Three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy of left femur foci does not damage the sciatic nerve
Wanlong Xu, Xibin Zhao, Qing Wang, Jungang Sun, Jiangbo Xu, Wenzheng Zhou, Hao Wang, Shigui Yan, Hong Yuan
1 People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
2 The Second Af fi liated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China
Three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy of left femur foci does not damage the sciatic nerve
Wanlong Xu1, Xibin Zhao1, Qing Wang1, Jungang Sun1, Jiangbo Xu1, Wenzheng Zhou1, Hao Wang1, Shigui Yan2, Hong Yuan1
1 People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
2 The Second Af fi liated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China
During radiotherapy to kill femoral hydatid tapeworms, the sciatic nerve surrounding the focus can be easily damaged by the treatment. Thus, it is very important to evaluate the effects of radiotherapy on the surrounding nervous tissue. In the present study, we used three-dimensional, conformal, intensity-modulated radiation therapy to treat bilateral femoral hydatid disease inMeriones meridiani. The focus of the hydatid disease on the left femur was subjected to radiotherapy (40 Gy) for 14 days, and the right femur received sham irradiation. Hematoxylin-eosin staining, electron microscopy, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-dUTP nick end labeling assays on the left femurs showed that the left sciatic nerve cell structure was normal, with no obvious apoptosis after radiation. Trypan blue staining demonstrated that the overall protoscolex structure in bone parasitized withEchinococcus granulosusdisappeared in the left femur of the animals after treatment. The mortality of the protoscolex was higher in the left side than in the right side. The succinate dehydrogenase activity in the protoscolex in bone parasitized withEchinococcus granulosuswas lower in the left femur than in the right femur. These results suggest that three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy achieves good therapeutic effects on the secondary bone in hydatid disease inMeriones meridianiwithout damaging the morphology or function of the sciatic nerve.
nerve regeneration; three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy; hydatid disease; sciatic nerve; neurons; radiation damage; succinate dehydrogenase; NSFC gran ts; neural regeneration
Funding:This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81360276; a grant from the Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in China, No. 2013911129; a grant from the Youth Science and Technology Innovation Talents Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region-Young Doctor Talents Training Project, No. 2013731013; the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2012211B34; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2014M552566XB.
Xu WL, Zhao XB, Wang Q, Sun JG, Xu JB, Zhou WZ, Wang H, Yan SG, Yuan H. Three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy of left femur foci does not damage the sciatic nerve. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(20):1824-1829.
Introduction
Hydatid disease, also called echinococcosis, is a parasitic disease ofEchinococcustapeworms, which is a zoonotic infection in humans (Wang et al., 2013). Bone hydatid disease occurs when echinococcus larvae parasitizes bone tissue. Recently, three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy has been frequently used clinically to treat tumors because of its advantages, including efficacy in killing tumors and protection of the peripheral organs. Conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy has been demonstrated to kill bone hydatid cyst cells without injuring the surrounding tissue (Xu et al., 2012a, b, d). However, because the anatomical structure of the femur is complex, it remains unclear whether conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy would harm the sciatic nerve. The aim of the present study was to assess the ef fi cacy of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy on killing hydatid cysts in the femur ofMeriones meridianiand whether it damages the sciatic nerve, in order to determine the efficacy and safety of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy in the treatment of hydatid disease in bone.
Materials and Methods
Establishment of animal models of hydatid disease in bone
One hundred and twenty purebred, clean, adult, maleMeriones meridianiaged 2-3 months and weighing 30.0 ± 6.5 g were provided by the Institute of Experimental Animals, Chinese Armed Police General Hospital (license No. SCXK (Jing) 2011-0012). The animals were housed in individual cages, fed with complete feed and clean water at 20-23°C and humidity of 40-60%, and ensured adequate sleep. The experimental protocol was approved by the AnimalEthics Committee of the People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in China (Ethical approval No. 20130301A41). The subperiosteum of the hind femurs ofMeriones meridianiwas selected as the best position for hydatid inoculation with a suspension of 12,000 scolex/mL. The hydatid suspension was injected into the subperiosteum of the hind femur ofMeriones meridianiusing a No. 7 needle. Three months later, X-ray and CT examinations veri fi ed a successful inoculation of secondary hydatid in the femur.
