New Exact Solutions to a Category of Variable-coefficient PDEs and Computerized Mechanization
LI Ba-cui
(Department of Public Management,Party School of CPC Fushun Municipal Committee,Fushun,Liaoning 113006)
1 Introduction
The study of exact solutions to nonlinear partial differential equations(PDEs)plays an important role in the research of nonlinear physical phenomena.Generally speaking,when describing nonlinear physical phenomena,variable-coefficient PDEs tend to be more comprehensive,accurate and effective than constant-coefficient PDEs[1].Recently,great progress has been made regarding the calculation of exact solutions to variable-coefficient PDEs and many significant methods have been established such as Lax pairs[2],Hamiltonian structure[3],bilinear Backlund transformation[4],symmetry algebra[5]and so on[6-8].
With the aid of symbolic computation software(MAPLE),a new algebraic method for solving variable-coefficient PDEs is proposed in this article,which is called the auxiliary elliptic-like equation method.By applying this method to the variable-coefficient Kadomtsev-Petviashvili equation,several new exact solutions are obtained which could not be found in the previous literature.This algorithm can also be applied to other variable-coefficient PDEs in mathematical physics.
2 The algorithm
Step 1For a given nonlinear PDE with one physical fieldu(x,y,t)in three variablex,y,t,
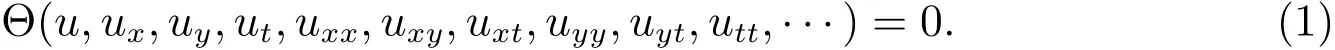
We seek its travelling wave solution,in the form ofu(x,y,t)=u(η),η=px+qy+lt+η0,wherep,q,landη0are constants to be determined.The nonlinear PDE(1)is reduced to a nonlinear ordinary differential equation

Step 2To seek the travelling wave solutions of(2),we assume that(2)has solutions in the form of
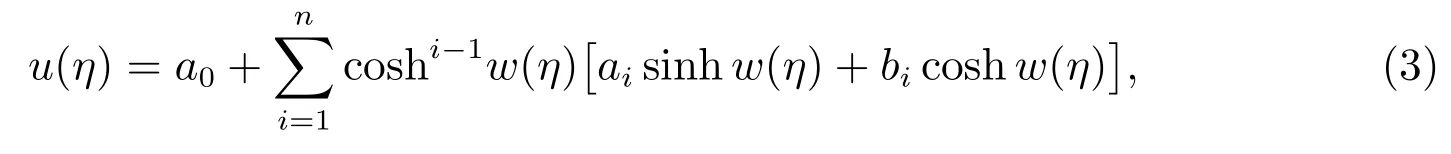
whereai(i=0,1,2,···)are constants to be determined,sinhw(η),coshw(η)are determined by the following hyperbolic auxiliary equation
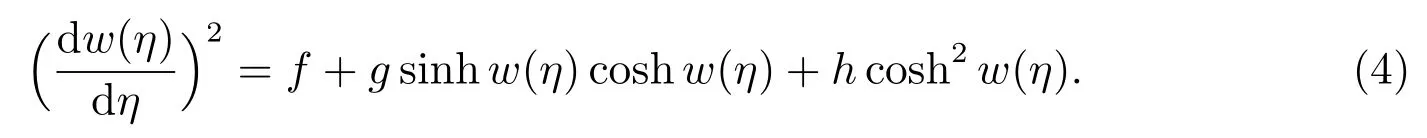
By balancing the highest degree linear term and nonlinear term in(2),we can determine the degreen.
Step 3Substituting(3)along with(4)into(2)and setting the coefficients of sinhpw(η)coshqw(η)(q=0,1;p=0,1,···,n+2)to zero,we will obtain a set of algebraic equations with respect to the parametersp,q,l,η0,ai,bi(i=0,1,2,···,n).
Step 4Solving the set of algebraic equations with the aid of the symbolic computation software(Maple),we would end up with the explicit expressions forp,q,l,η0,ai,bi(i=0,1,2,···,n).
Step 5By considering the value off,g,h,(4)has many kinds of dark solitary wave,bell profile solitary wave and Jacobian elliptic function solutions[9],which are listed as follows.
