On Primely Drazin Inverse in Rings
LI Jiechen, CHEN Huanyin
(School of Science, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 311121, China)
Abstract: An element a∈R has primely Drazin inverse in case there is an element b∈R satisfying bab=b, b∈comm2(a) and a-a2b∈P(R), where P(R) is the prime radical of R.The elementary properties of such Drazin inverse in rings are studied. And Jacobson’s lemma and Cline’s formula are proved to be applicable for primely Drazin inverse.
Key words: Drazin inverse; Jacobson’s lemma; Cline’s formula; Prime polarity
1 Introduction
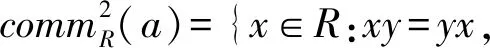
b=bab,ab=ba,a-a2b∈N(R).
The elementbabove is unique if it exists and is denoted byaD, and the nilpotency index ofa-a2bis called the Drazin index ofa, denoted byind(a). Moreover,aD∈comm2(a)(see [2]). Cline showed that ifabis Drazin invertible, then so isbaand in this case (ba)D=b((ab)D)2a. The concept of the generalized Drazin inverse in a Banach algebra was introduced in 1996 by Koliha(see [1]). Later, this notion was extended to elements in a ring by Koliha and Patricio(see [2]). An elementa∈Ris generalized Drazin invertible in case there is an elementb∈Rsatisfying
bab=b,b∈comm2(a),a-a2b∈Rqnil.
Suchb, if it exists, is unique, it is called the generalized Drazin inverse ofa, and will be denoted byad.
In this paper, we are concerned with a new kind of Drazin inverse. LetP(R) be the prime radical of a ringR. As is well known the prime radical is exactly the set of all strongly nilpotent elements inR. An elementa∈Rhas primely Drazin inverse in case there is an elementb∈Rsatisfyingbab=b,b∈comm2(a),a-a2b∈P(R). Elementary properties of such Drazin inverses in a ring are investigated. Jacobson’s Lemma and Cline’s formula for primely Draizn inverses are thereby obtained(see [3-5]).
2 Primely Drazin Inverses
We begin with a new concept:
Definition 1An elementa∈Rhas primely Drazin inverse if there existsb∈Rsuch that
bab=b,b∈comm2(a),a-a2b∈P(R).
Lemma 1LetRbe a ring, and leta∈R. Then the following are equivalent:
(1)a∈Rhas primely Drazin inverse.
(2) There exists an idempotente∈comm2(a) such thata+e∈U(R) andae∈P(R).
(3) There existsbsuch thatbab=b,b∈comm(a) anda-a2b∈P(R).
Proof(1)?(2) Choosee=1-ab.
Step 1e2=(1-ab)2=1-ab-ab+a2b2=a-2ab+ab=1-ab=e. Letx∈comm(a). Then (1-ab)x=x(1-ab) sincexa=ax,e∈comm2(a).
Step 2ae=a(1-ab)=a=a2b∈P(R). Thenae∈U(R).
Step 3be=b(1-ab)=b-b2a=b-ab2=eb=0 sinceb∈comm2(a). (a+e)(b+e)=ab+ae+eb+e=1-e+ae+e=1+ae∈U(R). Analogously, (b+e)(a+e)=1+ea∈U(R). Thusa+e∈U(R). Therefore,Ris primely polar.
(2)?(1) For anya∈R, there existse2=e∈comm2(a) such thatu=a+e∈U(R) andae∈P(R). Chooseb=(a+e)-1(1-e).
Step 1 Letx∈comm(a), thenax=xa,ex=xe. We getx(a+e)-1=(a+e)-1xsince (a+e)x=x(a+e). Hencexb=bx,b∈comm2(a).
Step 2 Since (a+e)(1-e)=(1-e)a, we getb=(a+e)-1(1-e)=b(1-e). Thenb=b2a.
Step 3a-a2b=a-a2(a+e)-1(1-e)=a-a(a+e)(a+e)-1(1-e)=a-a(1-e)=a-a+ae∈P(R).
(1)?(3) This is obvious.
(3)?(1) SinceP(R)?N(R),bis the Drazin inverse ofa, and sob∈comm2(a),as required.
□
Lemma 2Leta∈R. Thena∈RDif and only if there exists an idempotentpsuch thatp∈comm2(a),a+p∈U(R) andap∈N(R).
ProofSee [1, Lemma 2.4].
Theorem 1LetRbe a ring, and leta∈R. Then the following are equivalent:
(1)a∈Rhas primely Drazin inverse.
(2) There exists a unique idempotente∈comm2(a) such thata+e∈U(R) andae∈P(R).
Proof(2)?(1) This is obviou by Lemma 1.