Radiotherapy
The regions in the 120Meriones meridianiwith hydatid cysts were considered to be the target areas. A successful treatment strategy would not harm the surrounding blood vessels, tendons, nerves, and skin. CT scanning (Philips, Cleveland, OH, USA) and computer-aided design were used to outline the target areas. After formulating a radiotherapy plan, theMeriones meridianireceived inhalation anesthesia with desflurane and were placed in a restraint (Beijing Baiyou Putai Medical Products Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Using a three-dimensional treatment planning system (Novalis knife, Siemens, Munich, Germany), the focus of the hydatid disease in the left femur underwent image-guided radiotherapy (4 Gy) once a day for 10 sessions within 2 weeks (exposures occurred Monday through Friday; 10 separate days). The total dose was 40 Gy, with a dose rate of 300 cGy/min. The dose in the right femur was 0 Gy (control).
Sample collection
After conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy, theMeriones meridianiwith hydatid disease were subjected to inhalation anesthesia and euthanized by air embolism. Under an operating microscope (Sichuan Keaoda Company, The Institute of Optics and Electronics, The Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China), cysts from theEchinococcus granulosuswere harvested from the femoral marrow cavities bilaterally. Portions of the hydatid fl uid were aspirated from the cysts to stabilize intracapsular pressure. Then, the remaining protoscolex of theEchinococcus granulosusand hydatid fl uid were aspirated. All the obtained samples were mixed and made into suspensions, which were separately placed in sterile polyethylene tubes. Bilateral sections of the sciatic nerve after radiotherapy were obtained, rapidly fixed in 10% formaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde, and stored in liquid nitrogen. After paraf fi n imbedding, all samples were sliced into 4 μm-thick sections, dewaxed, hydrated, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The histological morphology of the sciatic nerves was observed under light microscopy (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).
Trypan blue staining to detect pathological changes in the boneEchinococcus granulosusand the protoscolex mortality after radiation therapy
The suspensions of protoscolex from theEchinococcus granulosusin sterile polyethylene tubes were stained with 1% trypan blue solution (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) for approximately 2 minutes and then smeared on the slides. The percentage of necrotic protoscolex was judged using visual fi elds on an inverted microscope (Leica). Dead protoscoleces show damaged structure and are stained with trypan blue, while live scolex have clear structure and are not stained with trypan blue. The percentage of necrotic cells was calculated as the number of protoscolex stained with trypan blue/the total number of protoscolex × 100%.
Enzyme histochemical staining to detect succinate dehydrogenase activity in protoscolex
The smears of the suspensions ofEchinococcus granulosusprotoscolex in the sterile polyethylene tubes were dried with a hair dryer using the nitroblue tetrazolium (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) method. Then, the samples were incubated in incubation solution at 25-30°C for 50 minutes until the blue color had fully developed. After being washed in distilled water, all the samples were fi xed in 10% calcium formate for 10 minutes, washed with running water for 3 minutes, and then observed with a microscope (Leica). Using the BT-2000 color pathology image analysis system (Hubei Botai Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, Hubei Province, China), 10 fields were randomly selected from each image and mean optical density was measured.
Ultrastructure of the sciatic nerve by transmission electron microscopy
After washing with buffer solution, the samples were prefi xed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 2 hours, post- fi xed in 1% osmic acid for 2 hours, and then washed with PBS. The samples were dehydrated with increasing concentrations of ethanol and acetone, embedded, dried at 37°C overnight, sliced into 50 nm-thick sections, and observed and imaged with a transmission electron microscope (Hitachi, Hokkaido, Japan).
Apoptosis of sciatic nerve neurons detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) after radiotherapy
Paraffin sections of the sciatic nerves were washed twice with xylene for 4-5 minutes, rehydrated through a graded alcohol series in 1 minute intervals, incubated in protease at 37°C for 20-30 minutes, incubated in transparent liquid for 6 minutes, and washed twice with PBS. When the slides were dry, the sections were incubated with 50 μL of TUNEL reagent (Boehringer Mannheim, Berlin, Germany) at 37°C for 1 hour, and then were washed three times with PBS. After the slides were dry, the sections were incubated with POD (Boehringer Mannheim) at 37°C for 30 minutes, washed three times with PBS, incubated with 100 μL of diaminobenzidine at 15-25°C for 10 minutes, washed three times with PBS, and then stained with hematoxylin and diaminobenzidine (Boehringer Mannheim). Next, the slides were dehydrated through a graded alcohol series, permeabilized with xylene, and mounted with a neutral resin. Using the BT-2000 color pathology image analysis system (Hubei Botai Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.), 10 fi elds at 20 × magni fication with densely distributed apoptotic cells were selectedfrom each section. The neuronal apoptotic index (%) was calculated as the mean optical density of the TUNEL-positive cells × the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells (from all types of cells in the fi eld) (Stock et al., 2012).