Case 1f=?2(1+m2),g=2(?1+m2),h=2(1+m2),
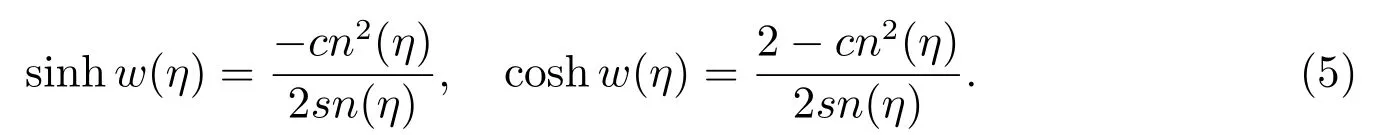
Case 2f=2(?1+m2),g=?2,h=?2(?1+2m2),

Case 3f=?2(?2+m2),g=?2m2,h=2(?2+m2),
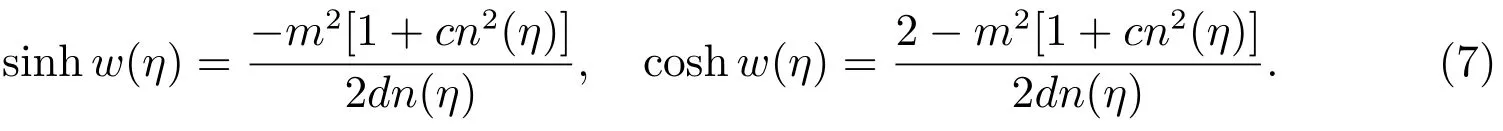
Case 4f=0,g=?2m2,h=?2(?2+m2),
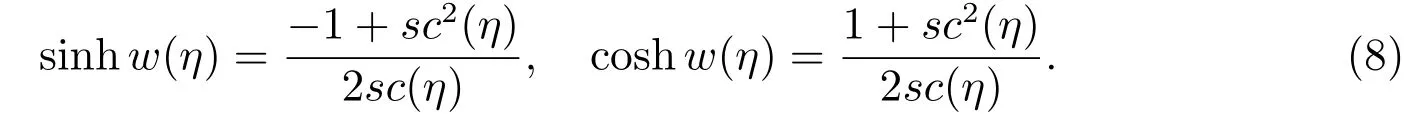
Case 5f=?2+3m2?m4,g=2(?1?m2+m4),h=2(1?m2+m4),
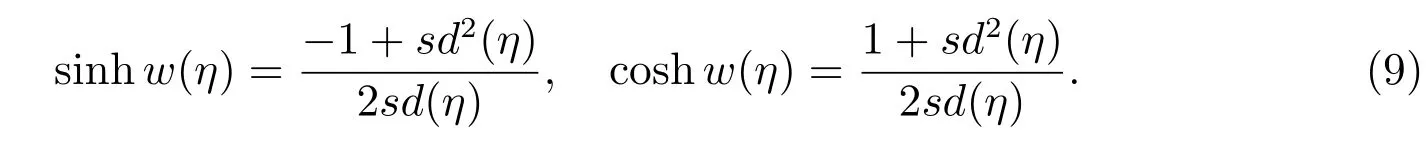
Case 6f=?2(1+m2),g=2(?1+m2),h=2(1+m2),
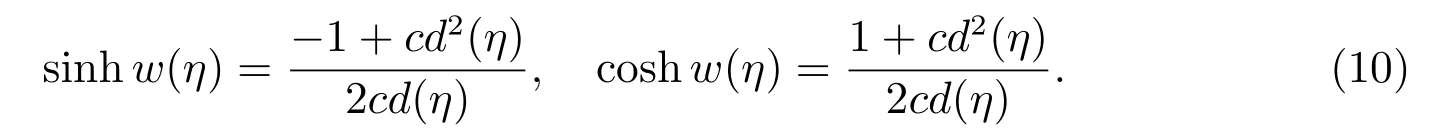
Case 7f=m2,g=0,h=1?m2,
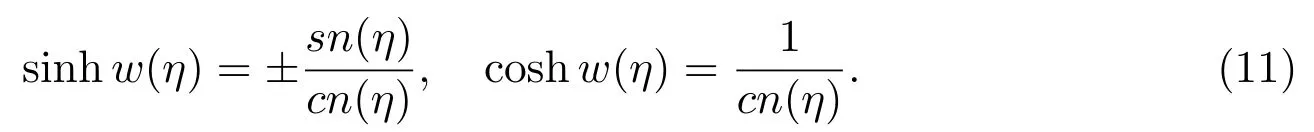
Case 8f=1,g=0,h=?1+m2,