(1)?(2) AsP(R)?N(R), we obtain the result by [2, Proposition 2.3].
Any elemente∈Rsatisfying the preceding condition isp-spectral idempotent ofa, denote it byae. Any elementb∈Rsatisfying these conditions is called the primely Drazin inverse ofa, and denote the primely Drazin inverse byap. We useRpto stand for the set of all primely Drazin invertible elements ofR.
3 Jaconson’s Lemma
The following lemma is known as Jacobson’s Lemma for invertible elements in a ring:
Lemma 3([6, Lemma 2.1]) Leta,b∈R. Ifα=1-ab∈U(R), thenβ=1-ba∈U(R) and (1-ba)-1=1+b(1-ab)-1a.
We now extend Jacobson’s Lemma to primely Drazin inverses in a ring.
Lemma 4Leta∈R. Ifahas primely Drazin inverse, thenahas Drazin inverse.
ProofWe know that a strongly nilpotent element is nilpotent. ThenP(R)?N(R). Henceahas Drazin inverse if it has primely Drazin inverse.
□
Theorem 2Letα=1-ab,β=1-ba. Thenα∈Rhas primely Drazin inverse if and only ifβ∈Rhas primely Drazin inverse. In this case,
βp=1+b(1-αeα)-1(αp-αe)a=1+b[αp-αe(1-αeα)-1]a,
and
βe=bαe(1-αeα)-1a.
ProofDenotep=αe. By Lemma 1,p2=p∈comm(α),αp∈P(R),α+p∈U(R). Hence, 1-αp∈U(R). Letq=bp(1-pα)-1a. Note thatβb=bαandαβ=αa. Thenβq=bαp(1-pα)-1a=bp(1-pα)-1αa=qβ. In what follows, by Lemma 1, we shall prove the following conditions hold: (a)β+q∈U(R); (b)βq∈P(R); (c)q2=q∈comm2(β).
(a) Writec=[p(1-pα)-1-1]a. Then we obtain 1+cb∈U(R). By Lemma 3, 1+bcis also invertible. Hence
β+q=1-ba+bp(1-pα)-1a=1+bc∈U(R).
(b) By hypothesis,αp∈P(R). Since the prime radicalP(R) is a two-sidedd ideal ofR, we have
βq=(1-ba)bp(1-pα)-1a=(b-bab)p(1-pα)-1a=
b(1-ab)p(1-pα)-1a=b(pα)(1-pα)-1a∈P(R).
(c) Note thatpab=p(1-pα). Then
q2=b(1-pα)-1pab(1-pα)-1pa=b(1-pα)-1pa=q.
As done in generalized Drazin inverse, we easily proveq∈comm2(β).
Therefore,qsatisfies (a),(b) and (c).
As we easily see that ifαhas primely Drazin inverse, then it has Drazin inverse, andαp=αD, we easily obtain the formula by [6, Theorem 2.3].
? This is symmetric.
□
Corollary 1LetA∈Mm×n(R),B∈Mn×m(R). ThenIm+AB∈Mm×m(R) has primely Drazin inverse if and only ifIn+BA∈Mn×n(R) has primely Drazin inverse.
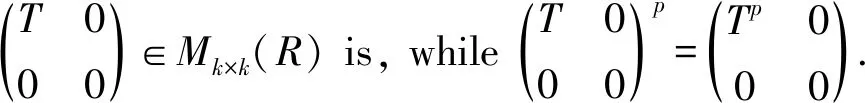
□
4 Cline’s Formula
Recall that for anya,b∈R,abhas Drazin inverse if and only ifbahas Drazin inverse. This is known as Cline’s formula for Drazin inverse. We have
Theorem 3Letα=ab,β=ba. Ifαhas primely Drazin inverse, then -β2has primely Drazin inverse, and
(-(ba)2)p=-(b((ab)p)2a)2.
ProofLetα=ab,β=ba. Setp=1-αpαandq=1-bαpa. Thenp∈comm2(α),α+p∈U(R) andαp∈P(R). In what follows, we prove that
(i)-β2+q∈U(R); (ii)-β2q∈P(R); (iii)q2=q∈comm(-β2).
First, we have 1+(a-αpa)b=α+(1-αpα)=α+p∈U(R). By Lemma 2,
β+q=β+(1-bαpa)=1+b(a-αpa)∈U(R).
To show (iii), we check that
q2=(1-bαpa)(1-bαpa)=1-2bαpa+bαpααpa=1-bαpa=q.
Note that
βq=ba(1-bαpa)=ba-babαpa=ba-bαpaba=(1-bαpa)β=qβ.
