Acupuncture intervening depressive disorder:research progress in its neurobiological mechanism
LI Pengfei (李芃菲), XIAO Min (肖敏), MA Xuejiao (馬雪嬌), YAN Xingke (嚴(yán)興科), MA Chongbing (馬重兵)School of Acupuncture and Tuina, Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, China
AbstractDepressive disorder seriously affects people’s physical and mental health.Acupuncture is a safe and effective treatment for depression, yet, its mechanism is unclear.Therefore, acupuncture’s action mechanism in intervening depression was summarized from several perspectives, including morphology and ultrastructure of neurons in depression-related brain areas, function and structure of glial cells, brain functional and structural connectivity, and neuroelectrophysiology.It’s discovered that acupuncture can repair the morphological and ultrastructural damage of neurons in the hippocampus and prefrontal lobe, mitigate the functional and structural injuries of glial cells in the hippocampus and prefrontal lobe,strengthen functional connectivity and heal structural connection, and promote neuroelectrophysiological activities,which possibly are the principal mechanisms of how acupuncture works in intervening depressive disorder.
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Brain; Neurons; Neuroglia; Electrophysiology; Depression
Depressive disorder, manifested as significant long-lasting feelings of down, slashed interest, and loss of pleasure, is a mental illness associated with various causes; it has high incidence, recurrence, suicide, and disability rates[1-2].To date, depression treatments mainly include pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, and physical therapy[3]; medications are the principal treatment in clinics but are limited by their slow onset of effect, low response rate, and too many adverse reactions[4].Acupuncture-moxibustion is safe and effective in treating depression[5-9].The majorly treated meridians are the Governor Vessel, Liver Meridian, and Bladder Meridian, and points such as Baihui (GV20),Yintang (GV29), Neiguan (PC6), and Taichong (LR3) are commonly used[10-11].Acupuncture-moxibustion has significant strengths in intervening depression: multiroutes, multi-levels, and multi-targets.Research on its action mechanisms focuses on perspectives like neurotransmitters, neurotrophic factors, and immune factors[12-14].In recent years, there have been emerging more and more studies revealing the pathogenesis of depression from brain function and structure.This article aims to review the mechanism of acupuncture in intervening depression given the following clues:acupuncture repairs the morphological and ultrastructural damage of neurons in the brain;mitigates functional and structural injuries of glial cells;strengthens functional connectivity and heals structural connectivity; boosts neuroelectrophysiological activities.
1 Acupuncture Repairs Morphological and Ultrastructural Damage of Neurons
Depressive patients are found to have abnormal functions and structures in certain brain areas, including the hippocampus, medial prefrontal lobe, dorsolateral prefrontal lobe, anterior cingulate gyrus, posterior cingulate gyrus, precuneus, amygdala, and caudate nucleus[15].The hippocampus and prefrontal lobe are the crucial brain regions in the onset of depressive disorder[16].
1.1 Acupuncture promotes hippocampal neurogenesis
Hippocampus is a main part of the limbic system and participates in basic functions, including memory,cognition, and emotion; functional and structural changes of the hippocampus are the pathophysiological basis for the development of depression[17].Neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and subventricular zone sustains till adulthood[18].The generation of novel neurons is vital for memory and other cognitive functions, as well as emotional adjustment[19-20].Declined hippocampal neurogenesis induced by stress and pressure is an important factor causing depressive disorder[21].Research has found decreased hippocampal neurogenesis in adult depression patients[22], and the changes are mostly found in the anterior and middle hippocampal dentate gyri, with 40% of the volumetric decrease in the anterior dentate gyrus and 50% in the middle dentate gyrus[23].
Acupuncture can boost hippocampal neurogenesis in adults.Chronic stress reduces neurogenesis in the rat’s hippocampal dentate gyrus; nevertheless, under continuous stress, the rat’s hippocampal neurogenesis can increase significantly and then return to the normal level after electroacupuncture (EA) treatment[24].Acupuncture can promote the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells and the repair of brain function, and the proliferated neural cells or glial cells can positively adjust hippocampal neurogenesis.Hence,promoting neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation,and survival to maintain the number of neurons for normal function may be associated with acupuncture treatment of depression[25].Besides, neurotrophic factors may be another route that acupuncture takes to regulate hippocampal neurogenesis.Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) boost the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells.After EA, the contents of hippocampal GDNF and BDNF and their receptor proteins increase, suggesting the participation of GDNF and BDNF both in the development of depression and acupuncture’s antidepressant effects[26].