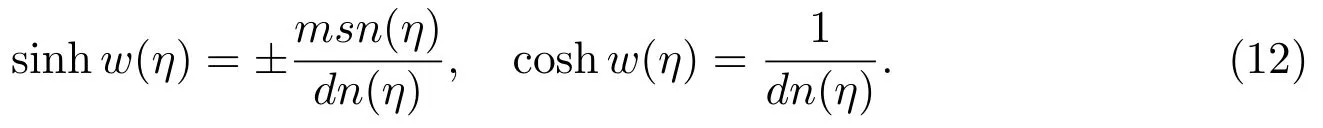
Case 9f=?1,g=0,h=m2,
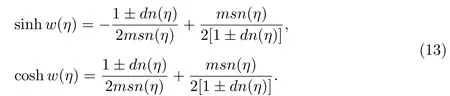
Case 10f=?m2,g=0,h=1,
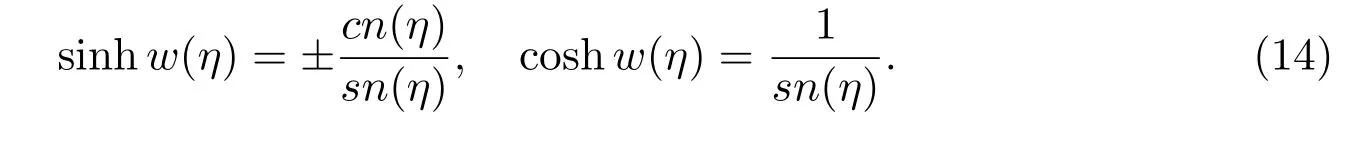
Case 11
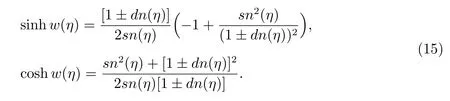
Case 12f=2,g=?2,h=?2,
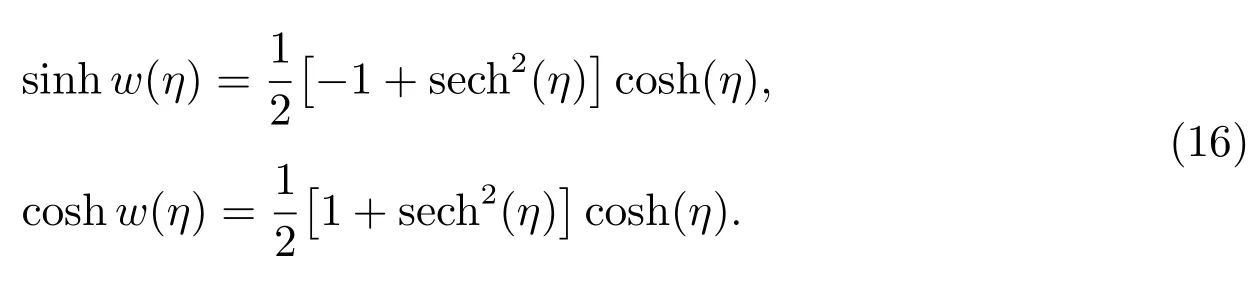
Case 13f=?4,g=0,h=4,
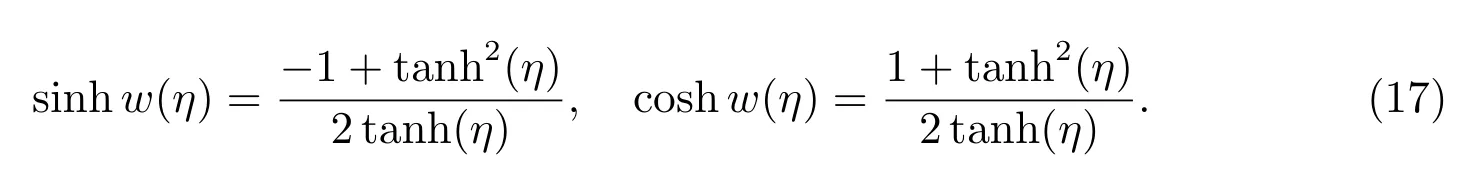
Case 14f=0,g=2,h=2,
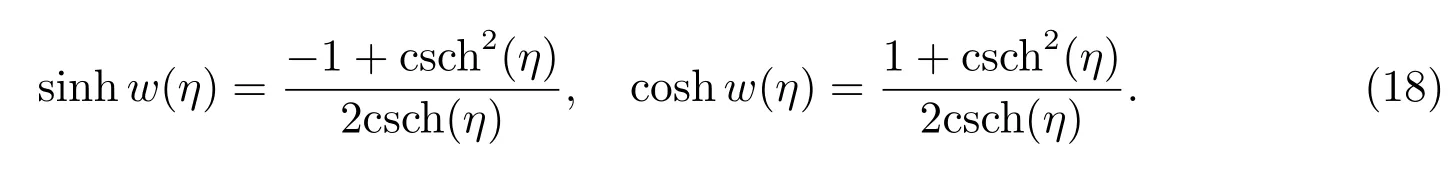
Considering the elliptic-like equation[10]
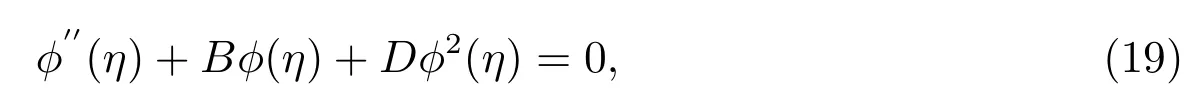
whereB,Dare arbitrary constants.
