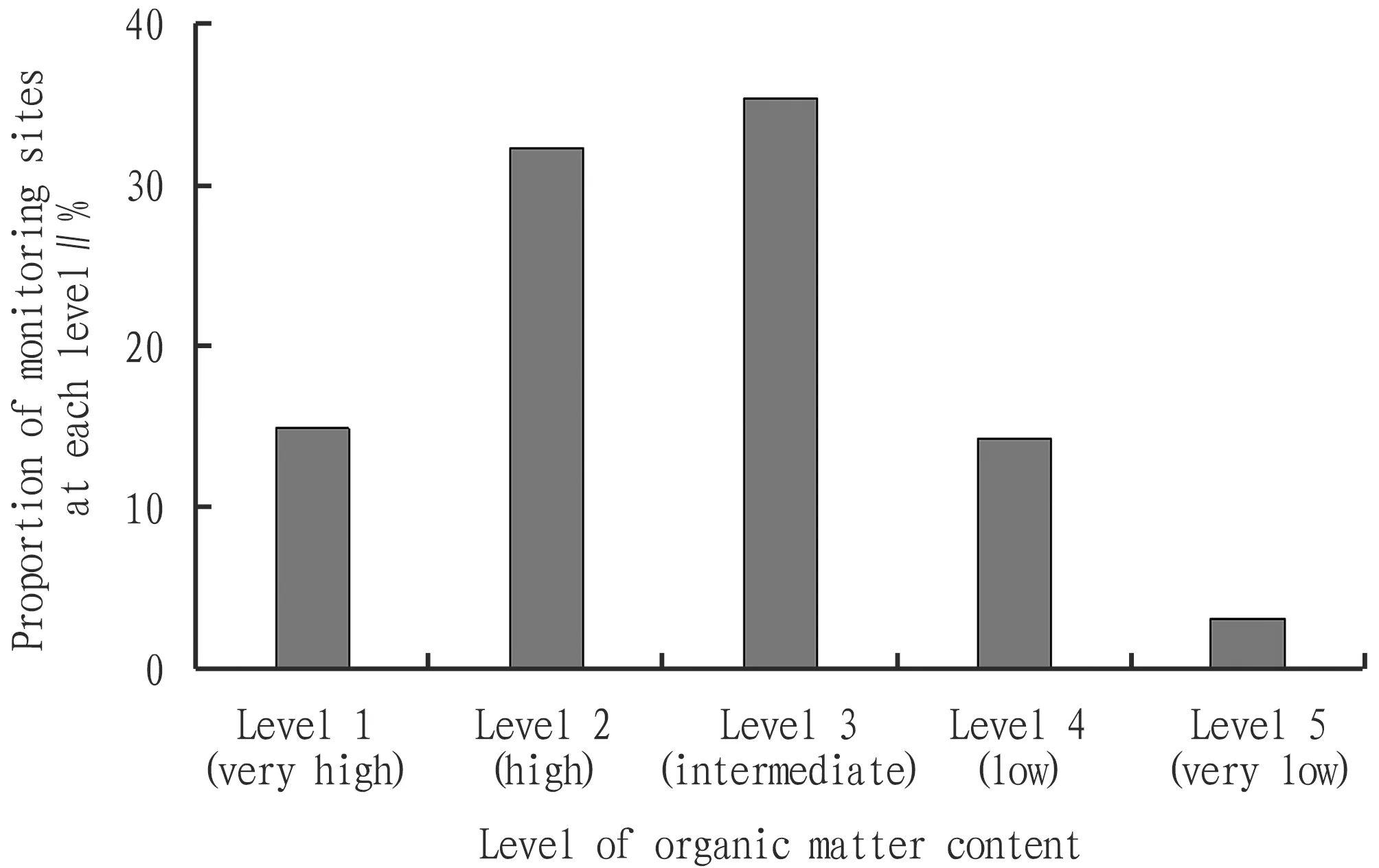
In 2018, the average content of soil organic matter in northeastern region of China was 31.4 g/kg, which was at the Level 2 (high level). According to statistics, there are 161 effective monitoring sites for organic matter content in the region. According to the classification standard of the main indicators for cultivated land quality monitoring in northeastern region of China, there were 24 monitoring sites at Level 1 (very high level), accounting for 14.9% of the total monitoring sites; 52 monitoring sites at Level 2 (high level), accounting for 32.3%; 57 monitoring sites at Level 3 (intermediate level), accounting for 35.4%; 23 monitoring sites at Level 4 (low low), accounting for 14.3%; and 5 monitoring sites at Level 5 (very low level), accounting for 3.1% (Fig.1). On the whole, the soil organic matter in the northeastern region showed a rising trend.