1.2 Acupuncture repairs morphological damage of neurons
Shrunk gray matter is found in depressed patients’hippocampus[27]and prefrontal lobe[28]and the size change shows a positive correlation with the duration and severity of depression[29].A similar shift in the hippocampus is also found in a rodent stress model,though the change of prefrontal lobe is inconsistent with that in humans[30].Atrophic neurons and reduced amount and density of synapses are detected in depressed animal models[31]and human beings[32]through brain autopsy.Anin vivostudy of depressed patients has discovered a negative correlation between the severity of depression and the synaptic density in the dorsolateral prefrontal lobe, hippocampus, and cingulated cortex[33].Furthermore, synaptic function-related gene expression drops along with decreased levels of synaptic signaling proteins[34].Under the light microscope, depressed rats’hippocampus is found to have fewer neurons[35].Also, electron microscopy reveals that hippocampal neurons in depressed rats present apoptotic features: shrunk cell membranes, condensed cytoplasm, chromatin margination, and apoptotic bodies[36].Moreover,transmission electron microscopy shows that hippocampal neurons in depressed rats have fewer synapses, larger synaptic spaces, reduced vesicles in the presynaptic membrane, loosely arrayed dense materials in the postsynaptic membrane, vague or fused boundaries between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, smaller synaptic interface curvature, and shortened synaptic active zone[37].
Acupuncture can repair the significant pathological damage in hippocampal CA1 and CA3 areas in depressed rats.After receiving acupuncture, in the hippocampal neurons of depressed rats, the nucleus and mitochondrion show an intact structure, and the myelin sheath wall is compact and thicker; the number of synapses increases, along with more presynaptic membrane vesicles, thicker dense materials in the postsynaptic membrane, clear boundaries between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, and longer synaptic active zone[38-39].Besides, heightened synaptic transmission efficiency and enhanced long-term synaptic plasticity are found in the hippocampus of depressed rats after acupuncture interventions[40].Moreover, for depressed rats, acupuncture can improve depressive symptoms by promoting the expression of synapse-related proteins in the prefrontal lobe,increasing dendritic spine density, and regulating synaptic plasticity[41].
2 Acupuncture Improves the Functional and Architectural Damage of Neuroglial Cells
Neuroglial cells support, nourish, and insulate adjacent neurons.Damage to the function and structure of neuroglial cells may be a pathogenic factor of depressive disorder[42].Autopsy of depressed patients has discovered abnormal neuroglial cells in density, number, and size, of which the loss of cells is most significant in the hippocampus and prefrontal lobe[43].In the hippocampus, the volume of glial cells decreases, the bulk density increases, and the number of mature granular cells decreases, along with a significant loss of astrocytes[44].Observation of rodent stress models reveals reduced astrocyte density,markers, and metabolism[45].Light microscopy finds astrocyte nucleus pyknosis, pyramidal cell degeneration and reduction, and granular cell cytoplasm vacuolization in depressed rat models; electron microscopy discovers rough endoplasmic reticulum expansion in the cytomatrix and loose mitochondrial crista.
Acupuncture can boost the activity of astrocytes in the hippocampus and prefrontal lobe of depressed rats.Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is an indicator of the activity of astrocytes.Astrocyte atrophy and reduced GFAP expression are found in the hippocampus and prefrontal lobe of depressed rats.Acupuncture can up-regulate the expression of relevant proteins like GFAP to improve the function of astrocytes to produce its antidepressant effects[46].Also, acupuncture can repair the morphological and ultrastructural damage of astrocytes in the hippocampus and prefrontal lobe in depressed rat models.After acupuncture, the number of astrocytes increases, and their appearance becomes normal, with rough endoplasmic reticulum expansion and loose mitochondrial crista improved; other cell organelles in the cytomatrix also show improvements.These phenomena suggest that acupuncture can encourage the synthesis of various proteins inside cells,which is a beneficial premise for cells’self-healing[47].
3 Acupuncture Regulates Brain Functional and Structural Connectivity
3.1 Acupuncture strengthens brain functional connectivity
Depressive disorder is related to aberrant restingstate functional connectivity across multiple brain networks participating in emotion processing, executive function, and reward processing[48].Changes in functional connectivity patterns are found in and between these networks in the resting state amongst depressed patients[49].Research finds that depressed people have a low connectivity pattern in the executive control network (ECN) and a hyper-connectivity pattern in the default mode network (DMN); an aberrant hyper-connectivity is also found between the ECN-DMN networks[50].Research further reveals that the functional connectivity damage in depressive disorder is progressive.Patients with first-episode depression have a low connectivity in the sensorimotor network, DMN,and dorsal attention network; patients with relapsed depression have a high connectivity in the sensorimotor network, salience network, executive control network,DMN, and dorsal attention network, as well as between the salience and executive control networks.The low connectivity in the first-episode depression patients and high connectivity in the recurrent depression patients are associated with the disease severity and duration[51].