Considering the homogeneous balance[11]between?′′(η)and?2(η)in(19),we suppose that the solution of(19)can be expressed by
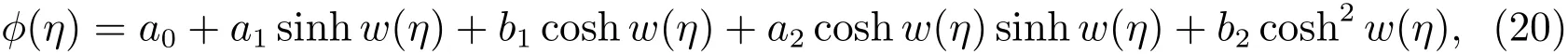
wherea0,a1,b1,a2,b2are constants to be determined,sinhw(η)and coshw(η)satisfy(4).
Substituting(20)along with(4)into(19)and collecting the coefficients of sinhpw(η),coshqw(η)(q=0,1;p=0,1,2,3,4),yields
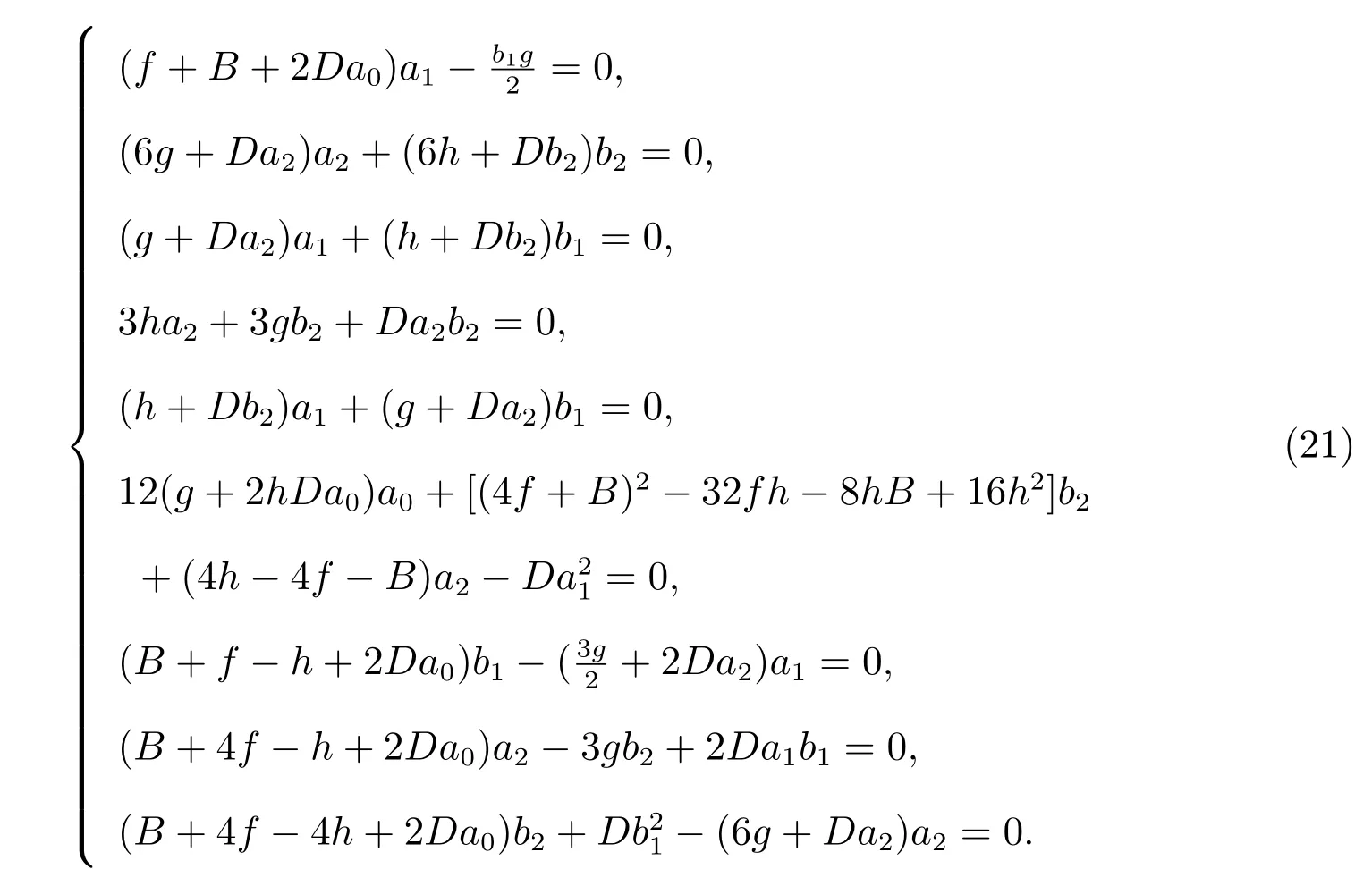
Solving the algebraic(21)with the aid of Maple,we get the following solution
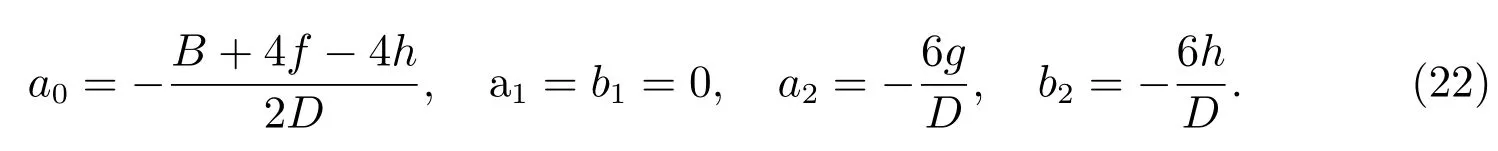