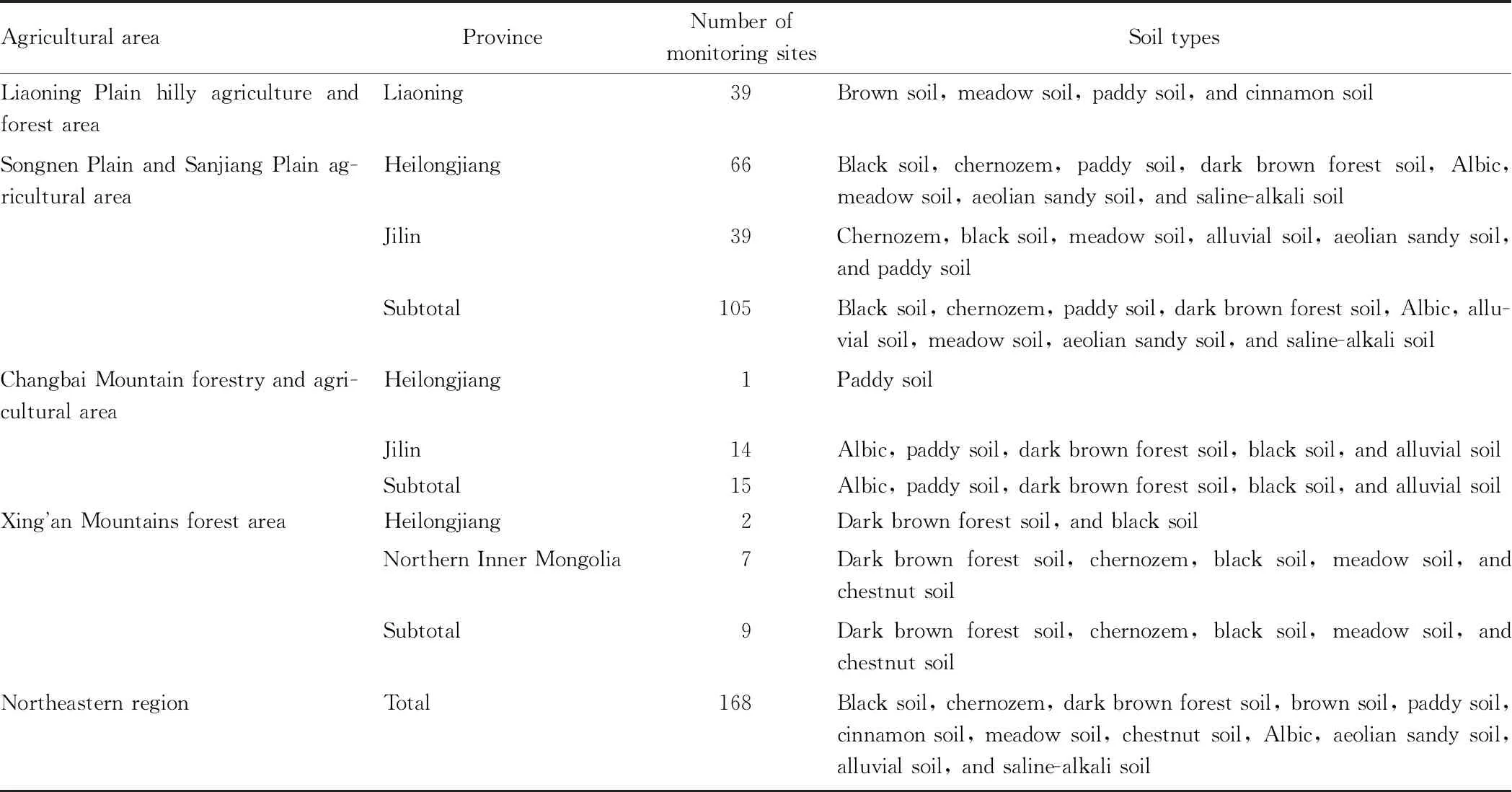
Table 1 General situation of monitoring sites for quality of national level cultivated land in northeastern region in 2018
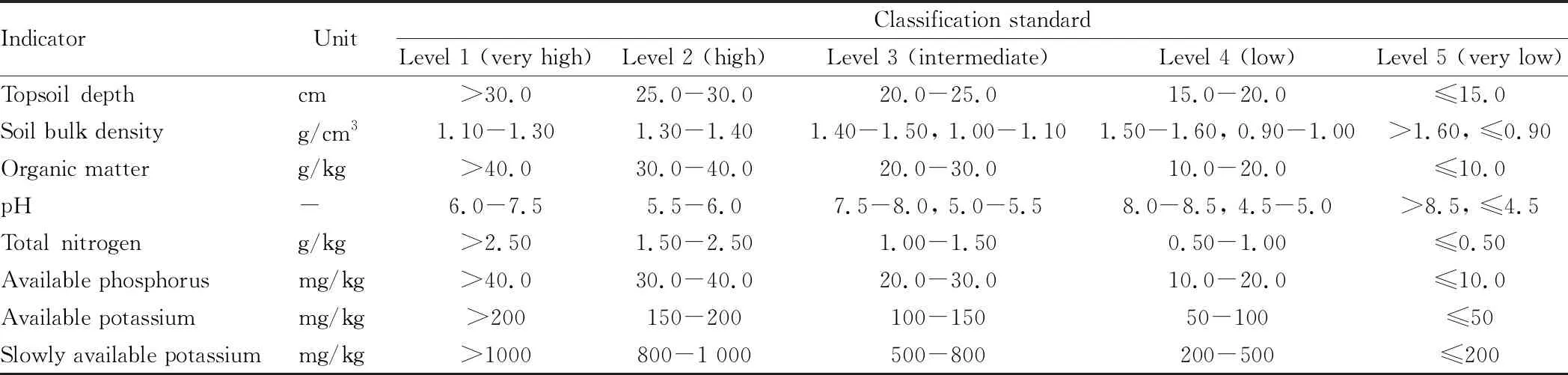
Table 2 Classification standards of main indicators for quality monitoring of cultivated land in northeastern region
Note: Level 1 (>40g/kg), Level 2 (30-40) g/kg, Level 3 (20-30) g/kg, Level 4 (10-20) g/kg, Level 5 (≤10 g/kg).
Fig.1 Proportion of soil organic matter content in each level interval in northeastern region in 2018
The monitoring results of cultivated land quality in 2018 showed that the average value of soil organic matter content in the second-level agricultural areas in northeastern region had large difference and the average value of soil organic matter gradually increased from south to north (from low to high latitude). Regions under the jurisdiction of the northern Xing’an Mountains forest area had the highest organic matter content, with an average of 60.92 g/kg, which was at Level 1 (very high level). The Liaoning Plain hilly agriculture and forest area in the south contained the lowest organic matter, with an average of 21.76 g/kg, which was at Level 3 (intermediate level). Songnen Plain and Sanjiang Plain agricultural area and Changbai Mountain forestry and agricultural area were in the middle, with average values of 31.89 and 35.31 g/kg, respectively, both at Level 2 (high level), as shown in Fig.2.
3.1 Content changesIn 2004-2018, there were little changes in the average content of soil organic matter at monitoring sites in the northeastern region, the organic matter content was basically stable, and slightly increased, with an average annual increase of 0.2 g/kg (Fig.3). Among the secondary agricultural areas, the levels and changes of organic matter content in Songnen Plain and Sanjiang Plain agricultural areas were basically the same as those in northeastern region; the Liaoning Plain hilly agriculture and forest area showed a fluctuating trend of first falling and then rising; the average content of soil organic matter in Changbai Mountain forestry and agricultural area fluctuated greatly, showing a trend of rising first and then falling. Xing’an Mountains forest area had few monitoring sites, and the organic matter content in this area showed an upward trend in 2016-2018.