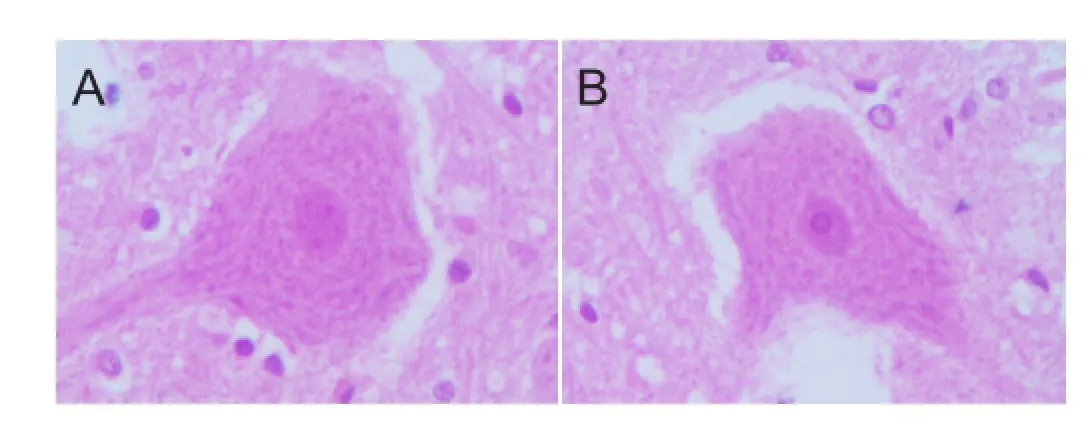
Figure 1 Effects of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy on the morphology of sciatic nerve neurons in the femur ofMeriones meridianiwith secondary hydatid disease (hematoxylin-eosin staining, light microscopy, × 400).
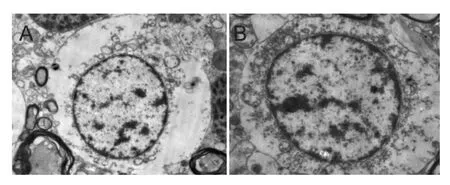
Figure 2 Effects of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy on the ultrastructure of sciatic nerve neurons in the femur ofMeriones meridianiwith secondary hydatid disease (electron microscopy, × 8,000).
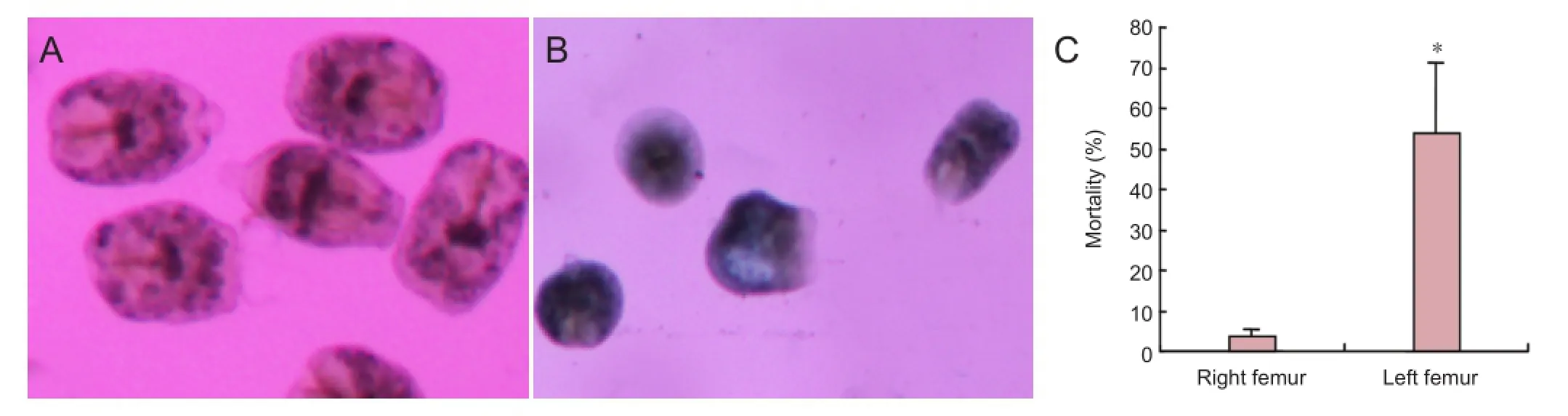
Figure 3 Effects of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy on the protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosus.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 19.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) and expressed as the mean ± SD. The group means were compared using Student’st-tests (α= 0.05). Values ofP< 0.05 were considered statistically signi fi cant.