Substituting(22)along with(5)—(18)into(20),we can obtain many kinds of dark solitary wave,bell profile solitary wave and Jacobian elliptic function solutions of(19).
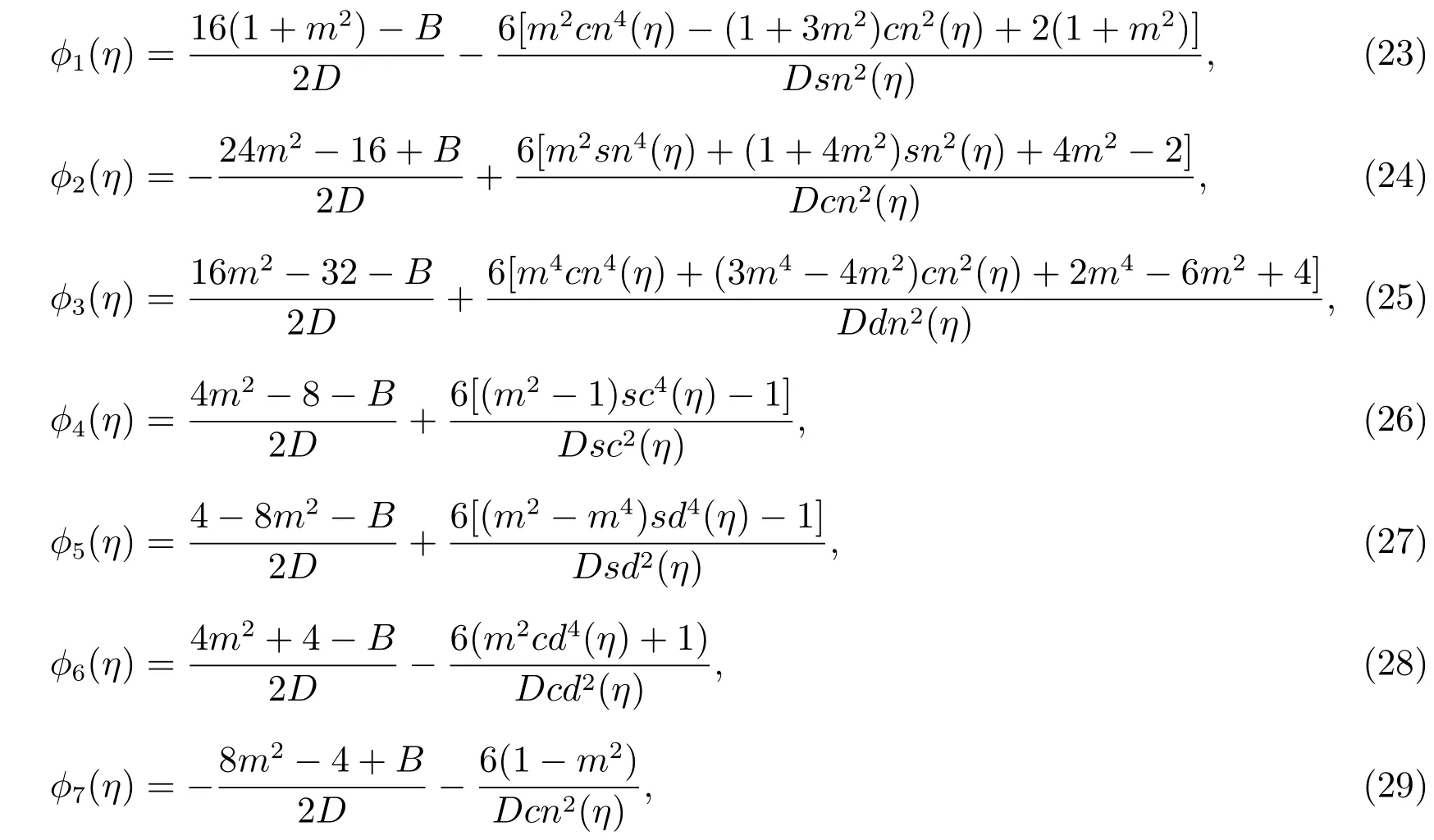
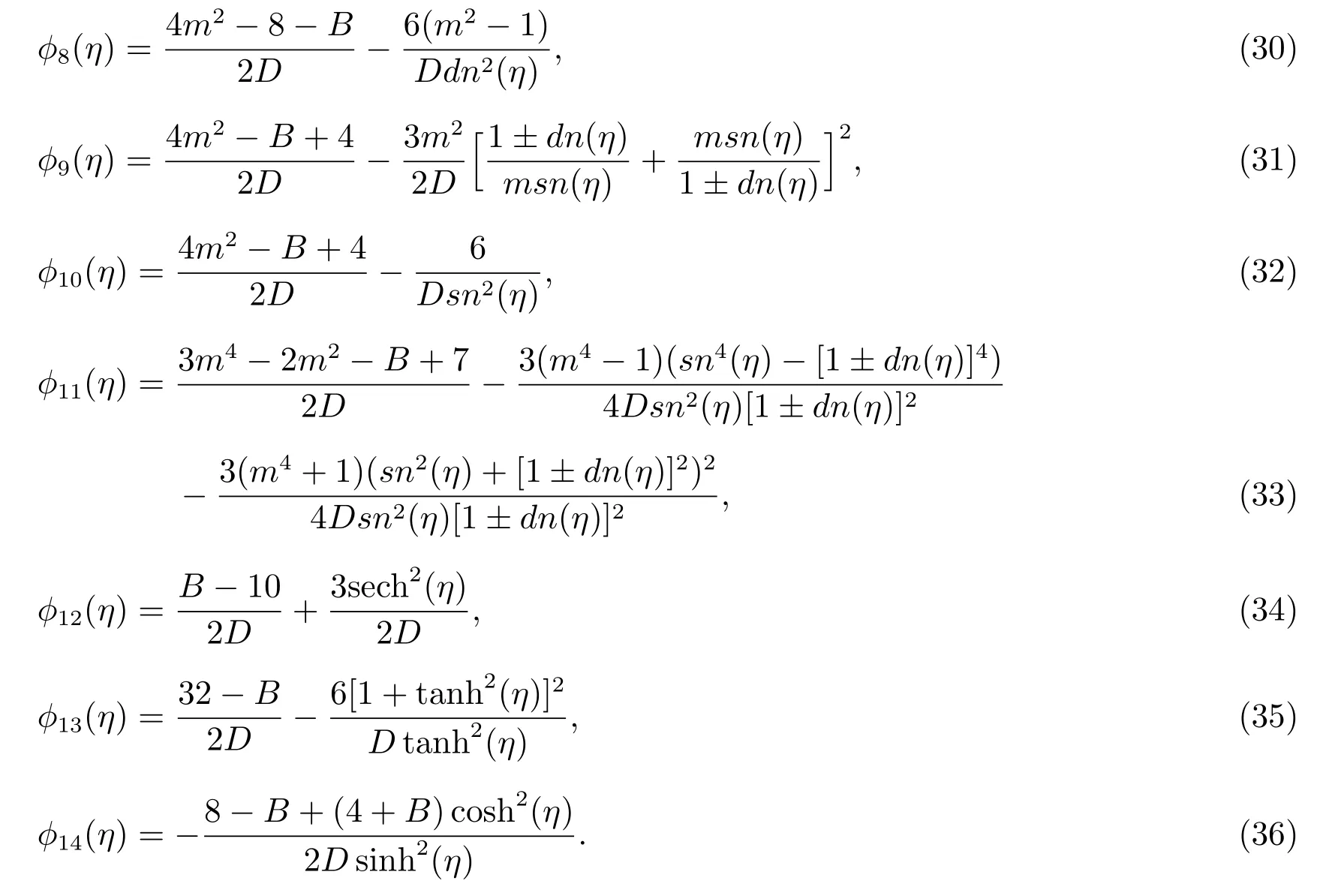
3 Applications to the variable-coefficient KP equation
The general variable-coefficient Kadomtsev-Petviashvili(KP)equation reads

with
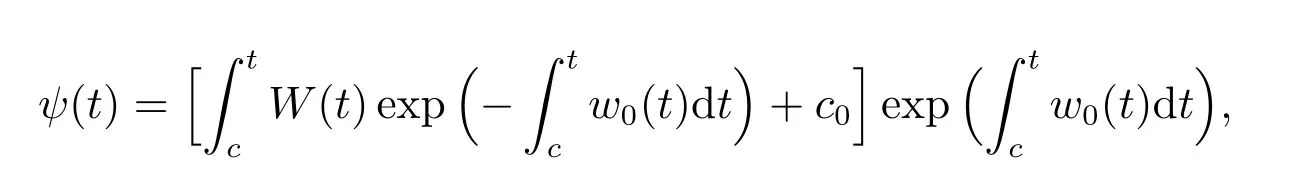
whereuis a differentiable function ofx,yandt,andwi(t)(i=0,1,2,3,4),vi(t)(i=2,3),si(t)(i=1,2)are all analytic,sufficiently differentiable functions.