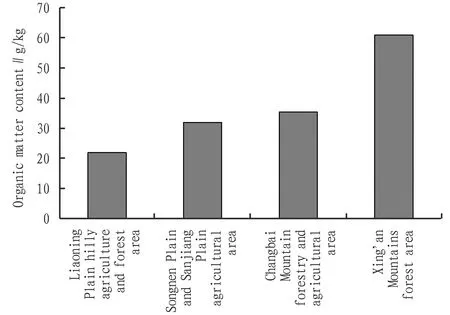
Fig.2 Soil organic matter content in secondary agricultural areas in northeastern region in 2018
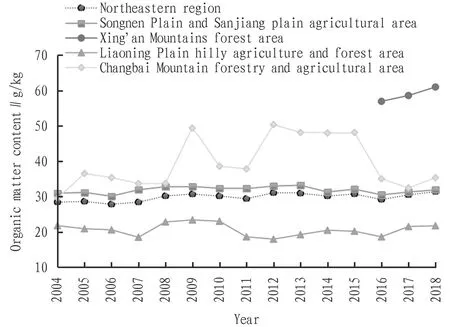
Fig.3 Changes of soil organic matter content in northeastern region
3.2 Frequency changesIn 2004-2018, the soil organic matter content of monitoring sites in northeastern region was mainly concentrated in Level 2 and Level 3, accounting for 67.7% in 2018. Specifically, the proportion of monitoring sites with soil organic matter content in Level 1 (very high level) increased from 7.5% to 14.91%; the proportion of monitoring sites in Level 2 (high level) and Level 3 (intermediate level) declined from 46.34% and 39.02% to 32.30% and 35.40%, respectively; the proportion of monitoring sites in Level 4 (low level) fluctuated greatly, and declined slightly from 14.63% to 14.29%; the proportion of monitoring sites whose soil organic matter content was at Level 5 (very low level) has always been at a low level (Fig.4).
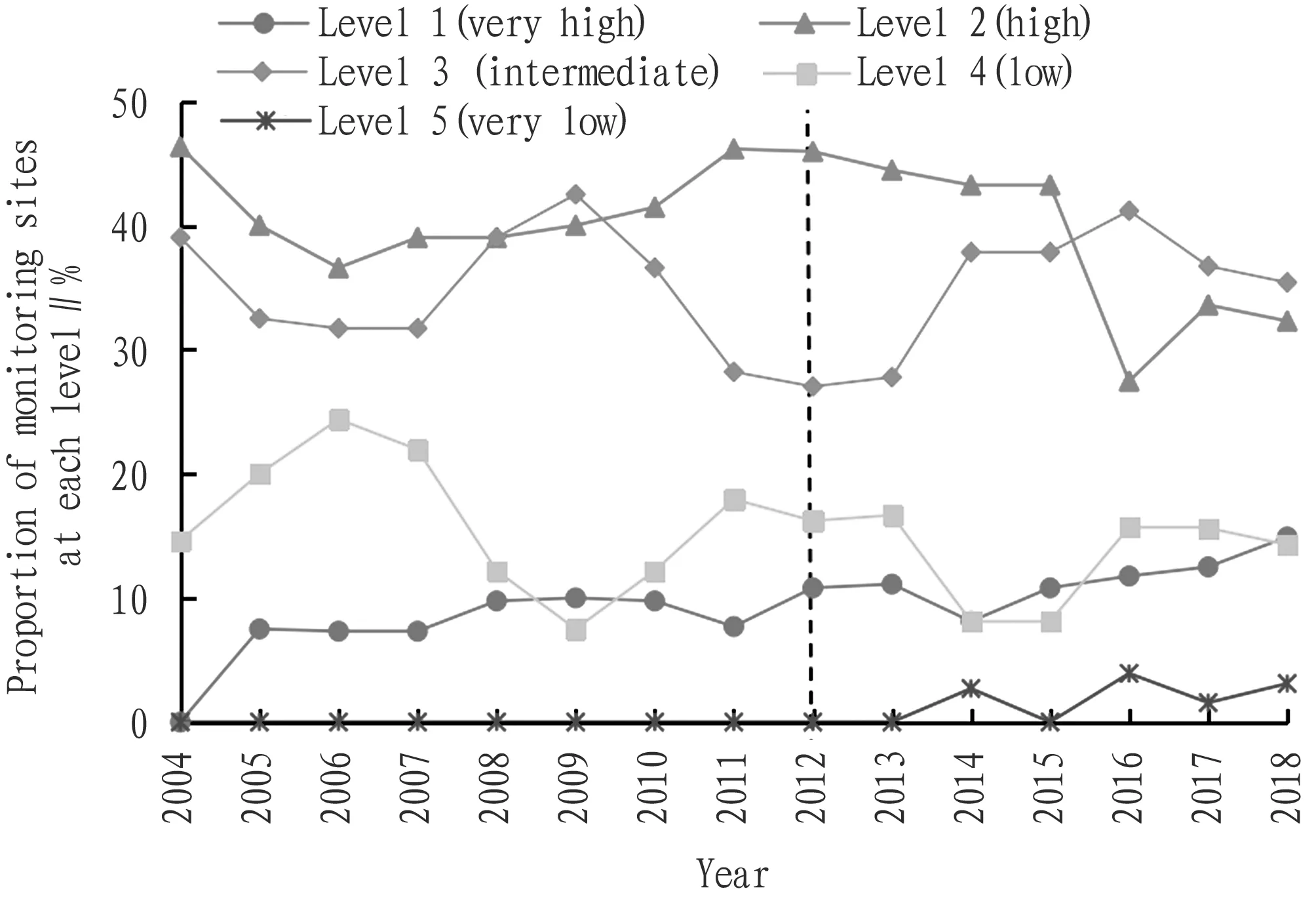
Fig.4 Frequency changes of soil organic matter content of each level in northeastern region
4 Causes for low soil organic matter content and countermeasures for improvement soil fertility
4.1 Cause analysisSoil plowing is conducive to soil microbial activity, the release of soil nutrients, and accelerating the mineralization rate of soil materials. However, after plowing, the topsoil of black soil will become much looser, which also accelerates the wind and water erosion of the soil. In addition, the decomposition rate of organic matter is faster than the synthesis rate, and soil organic matter begins to decrease greatly. In order to reduce pests, weeds and rodents and promote stable and high agricultural yields, a large amount of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides have been put into the soil, which accelerates the soil mineralization rate, and the soil microbial flora also changes, accordingly destroying the soil aggregate structure, deteriorating the physical properties of the soil, and severely reducing the soil fertility. What’s