Results
Conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy did not alter the morphology of sciatic nerve neurons in the femur ofMeriones meridianiwith secondary hydatid disease
Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed a normal morphology of the sciatic nerve neurons in the left femur ofMeriones meridianiwith osseous hydatid disease after radiotherapy. Although a few neuronal cells showed reversible changes, most cells were triangular or polygonal with clear dendrites and axons. The nuclei were plump, and the nuclear structure was normal. Abundant Nissl’s bodies were uniformly distributed in the cytoplasm, and no clear differences were found between the sciatic nerve neurons in the right side that did not receive radiotherapy (Figure 1).
The transmission electron microscopy results demonstrated that the sciatic nerve neurons in the left side ofMeriones meridianiwith osseous hydatid disease were normal after conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy. The cell membranes were not ruptured, the organelles in the cytoplasm were complete, and the nuclei were in the center, with no visible pyknosis. No significant differences were found compared to the neurons in the right side that did not receive radiotherapy (Figure 2).
Conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy increased the percentage of dead protoscolex in the boneEchinococcus granulosus
In the right femur, which did not receive radiotherapy, the shape of the protoscolex of theEchinococcus granulosuswas normal in the region with echinococcosis granulosa, and the edge was distinct, repelling trypan blue and remaining unstained. However, after radiotherapy, the protoscolex in the left femur disappeared in the region withEchinococcus granulosus, the cell edges were not distinct, and the cells stained positively for trypan blue. The percent age of dead protoscolex in the osseous hydatid was increased in the region with echinococcosis granulosa after radiotherapy (P<0.05; Figure 3).
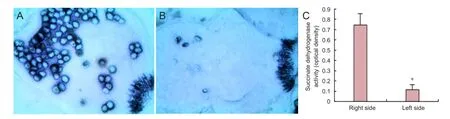
Figure 4 Effects of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy on succinate dehydrogenase activity in the protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosus.
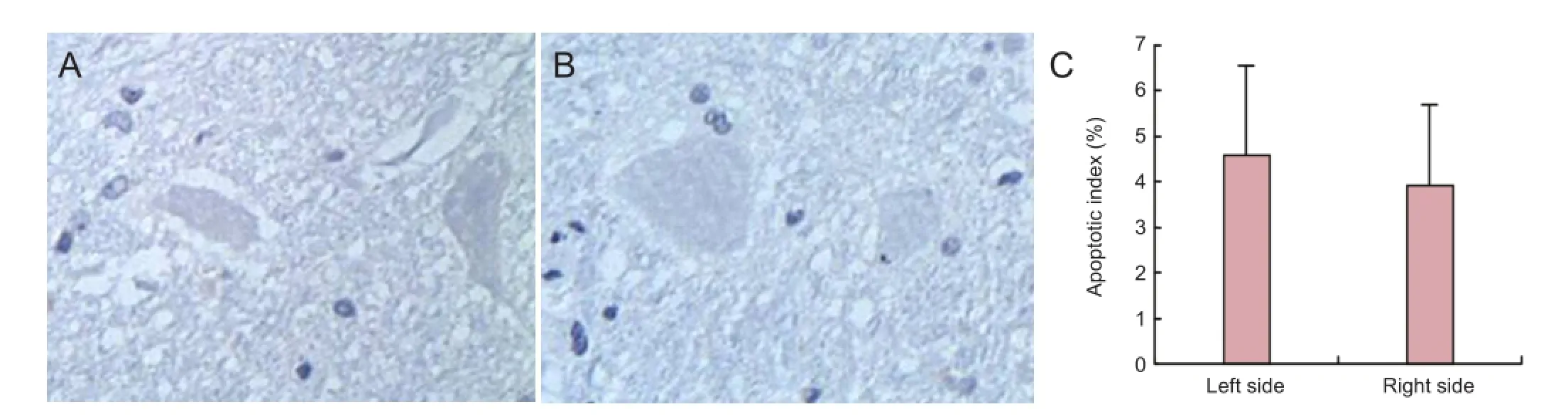
Figure 5 Effects of conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy on the apoptosis of sciatic nerve neurons inMeriones meridianiwith secondary hydatid disease.
Conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy decreased succinate dehydrogenase activities in protoscolex
Enzyme histochemical staining showed a high activity of succinate dehydrogenase in the protoscolex of the osseous hydatid in the right femur, which did not receive radiotherapy. The succinate dehydrogenase activity was decreased by radiotherapy in the left femur. The mean optical density of the protoscolex in the osseous hydatid was lower in the left femur than in the right femur (P< 0.05; Figure 4).
Conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy did not alter the apoptosis index of sciatic nerve neurons inMeriones meridianiwith secondary hydatid disease
The apoptotic index, calculated from the TUNEL staining, was not different between the left and right femurs in the animals (P> 0.05; Figure 5).
Discussion
Since the turn of the century, the rapid progress in imaging and computer technologies has created an era of precision radiotherapy. Of the different radiotherapy techniques, three-dimensional conformal intensity-modulated radiation therapy has become the most widely used. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy controls the direction of the radiation using a computer. Precise, high-dose radiation can be focused on the diseased tissue area of concern, while only rarely damaging the surrounding tissue. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy is a reliable, high-precision radiation therapy used in the clinic, which is also highly praised by scholars (Xilinbaoleri et al., 2009; Cho et al., 2010; Hevezi, 2010; Lisbona et al., 2010; Nagesha et al., 2010; Barney et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2011; Li et al., 2011; Peng et al., 2011; Sangalli et al., 2011; Shi et al., 2011; Teke et al., 2011; Valeriani et al., 2011; Graff et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2012; Mohammed et al., 2012; Stock et al., 2012; Bettington et al., 2013; Bonnette, 2013; Ichinohe et al., 2013; Kim et al., 2013; Kobayashi et al., 2013; Li et al., 2013; Margaritora et al., 2013; Perri et al., 2013; Qian et al., 2013; Salama and Vokes, 2013; Sun et al., 2013; Sung et al., 2013; Tao et al., 2013; Yin et al., 2013;Zhang et al., 2013). Because intensity-modulated radiation therapy is effective at killing tumor cells, we believed that it would be effective for killing the protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosus. Thus, in the present study, we performed intensity-modulated radiation therapy, trypan blue staining, and histochemical staining, which showed that intensity-modulated radiation therapy effectively killed the protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosuswithin the cancellous bone and trabeculae and decreased the residual and relapse rates of bone hydatid.
The results of this study indicated that intensity-modulated radiation therapy at the therapeutic dose (40 Gy) used on benign tumors was effective at killing protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosus. Moreover, the histochemical staining results showed that intensity-modulated radiation therapy decreased the activity of succinate dehydrogenase in the protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosus. Succinate dehydrogenase is a rate-limiting enzyme in the Krebs cycle and cell respiration chain, is involved in cellular energy metabolism and oxygen utilization, and is necessary for cell metabolism and vital movement. The succinate dehydrogenase activity re fl ects the workings of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and indirectly re fl ects the levels of cellular aerobic glucose metabolism (Xu et al., 2014). In the present study, intensity-modulated radiation therapy decreased the succinate dehydrogenase activity in the protoscolex ofEchinococcus granulosus, likely causing a reduction in cellular energy metabolism and eventually cell death. Our experimental results are consistent with those of other papers. Chen and Xie (2014) reported that radiotherapy was effective for treating bone hydatid disease in mice, with different radiation doses leading to different hydatid scolex mortalities, but none of the various radiation doses injured the mice. Xu et al. (2012c) performed intensity-modulated radiation therapy for bone hydatid for 1 month and found that the apoptotic index of the cells in the germinal layer of the hydatid cysts was positively correlated with the dose of radiotherapy. Wang et al. (2009) reported that X-ray irradiation could kill echinococcus isolated from rats, and this lethal effect was dose-dependent. Zhang et al. (2011) demonstrated that an appropriate radiation dose inhibited the growth of alveolar hydatid in rats with hydatid disease. Yuan et al. (2013) showed thatEchinococcus granulosusprotoscoleces were directly killed by γ-ray irradiationin vitroand that the protoscolex cells were apoptotic.