Equation(37)can reduce to a series of integrable models.It can describe physical phenomena such as electrostatic wave potential in plasma physics,amplitude of the shallow-water wave,surface wave in fluid dynamics and so on[12].For describing the propagation of solitary waves in inhomogeneous media,(37)have been derived from many physical applications in plasma physics,fluid dynamics and other fields.The(37)have been studied by some authors[13-15].Here,we will find some new solutions of(37)by the method proposed above.
Considering the transformation
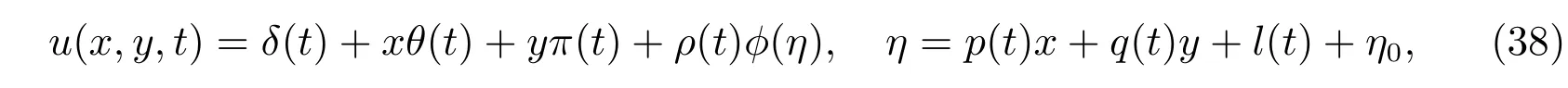
whereδ(t),θ(t),π(t),ρ(t),?(η),p(t),q(t)andl(t)are functions to be determined,η0is an arbitrary constant.
Substituting(38)into(37),yields
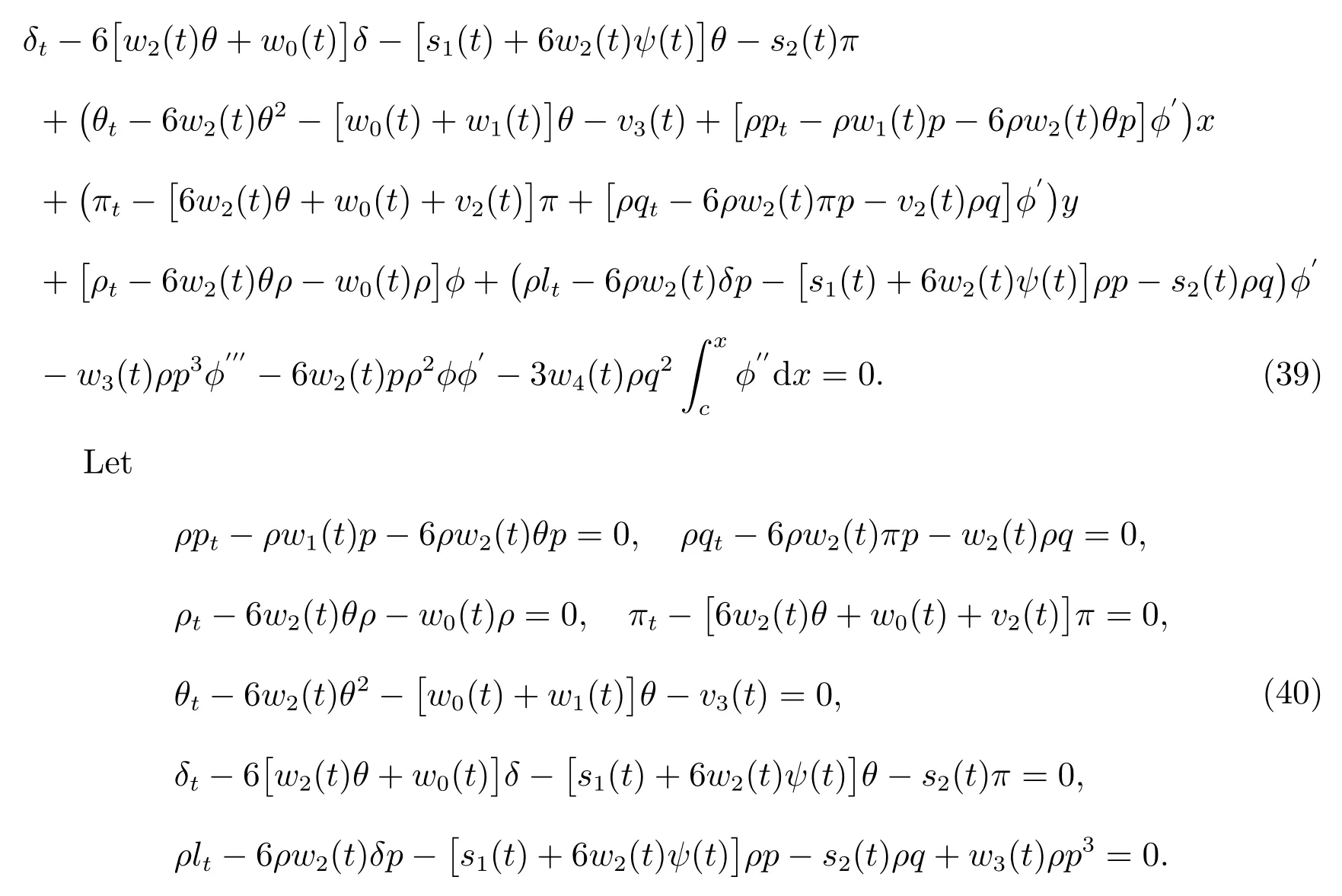
Solving the equations above,yields
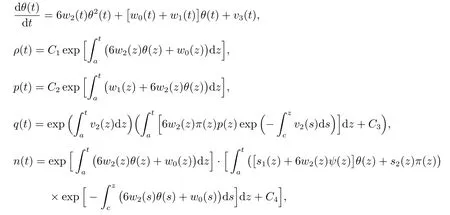
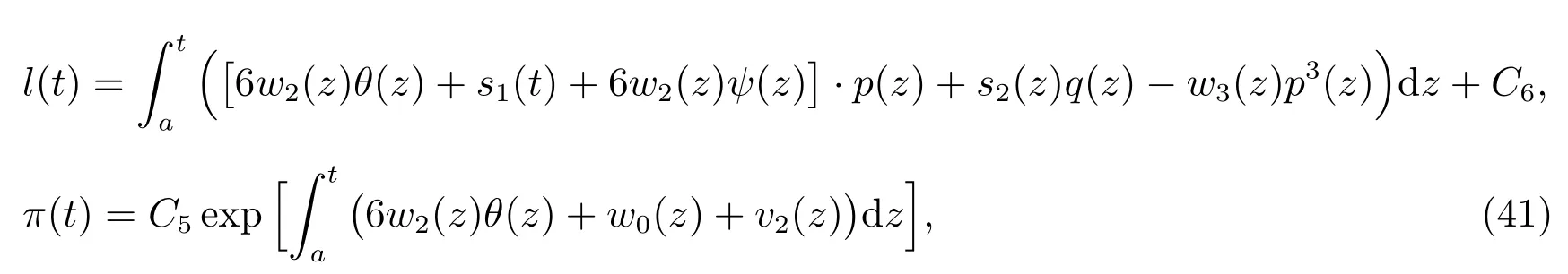
whereC1,C2,C3,C4,C5,C6are integration constants.