worse, most farmers usually adopt the predatory management method of extensive planting and low harvesting, and the nutrients supplied by cultivated land to crops cannot be compensated, thus causing the soil nutrient to be out of balance. According to reports, the annual loss of nitrogen in Heilongjiang Province was 219 000-384 000 t, phosphorus 164 000-288 000 t, equivalent to 476 000-835 000 t of urea, and 911 000-1.6 million t of superphosphate. According to statistics, in the past 50 years, the soil organic matter in northeastern region has dropped from 3%-6% at the beginning of reclamation to the current 2%-3%. The decline in organic matter content leads to the decrease of soil fertility, the increase of bulk density, the deterioration of permeability, and the weakening of water and fertilizer retention capacity, accordingly influencing the output capacity of cultivated land. In recent years, with the support of the central government and local finance, many regions have actively implemented projects such as fertilizing by soil testing, cultivated land quality protection and improvement, and black soil protection and utilization pilot projects, and a series of technical measures to improving soil fertility such as promoting the technology of returning straw to the field, increasing the application of organic fertilizers and crop rotation of grain and beans. These measures have improved soil organic matter, but the overall level is still low and there is room for improvement.
4.2 Measures for improving soil fertility
4.2.1Actively promoting the quality protection technology model of cultivated land such as straw returning in accordance with local conditions. It is recommended to take ecological balance as the core of cultivated land quality protection, instead of focusing on increasing plant nutrients. Besides, it is recommended to take maintaining and improving the soil nutrient environment conditions of plants as the primary measure, use organic matter such as straw in a rational and economical manner to foster and apply fertilizer, restore and maintain soil fertility.