Sciatic nerve is the tissue that most needs protection during radiotherapy for femoral lesions. However, the light microscopy, electron microscopy, and TUNEL assay results here indicated that the morphology of sciatic nerve neurons was normal after radiotherapy, suggesting that intensity-modulated radiation therapy during the treatment of osteohydatidosis is relatively safe for the surrounding tissues.
In summary, intensity-modulated radiation therapy was effective for the treatment of secondary osteohydatidosis and safe for the surrounding tissue. However, this was a preliminary study using an animal model. Additional clinical studies should be performed before applying the above results in the clinic.
Acknowledgments:We are very grateful to Zhang C from the Animal Laboratory of the First Teaching Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University in China and Zhang YJ from the People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in China for their technical support.
Author contributions:Xu WL provided data, ensured the integrity of the data and wrote the manuscript. Yuan H participated in study concept and design, and obtained the funding. Zhao XB was in charge of manuscript authorization. Sun JG, Xu JB, Zhou WZ and Wang H provided technical or data support, and served as the principle investigators. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Con fl icts of interest:None declared.
Barney BM, Lee RJ, Handrahan D, Welsh KT, Cook JT, Sause WT (2011) Image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) for prostate cancer comparing kV imaging of fi ducial markers with cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80:301-305.
Bettington CS, Tripcony L, Bryant G, Hickey B, Pratt G, Fay M (2013) A retrospective analysis of survival outcomes for two different radiotherapy fractionation schedules given in the same overall time for limited stage small cell lung cancer. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 57:105-112.
Bonnette P (2013) Chemo-radiotherapy before surgery in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Rev Mal Respir 30:105-114.
Chen G, Xu WL, Xilinbaoleri, Bai JP (2011) Evaluation of radiation damages of vertebral bone cells after radiotherapy in dogs. Jiangsu Yiyao 37:1882-1884.
Chen L, Xie ZR (2014) The research progress of echinococcosis radiotherapy. Xinjiang Yike Daxue Xuebao 36:557-559.
Cho B, Poulsen PR, Keall PJ (2010) Real-time tumor tracking using sequential kV imaging combined with respiratory monitoring: a general framework applicable to commonly used IGRT systems. Phys Med Biol 55:3299-3316.
Graff P, Hu W, Yom SS, Pouliot J (2012) Does IGRT ensure target dose coverage of head and neck IMRT patients? Radiother Oncol 104:83-90.
Hevezi JM (2010) Current IGRT, SBRT, and SRS procedures and reimbursement. J Am Coll Radiol 7:739-740.
Ichinohe K, Ijima M, Usami T, Baba S (2013) Complete remission of primary retroperitoneal transitional cell carcinoma after radiotherapy and oral chemotherapy: a case report. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 95:e52-54.
Kim MJ, Yeo SG, Kim ES, Min CK, Se An P (2013) Intensity-modulated stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 5:840-844.
Kobayashi N, Nakayama H, Osaka Y, Tachibana S, Nogi S, Tajima Y, Okubo M, Mikami R, Kanesaka N, Sugahara S, Hoshino S, Tsuchida A, Tokuuye K (2013) Tumor response after low-dose preoperative radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy for squamous cell esophageal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 33:1157-1161.
Lee JH, Wu HG, Kim HJ, Kim DW, Lee SH, Kim TM, Kim YW, Heo DS (2012) Influence of comorbidities on the efficacy of radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy in elderly stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Res Treat 44:242-250.
Li F, Song D, Lu Y, Zhu H, Chen Z, He X (2013) Delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) immune response related with EBV-DNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with autologous dendritic cell vaccination after radiotherapy. J Immunother 36:208-214.