Acupuncture can strengthen brain functional connectivity in depressed patients[52].The functional connectivity is weak between the brain areas in front and behind the DMN.Precuneus is a vital part of DMN and participates in self-related information processing and episodic memory processing[53].EA can heighten the resting-state functional connectivity in the precuneus and lingual gyrus and regulate DMN in depressed patients and mitigate their depression symptoms[54].Besides, acupuncture also can enhance the functional connectivity among the lower ventral striatum, medial prefrontal cortex, ventral rostral putamen, amygdale/parahippocampus, caudate gyrus,and middle temporal gyrus.These findings all suggest that acupuncture can play its therapeutic role by regulating the corticostriatal reward circuitry in patients with depressive disorder[55].
3.2 Acupuncture repairs brain structural connectivity
Brain structural and functional network disruptions exist in depressive disorder[56], and widespread disconnections between regions may cause depressed patients to have reduced global network integrity.The integral abnormality of white matter fiber tracts (WMT)may exacerbate dysfunctions in cortical junction and subcortical regions, resulting in depression symptoms[57].Research has discovered white matter disconnections in DMN and frontal subcortical networks in depressed people[58].It is known that DMN plays a role in emotion and self-processing, and the frontal lobe-subcortex network is vital for mood regulation and cognitive function; these abnormalities are possibly the structural foundation for individual dysfunctions and behavioral deficits in depression[59].WMT connection abnormalities in depressive disorder involve the cingulate gyrus, uncinate fasciculus, medial forebrain bundle, anterior thalamic radiation, frontal zone of the corpus callosum radiation, superior longitudinal fasciculus, and corticospinal tract[60].The fractional anisotropy (FA) of fiber tracts declines significantly from the anterior corpus callosum to the anterior cingulate gyrus; the lower the FA, the higher the risk of depressive disorder[61].
Acupuncture can repair brain functional connections in depressed patients.Notable FA alterations have been found in six brain zones in the depressed population,which are the left cingulate gyrus, splenium of the corpus callosum, bilateral inferior parietal white matter,bilateral frontal white matter, bilateral inferior temporal white matter, and bilateral deep temporo-occipital white matter.To some extent, acupuncture repairs the damaged microstructure of WMT by enhancing FA of bilateral frontal white matter, bilateral inferior temporal white matter, and bilateral deep temporo-occipital white matter[62].
4 Acupuncture Promotes Neuroelectrophysiological Activities
Electroencephalograph (EEG) can detect changes in neuroelectrical activities in the brain cortex[63].EEG signals can be taken as a measure of acupuncture efficacy and a way to analyze acupuncture’s mechanism of action[64].Exploring potential biomarkers of depressive disorder using EEG can be applied to diagnosis or treatment result prediction[65].
4.1 Acupuncture balances the power of brainwaves of different frequencies
Brainwaves have different frequencies, and each reflects its distinct brain mechanism.For example, alpha frequency demonstrates that the brain is in resting or relaxation.Those suffering from depression and having suicidal ideation have increased alpha activity over night sleep[66].Alpha lateralization correlates with the avoidance mode[67]and can anticipate specific symptoms such as dysphoria and lassitude[68]as well as unipolar depression as opposed to bipolar depression[69].Anxiety has the potential to alter alpha lateralization and makes depression diagnosis a difficulty[70].Beta frequency is associated with anxiety and rumination, and a decreased beta power is found in the left brain hemisphere of depressed patients[71].Theta frequency has something to do with emotion processing, and strengthened theta activity can be found in the occipital and parietal regions of the brain in depressed patients[72].Gamma band is related to feelings and mood swings, and an appropriate gamma power guarantees a stable mood in people suffering from depression[73].Besides, delta frequency is associated with deep sleep.A larger delta amplitude is found in the central-parietal and lateral electrodes in depressed patients facing a negative target[74].
Acupuncture can balance the power of brainwaves of different frequencies in people with depression.A study observed 26 depressed patients after 8-week acupuncture treatments, finding a notable increase in alpha’s relative power and a significant decrease in the relative power of theta and beta; there was a negative correlation between the reduction rate of Hamilton depression scale score and the relative power difference of theta and a positive correlation between the score reduction rate and the relative power difference of alpha; the association between the change in theta’s relative power and acupuncture’s efficacy mainly manifests in the frontal zone of the right brain hemisphere.These findings suggest that acupuncture improves depressive symptoms by balancing theta activity in the frontal zone of the right brain hemisphere[75].
