具有脈沖毒素投放和營養(yǎng)再生的恒化器模型
傅曉釩,張樹文
(集美大學(xué)理學(xué)院,福建 廈門 361021)
具有脈沖毒素投放和營養(yǎng)再生的恒化器模型
傅曉釩,張樹文
(集美大學(xué)理學(xué)院,福建 廈門 361021)
研究具有脈沖毒素投放和營養(yǎng)再生的恒化器模型.利用脈沖微分方程的比較定理和小擾動方法得到了邊界周期解全局漸近穩(wěn)定的充分條件,進而得到了系統(tǒng)持續(xù)生存的充分條件.結(jié)果表明毒素環(huán)境將會導(dǎo)致微生物種群的滅絕.
脈沖毒素投放;營養(yǎng)再生;恒化器;持續(xù)生存
1 引言
恒化器是進行微生物連續(xù)培養(yǎng)的一種實驗裝置,用于研究微生物在一個連續(xù)培養(yǎng)環(huán)境中的生長狀況.恒化器模型的設(shè)計和研究對于食品加工,污水處理,轉(zhuǎn)基因微生物的培養(yǎng)等都具有積極作用.近年來,已經(jīng)有許多學(xué)者利用脈沖微分方程理論[12]解決各類生態(tài)學(xué)問題,如捕食-食餌系統(tǒng)[34],并且對各類條件下的恒化器模型進行了大量研究[57].文獻[5]研究了具有階段結(jié)構(gòu)的單種群恒化器模型,文獻[6]研究了具有脈沖輸入和營養(yǎng)回收的單種群恒化器模型.文獻[7]研究了具有脈沖擴散的污染環(huán)境下的恒化器模型.在自然環(huán)境中,潮水的沖刷既給微生物帶來營養(yǎng)物,也帶來了環(huán)境毒素.因此,本文建立了具有脈沖毒素投放的恒化器模型,用定期脈沖投放來模擬自然因素對微生物的影響,并且對死去微生物考慮營養(yǎng)回收的作用.
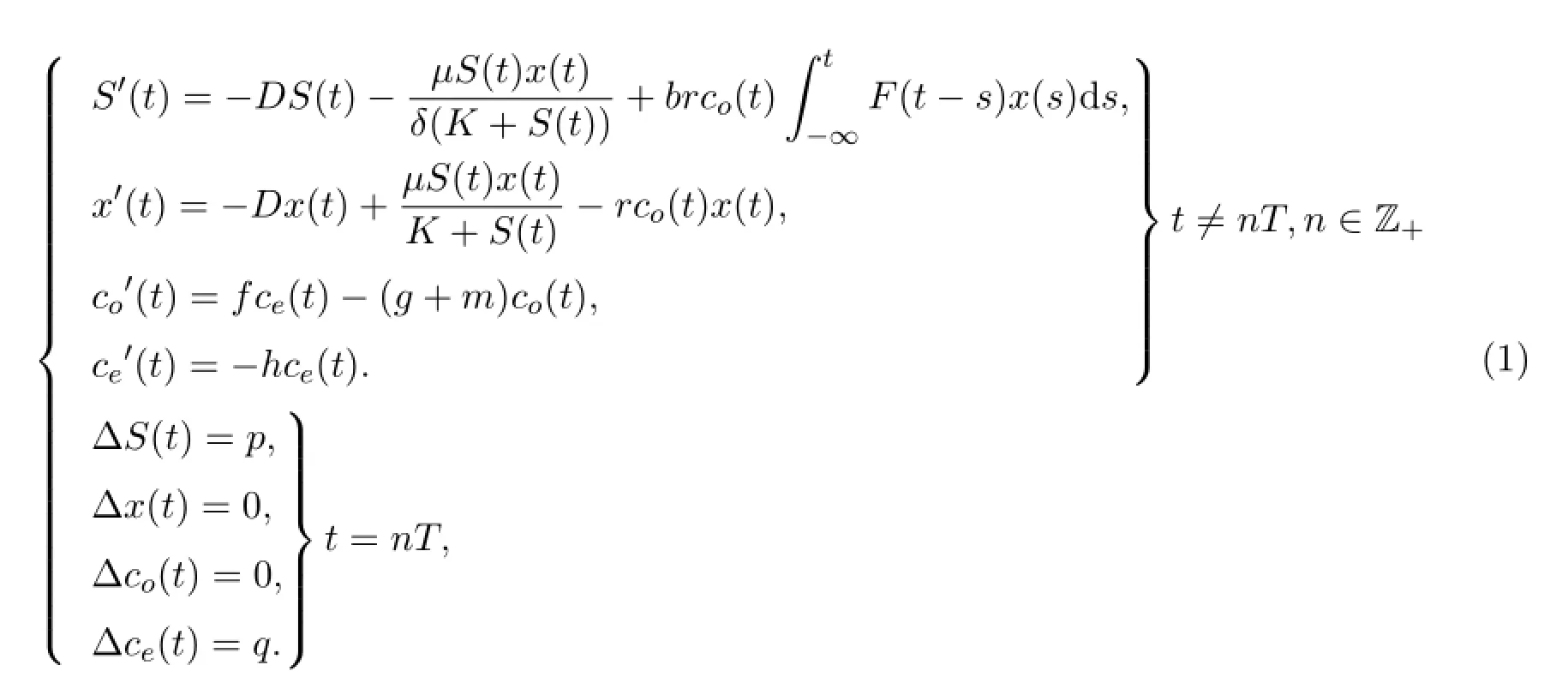
其中F(t)=a e-at,a>0,且滿足0≤b≤1,1δ≥1.S(t)表示t時刻營養(yǎng)物質(zhì)的濃度,x(t)表示t時刻微生物的濃度,co(t)表示微生物體內(nèi)毒素的濃度,ce(t)表示環(huán)境毒素的濃度,fce(t)表示微生物從環(huán)境中吸收毒素的濃度,-gco(t),-m co(t)分別表示微生物消除和凈化毒素的濃度,-hce(t)表示流失的環(huán)境毒素的濃度,T表示脈沖周期,D表示沖洗速率,p表示投放的營養(yǎng)物質(zhì)的濃度,q表示投放的環(huán)境毒素的濃度,b表示死去的微生物被重新轉(zhuǎn)化為營養(yǎng)的部分,δ表示微生物的產(chǎn)生和消耗的營養(yǎng)物的比,r表示微生物的死亡率.
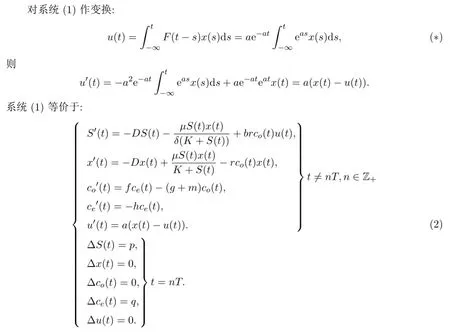
2 預(yù)備引理