Li T, Thongphiew D, Zhu X, Lee WR, Vujaskovic Z, Yin FF, Wu QJ (2011) Adaptive prostate IGRT combining online re-optimization and re-positioning: a feasibility study. Phys Med Biol 56:1243-1258.
Lisbona A, Averbeck D, Supiot S, Delpon G, Ali D, Vinas F, Diana C, Murariu C, Lagrange JL (2010) IMRT combined to IGRT: increase of the irradiated volume. Consequences? Cancer Radiother 14:563-570.
Margaritora S, Cesario A, Cusumano G, Dall’armi V, Porziella V, Meacci E, Lococo F, D’Angelillo R, Congedo MT, Granone P (2013) Pneumonectomy with and without induction chemo-radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: short and long-term results from a single centre. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:29-40.
Mohammed N, Kestin L, Grills I, Shah C, GlideHurst C, Yan D, Ionascu D (2012) Comparison of IGRT registration strategies for optimal coverage of primary lung tumors and involved nodes based on multiple four-dimensional CT scans obtained throughout the radiotherapy course. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1541-1548.
Nagesha DK, Tada DB, Stambaugh CKK, Gultepe E, Jost E, Levy CO, Cormack R, Makrigiorgos GM, Sridhar S (2010) Radiosensitizer-eluting nanocoatings on gold fi ducials for biological in-situ image-guided radio therapy (BIS-IGRT). Phys Med Biol 55:6039-6055.
Peng JL, Kahler D, Li JG, Amdur RJ, Vanek KN, Liu C (2011) Feasibility study of performing IGRT system daily QA using a commercial QA device. J Appl Clin Med Phys 12:3535.
Perri F, Muto P, Argenone A, Ionna F, Longo F, Fulciniti F, Sandomenico F, Daponte A, Caponigro F (2013) Induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin and capecitabine, followed by combined cetuximab and radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced inoperable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a phase I-II study. Oncology 84:251-254.
Qian D, Zhang B, He LR, Cai MY, Mai SJ, Liao YJ, Liu YH, Lin MC, Bian XW, Zeng YX, Huang JJ, Kung HF, Xie D (2013) The telomere/ telomerase binding factor PinX1 is a new target to improve the radiotherapy effect of oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol 229:765-774.
Salama JK, Vokes EE (2013) New radiotherapy and chemoradiotherapy approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:1029-1038.
Sangalli G, Passoni P, Cattaneo GM, Broggi S, Bettinardi V, Reni M, Slim N, Muzio ND, Calandrino R (2011) Planning design of locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma using 4DCT and IMRT/IGRT technologies. Acta Oncol 50:72-80.
Shi W, Li JG, Zlotecki RA, Yeung A, Newlin H, Palta J, Liu C, Chvetsov AV, Olivier K (2011) Evaluation of kV cone-beam CT performance for prostate IGRT: a comparison of automatic grey-value alignment to implanted fi ducial-marker alignment. Am J Clin Oncol 34:16-21
Stock M, Palm A, Altendorfer A, Steiner E, Georg D (2012) IGRT induced dose burden for a variety of imaging protocols at two different anatomical sites. Radiother Oncol 102:355-363.
Sun W, Song L, Ma J, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Gao Y, Ai T (2013) Scope and method of image registration and clinical target volume margin for central-type non-small cell lung cancer in image-guided radiotherapy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 38:132-137.
Sung KW, Lim do H, Son MH, Lee SH, Yoo KH, Koo HH, Kim JH, Suh YL, Joung YS, Shin HJ (2013) Reduced-dose craniospinal radiotherapy followed by tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with high-risk medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol 15:352-359.
Tao Y, Bardet E, Rosine D, Rolland F, Bompas E, Daly-Schveitzer N, Lusinchi A, Bourhis J (2013) Phase I trial of oral etoposide in combination with radiotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma - GORTEC 2004-02. Radiat Oncol 8:40.
Teke T, Gill B, Duzenli C, Popescu IA (2011) A Monte Carlo model of the Varian IGRT couch top for RapidArc QA. Phys Med Biol 56:N295-305.
Valeriani M, Monaco F, Osti MF, DE Sanctis V, Minniti G, Enrici RM (2011) Hypofractionated radiotherapy with or without IGRT in prostate cancer: preliminary report of acute toxicity. Anticancer Res 31:3555-3558.