4.2 Acupuncture regulates evoked potentials
Evoked potentials are bioelectrical activities produced by the central nervous system during perceiving external or internal stimuli and can reflect altered cerebral function in depressed patients[76].Event-related potentials (ERP) are a special group of evoked potentials generated when an individual receives a type of stimulation (visual, auditory, or tactile stimulation), reflecting neuroelectrophysiological changes in the brain during the cognitive process[77].P300 is a classic endogenous ERP.It participates in psychological processing and cognitive process and thus is often used to evaluate cognitive impairment in depressed patients[78].P300 latency indicates nerve conduction velocity when the brain responds toward an external stimulation and indicates cognitive function efficiency[79].P300 amplitude reflects how effectively recourses are mobilized when the brain processes information; P300 latency extends and amplitude decreases with difficulty differentiating target stimulation[80].According to the research, depressed people have an extended P300 latency and a decreased P300 amplitude, suggesting an impaired cognitive function and a close association between the frontal lobe and cognitive dysfunction[81].
Acupuncture can effectively shorten P300 latency,heighten P300 amplitude, improve target stimulationrelated behavioral indicators, enhance the activity level and execution and control abilities of the frontal lobe,repair the damaged processing and cognitive functions,and mitigate depression[82-83].
5 Summary
The onset of depressive disorder is highly related to aberrant and disconnected brain function and structure.The core pathogenesis may involve decreased hippocampal neurogenesis, impaired neural and prefrontal neuron morphology and ultrastructure,damaged glial function and architecture, and neuron electrical conduction and integration abnormalities,which can further result in functional and structural disconnection, leading to a disordered environment inside the central nervous system and presenting depressive symptoms.
Regarding brain function and architecture,acupuncture can repair the damaged hippocampal and prefrontal neuron morphology and ultrastructure and improve the function and structure of astrocytes by promoting the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells to boost hippocampal neurogenesis.Concerning neuron synaptic plasticity, acupuncture can modulate synaptic plasticity by enhancing the expression of pertinent proteins and BDNF to nourish and protect hippocampal and prefrontal neurons.Finally, regarding functional connectivity, acupuncture can encourage neuroelectrophysiological activities and modulate topical field potential and power to enhance functional connectivity and repair structural connection.
The action mechanism of acupuncture in treating depressive order is shown in Figure 1.
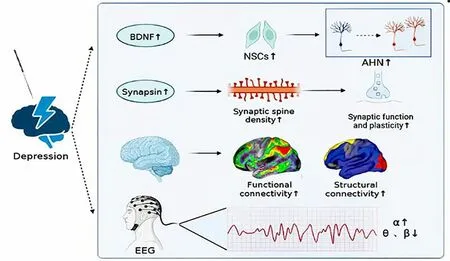
Figure 1 Illustration of acupuncture’s mechanism of action[50]
6 Discussion
In brief, there is a tight link between depression and hippocampal and prefrontal neuron functional remodeling dysfunction and structural alterations.By repairing damaged neuron morphology and ultrastructure in relevant brain regions, improving the function and structure of astrocytes, promoting neuroelectrophysiological activities, and strengthening functional connections, acupuncture can finally achieve the purpose of treating depressive disorder.The mechanism of acupuncture in treating depression requires further research.The following aspects may be worth concerning: to explore the influence of acupuncture on various complex connections of neurons of different natures and functions from the perspective of neural circuits; to study the regulatory effect of acupuncture on crosstalk or interference between different signaling pathways from the perspective of neural signaling pathways; to discover the effect of acupuncture on the functional connection between white matter and gray matter from the perspective of functional connectivity.Meanwhile, the results can be inconsistent due to the varieties in the point selection theory, needling angle and manipulation,stimulation dosage and intensity, and needle retaining duration in different studies.Therefore, a standardized treatment protocol should be a premise for the mechanism research on how acupuncture interferes with depressive disorder.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Scientific Research and Innovation Funds Project of Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (甘肅中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)科學(xué)研究與創(chuàng)新基金項(xiàng)目, No.2021KCYB-1).
Received: 19 September 2022/Accepted: 25 November 2022
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2023年3期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2023年3期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina ScienceInstructions for Authors
- Editorial Members of Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science
- Efficacy and safety of acupuncture-moxibustion for cerebral palsy-induced speech impairment:a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Clinical observation of acupuncture treatment for children with accommodative myopia
- Clinical observation of Tuina combined with Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang in the treatment of rectocele
- Clinical study of treating somatoform pain disorder with the combination of electroacupuncture and duloxetine