4.2.2Expanding organic fertilizer sources and increasing application of organic fertilizers. The northeastern region of China has a wide range of organic fertilizer sources, such as livestock and poultry manure, straw,etc.Collecting and piling up these organic fertilizer sources for fermenting and decomposing can produce organic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers contain rich organic matter. After being applied to the soil, the content of soil organic matter can be significantly increased, thereby improving soil fertility and improving soil physical and chemical properties.
4.2.3Implementing reasonable crop rotation, planting green manure crops such as legumes, and realizing the combination of land use and land cultivation. Reasonable crop rotation can maintain and improve soil organic matter content, increase the proportion of soil microaggregates, and improve soil water and fertilizer retention capacity. Besides, reasonable crop rotation is also an effective measure to effectively control soil acidification. Long-term planting of a crop on the soil will cause the enrichment of certain nutrient elements, leading to aggravation of acidification. In addition, reasonable crop rotation can reduce soil-borne diseases and insect pests resulted from continuous cropping, thereby reducing the use of pesticides and other chemicals, which not only ensures the quality and safety of grain, but also effectively controls soil acidification, and also improves the soil fertility.
4.2.4Establishing a reasonable fertilization system, combining organic and inorganic fertilizers with scientific fertilization, increasing fertilizer efficiency and reducing the application of chemical fertilizers. Both chemical fertilizers and organic fertilizers contain a large amount of organic acids, so improper fertilization will lead to aggravation of soil acidification. It is recommended to carry out scientific fertilization ratio according to soil fertility to achieve the optimal utilization effect and have a positive effect on reducing soil acidification. The application of organic fertilizers is a practical and effective way to improve the soil fertility. It can not only renew and improve the composition of soil humus, but also coordinate many factors of soil fertility. However, at the same time of increasing the application rate, it is necessary to monitor the environmental quality of organic fertilizers and soils to prevent harmful substances such as heavy metals from contaminating the cultivated soil and affecting the quality of the cultivated land. On the basis of increasing the application of organic fertilizers, returning straws to the field or planting leguminous green manure crops in rotation, it is recommended to adjust the nitrogen fertilizers in stages to reduce application and increase efficiency. It is recommended to take advantage of after-effect of phosphate fertilizer utilization, reduce application, and take constant control. For high-content plots, it is possible to reduce application by 30% for two consecutive years, and then determine a reasonable amount according to soil testing results. Potassium fertilizer should be controlled by a constant amount, and increased in an appropriate amount. Secondary and trace elements can be supplemented based on soil tests to continuously improve fertilizer benefits.
4.2.5Increasing financial investment and promoting the integration of funds related to cultivated land protection. It is recommended to implement pilot projects for the protection and utilization of black soil, subsidy projects for the protection and improvement of cultivated land quality, and projects for reducing the amount of chemical fertilizers and increasing efficiency. Besides, it is necessary to establish and improve the investment guarantee mechanism for projects related to cultivated land protection, improve support policies, mobilize the enthusiasm of farmers, farmers’ professional cooperative organizations, agricultural enterprises and other input subjects, and take advantage of market mechanisms to encourage and attract financial capital and private capital to actively invest in cultivated land protection. The government of the planning area should strengthen the organic integration of funds from different channels, such as land transfer funds and investment in the planning of new 50 billion kg of grain production capacity, concentrate the investment, conduct contiguous governance, and promote the whole county to increase the efficiency of capital use.
 Asian Agricultural Research2022年3期
Asian Agricultural Research2022年3期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Discussion on Soil Sampling Technology Based on the Experience of Yuanzegou Small Watershed
- Development Model of Daren Village Pastoral Complex in Ningbo in the Context of Rural Revitalization Strategy
- Development Status and Countermeasures of Potato Industry in Zaozhuang City
- Evaluation Model of Rural Drinking Water Project Based on Entropy Weight and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method
- Effects of Emulsifier on Fermentation Performance of Active Dry Wine Yeast
- Key Technology for Virus-free Seed Potatoes Pre-elite Breeding