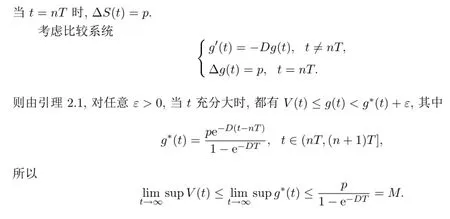
3 滅絕和持續(xù)生存



4 結(jié)論
通過上述討論,得到了系統(tǒng)的一個臨界值:

當(dāng)Δ<0時,系統(tǒng)(2)的邊界周期解(S*(t),0,c*o(t),c*e(t),0)是全局漸近穩(wěn)定的,這意味著微生物將趨于滅絕.當(dāng)Δ>0時,系統(tǒng)(2)是持續(xù)生存的.
[1] Laksmikantham V, Bainov D D. Theory of Impulsive Differential Equation[M]. Singapore: World Science, 1989.
[2] Bainov D D, Simeonov P S. Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications[M]. London: Longman, 1993.
[3] 張樹文,張耘嘉,譚德君.具脈沖效應(yīng)和Beddington-DeAnglis功能反應(yīng)時滯周期捕食系統(tǒng)[J].純粹數(shù)學(xué)與應(yīng)用數(shù)學(xué),2010,26(4):534-540.
[4] Zhang Shuwen, Tan Dejun. Permanence in a food chain system with impulsive perturbations[J]. Chaos, Solitions and Fractals, 2009,40:392-406.
[5] Li Shuping, Pei Yongzhen. Stability analysis for a single-species chemostat model with age structure and contribution of population to resource[J]. Math. Chem., 2010,47:111-122.
[6] Teng Zhidong, Gao Rong. Global behaviors of Monod type chemostat model with nutrient recycling and impulsive input[J]. Math. Chem., 2010,47:276-294.
[7] Jiao Jianjun, Ye Kaili, Chen Lansun. Dynamical analysis of a five-dimensioned chemostat model withimpulsive diffusion and pulse input environmental toxicant[J]. Chaos, Solitions and Fractals, 2011,44:17-27.
A chemostat model with impulsive toxicant input and nutrient recycling
Fu Xiaofan,Zhang Shuwen
(School of Sciences, Jimei University, Xiamen 361021, China)
In this paper, we consider a chemostat model with impulsive toxicant input and nutrient recycling. By comparison theory and small amplitude perturbation method, we obtain the su±cient condition for the global asymptotic stability of boundary periodic solution. Furthermore, the su±cient condition for the permanence of the system is obtained. The results show that poisonous environment will lead the microorganism species to be extinct.
impulsive toxicant input, nutrient recycling, chemostat, permanence
O175.12
A
1008-5513(2012)02-0262-07
2011-12-09.
福建省自然科學(xué)基金(2008J0199).
傅曉釩(1987-),碩士生,研究方向:生物數(shù)學(xué).
2010 MSC:34D05,34D20