(1)
Lety∈Rbe such thatyβ=βy, i.e.,
y(ba)=(ba)y.
(2)
As done in Cline’s formula combining this with Eq.(1) and (2), one has
(1-βq)yq(1-βq)=(1-βq)qy(1-βq).
We now check that
-β2q=-β2(1-bαpa)=-ba(1-bαpa)ba=-b(ab-abαpab)a=-b(pα)a∈P(R).
Thus, -β2q2=-(βq)2∈P(R); hence,βq∈Ris nilpotent. So 1-βq∈U(R). Hence,yq=qy,q∈comm2(β). This shows thatq∈comm(-β).
Sinceβq∈Ris nilpotent, we see that
(β-q)2=(β+q)2-4βq∈U(R).
It follows thatβ-q∈U(R). By the preceding proof,β+q,β-q∈U(R), we see thatβ2-q=(β+q)(β-q)∈U(R). So -β2+q∈U(R) andq∈comm(-β2). Then (i) and (iii)follow. Therefore, -β2has primely Drazin inverse.
Moreover,
(-β2)p=(-(ba)2)p=(-(ba)2)D=-((ba)D)2=-(b((ab)D)2a)2=-(b((ab)p)2a)2.
This completes the proof.
□
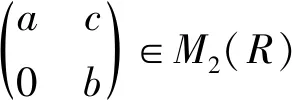
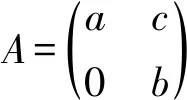
□
Theorem 4LetRbe a ring, and leta,b∈Randab=0. Ifa,bhave primely Drazin inverses, then -(a+b)2has primely Drazin inverses.
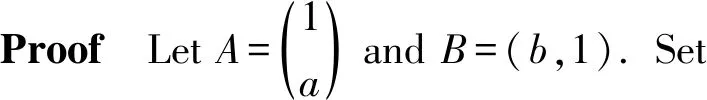
We see that
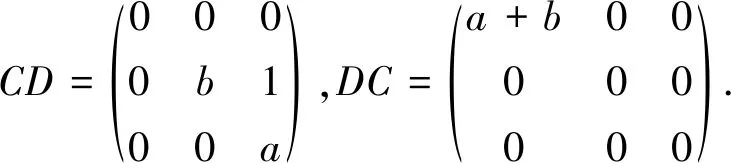
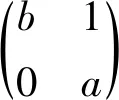
□
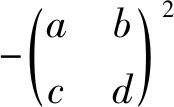
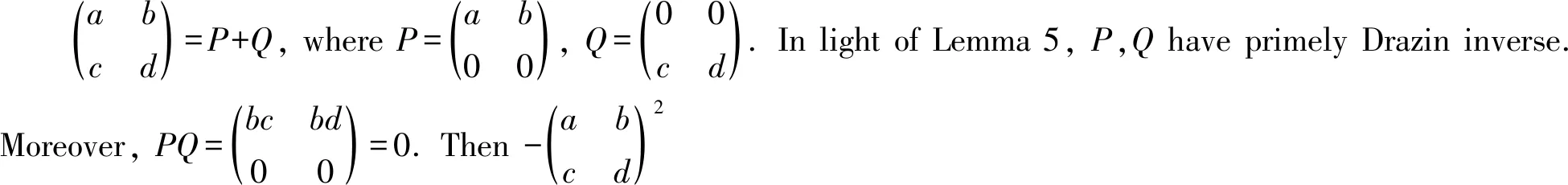
□
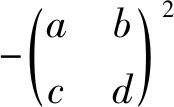
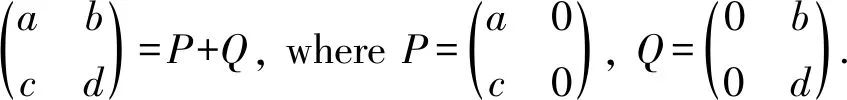
□
Furthermore, we can derive the following:
Theorem 5LetRbe a ring, and leta,b∈Randa2b=0,bab=0. Ifa,bhave primely Drazin inverses, then -(a+b)8has primely Drazin inverses.
where
As the primely Drazin inverse is Drazin inverse andP(R) is an ideal, we check thata2,b2have primely Drazin inverses. In view of Lemma 5, we see thatP,Qhave primely Drazin inverses. Sincea2b= 0 andbab= 0, we verify that
By virtue of Theorem 4, -M2has primely Drazin inverse. One easily checks that
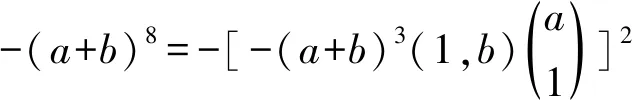
□