Substituting(40)into(39),we obtain
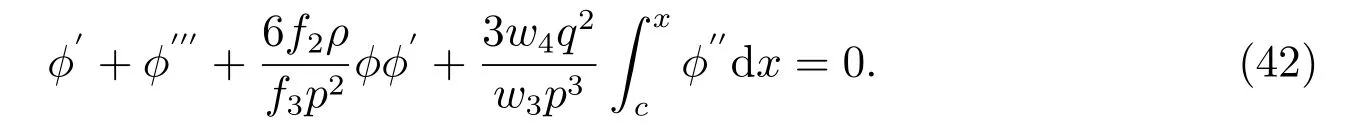
Differentiating the above equation with regard tox,yields
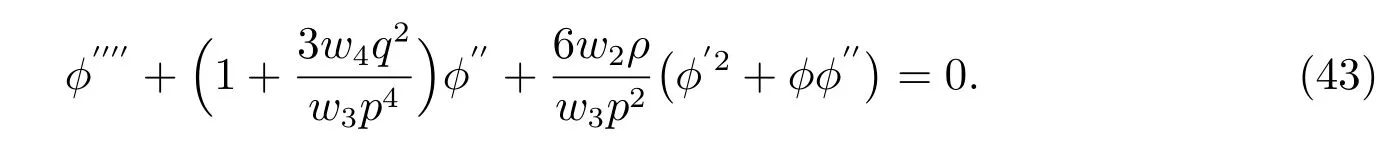
Integrating the above equation twice with regard toη,we obtain
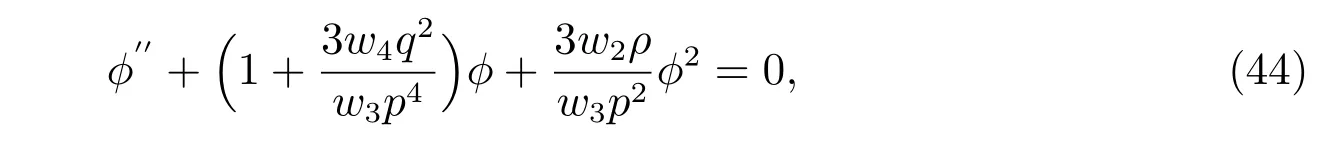
with the integration constants taken to be zero.
Then(37)becomes
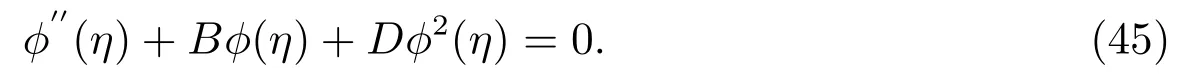
Equation(45)coincides with(19),where
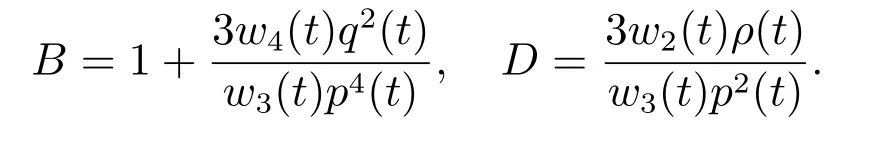
Then the solutions of(37)are
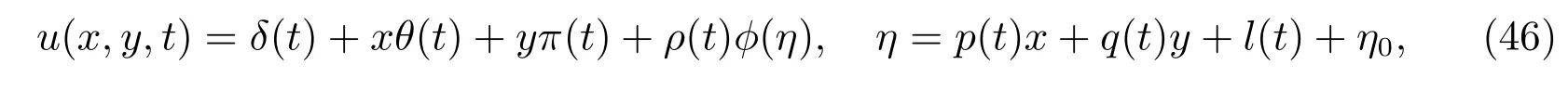
whereδ(t),θ(t),π(t),ρ(t),p(t),q(t),l(t)are defined by(41)and?(η)appearing in these solutions are given by(23)—(36).
Substituting(23)—(36)into(46),we obtain the following dark solitary wave,bell profile solitary wave and Jacobian elliptic function solutions of the general variablecoefficient Kadomtsev-Petviashvili equation(37).