Wang K, Zhang X, Jin Z, Ma H, Teng Z, Wang L (2013) Modeling and analysis of the transmission of Echinococcosis with application to Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China. J Theor Biol 333:78-90.
Wang X, Wang XH, Bao GS, Liu J, Han J, Jing T (2009) The experimental study on the radiotherapy of echinococcosis. Zhongguo Ren Shou Gonghuanbing Xuebao 25:653-656.
Xilinbaoleri, Xu WL, Wang RZ, Liu H, Zhang JR, Bai JP (2009) The apoptosis of neurons after intensity modulated radiotherapy and conventional radiation therapy of the spine. Xinjiang Yike Daxue Xuebao 32:1645-1647.
Xu WL, Xilinbaoleri, Liu H, Wang RZ, Bai JP (2012a) Spinal cord biological safety of image-guided radiation therapy versus conventional radiation therapy. Neural Regen Res 7:2755-2760.
Xu WL, Miao XG, Tayierjiangjulaiti, Zhao XB, Wang H, Yuan H (2012b) Effect of intensity modulated radiation therapy on echinococcosis of bone in rat of Xinjiang. Zhongguo Shiyong Yikan 39:41-43.
Xu WL, Miao XG, Tayierjiangjulaiti, Zhao XB, Wang H, Yuan H (2012c) Effect of perutaneous pedicle screw fi xation on thoraco-lumbar fractures. Zhongguo Shiyong Yikan 39:41-43.
Xu WL, Waresijiangniyazi, Tayierjiangjulaiti, Miao XG, Zhao XB, Wang H, Yuan H (2012d) Studies on the killing effect of echinococcosis of bone by intensity modulated radiation therapy combined with Albnedazole in rat of Xinjiang. Yixue Dongwu Fangzhi 28: 1181-1183.
Xu WL, Xu JB, Sun JG, Zhou WZ, Zhao XB, Wang H, Yuan H (2014) Experimental study on the killing effect of protoscolex of bone echinococcosis by intensity modulated radiation therapy. Xinjiang Yike Daxue Xuebao 37:817-820.
Yin LJ, Yu XB, Ren YG, Gu GH, Ding TG, Lu Z (2013) Utilization of PET-CT in target volume delineation for three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and atelectasis. Multidiscip Respir Med 8:21.
Yuan Q, Li B, Hu K, Zhang MY, Duo J, Chen C, Li X, Xiang ZW (2013) Killing effect on in vitro exposure of Echinococcus protoscoleces to Gamma-ray. Zhongguo Ren Shou Gonghuanbing Xuebao 29:904-908.
Zhang XM, Li YX, Wang WH, Jin J, Wang SL, Liu YP, Song YW, Ren H, Fang H, Zhou LQ, Chen B, Qi SN, Liu QF, Lu NN, Liu XF, Yu ZH (2013) Favorable outcome with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy and radiotherapy for adult patients with early stage primary systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 90:195-201.
Zhang YF, Xie ZR, Ni YQ, Mao R, Qi HZ, Yang YG, Jiang T, Bao YX (2011) Curative effect of radiotherapy at various doses on subcutaneous alveolar echinococcosis in rats. Chin Med J (Engl) 124:2845-2848.
Copyedited by McCarty W, Hindle A, Yu J, Qiu Y, Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
Hong Yuan, People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China, Doctoryuanhong@sina.com.
10.4103/1673-5374.143430
Shigui Yan, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China, zrjwsj@zju.edu.cn.
http://www.nrronline.org/
Accepted: 2014-07-08
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Meta analysis of olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation promoting functional recovery of motor nerves in rats with complete spinal cord transection
- Ultrasonographic reference values for assessing normal radial nerve ultrasonography in the normal population
- Penile erectile dysfunction after brachial plexus root avulsion injury in rats
- Synergistic actions of olomoucine and bone morphogenetic protein-4 in axonal repair after acute spinal cord contusion
- Ganglioside promotes the bridging of sciatic nerve defects in cryopreserved peripheral nerve allografts
- Combining acellular nerve allografts with brainderived neurotrophic factor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells restores sciatic nerve injury better than either intervention alone