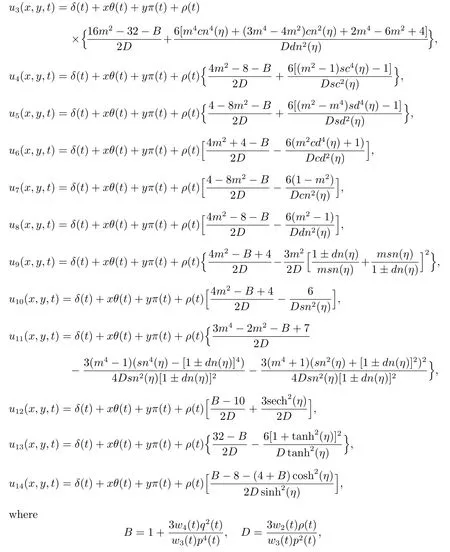
δ(t),θ(t),π(t),ρ(t)are defined by(41)andη0are arbitrary constant.
Remark 1If the modulusm→1,some solitary wave solutions can be obtained where some trigonometric function solutions can also be obtained if the modulusm→0.Here we omit them.
Remark 2To the best of our knowledge,the solutionsu1?u6,u9andu11of(37)are new,which can not be found in[13—15].
Remark 3The proposed algorithm can also be applied to other variable-coefficient PDEs in mathematical physics.For some signi fi cant variable-coefficient PDEs in the fi elds of mathematics and physics,if it can be transformed into the form of elliptic equation(19),then the solutions to variable-coefficient PDEs are readily obtained.
4 Conclusions
In summary,the auxiliary elliptic-like equation method is presented and applied to the variable-coefficient Kadomtsev-Petviashvili equation.As a result,several new exact solutions are obtained which include dark solitary wave solutions,bell profile solitary wave solutions and Jacobian elliptic function solutions.This method is standard,direct and realized by computer mechanization,which is useful for describing certain nonlinear physical phenomena as well as can be applied to other variable-coefficient PDEs in mathematical physics.
In addition,Fan and Chow[16]once applied the Bell polynomials to deduce the Darboux covariant Lax pairs and infinite conservation laws of some(2+1)-dimensional nonlinear evolution equations.Based on this theory,we hope investigate some corresponding properties of(37)presented in the paper in future.
References:
[1]Ablowitz M J,Clarkson P A.Solitons,Nonlinear Evolution Equations and Inverse Scattering[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,1991
[2]Lamb G L.Analytic descriptions of ultrashort optical pulse propagation in a resonant medium[J].Reviews of Modern Physics,1971,43(2):99-124
[3]Gu C H.Darboux Transformation in Soliton Theory and its Geometric Applications[M].Shanghai:Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers,1999
[4]Malfliet W.Solitary wave solutions of nonlinear wave equations[J].American Journal of Physics,1992,60(4):650-654
[5]Zhang Y F,Tam H,Feng B L.A generalized Zakharov-Shabat equation with finite-band solutions and a soliton-equation hierarchy with an arbitrary parameter[J].Chaos,Solitons and Fractals,2011,44(5):968-976
[6]Fan E G.Integrable System and Computer Algebra[M].Beijing:Science Press,2004
[7]Zhang Y F,Fan E G,Zhang Y Q.Discrete integrable couplings associated with Toda-type lattice and two hierarchies of discrete soliton equations[J].Physics Letters A,2006,357(6):454-461
[8]Zhang Y F,Guo F K.Matrix lie algebras and integrable couplings[J].Communications in Theoretical Physics,2006,46(5):812-818
[9]Fan E G.Extended tanh-function method and its applications to nonlinear equations[J].Physics Letters A,2000,277(4-5):212-218
[10]Li B C,Zhang Y F.Explicit and exact traveling wave solutions for Konopelchenko-Dubrovsky equation[J].Chaos,Solitons and Fractals,2008,38(4):1202-1208
[11]Wang M L.Solitary wave solutions for variant Boussinesq equations[J].Physics Letters A,1995,199(3-4):169-172
[12]Yan Z Y,Zhang H Q.New explicit solitary wave solutions and periodic wave solutions for Whitham-Broer-Kaup equation in shallow water[J].Physics Letters A,2001,285(5-6):355-362
[13]Zhang Y F,Wang Y.A higher-dimensional Lie algebra and its decomposed subalgebras[J].Physics Letters A,2006,360(3):92-98
[14]Ghosh S,Kundu A,Nandy S.Soliton solutions,Liouville integrability and gauge equivalence of Sasa-Satsuma equation[J].Journal of Mathematical Physics,1999,40(4):1993-2000
[15]Yan Z Y,Zhang H Q.Similarity reductions for 2+1-dimensional variable coefficient generalized Kadomtsev-Petviashvili equation[J].Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,2014,21(4):645-651
[16]Fan E G,Chow K W.Darboux covariant Lax pairs and infinite conservation laws of the(2+1)-dimensional breaking soliton equation[J].Journal of Mathematical Physics,2011,52(2):1-10
 工程數(shù)學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)2016年3期
工程數(shù)學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)2016年3期
- 工程數(shù)學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)的其它文章
- Numerical Simulation of Free Surface for Navier-Stokes Equations?
- A Balanced Finite Element Method of Least-squares Formulation for Singularly Perturbed Reaction-diffusion Problems?
- 可壓縮歐拉方程在不變子空間中的精確解?
- 基于圖模型方法的Granger因果性檢驗(yàn)?
- 基于代數(shù)決策圖的貝葉斯網(wǎng)絡(luò)參數(shù)簡(jiǎn)化技術(shù)?
- 基于SCAD的壓縮感知閾值迭代算法的收斂性分析?
