Publication trends in studies examining radix notoginseng as a treatment for ischemic brain injury
Haiping Li, Luo Qiang, Chunyang Zhang, Chaohui Wang, Zhenxing Mu, Ligang Jiang
Department of Neurology, Af fi liated Hospital of Beihua University, Jilin, Jilin Province, China
Publication trends in studies examining radix notoginseng as a treatment for ischemic brain injury
Haiping Li, Luo Qiang, Chunyang Zhang, Chaohui Wang, Zhenxing Mu, Ligang Jiang
Department of Neurology, Af fi liated Hospital of Beihua University, Jilin, Jilin Province, China
Acute ischemic stroke has become a major disease burden with high mortality and morbidity rates. There is a lack of evidence-based medicine con fi rming the ef fi cacy of common treatments. Panax notoginseng saponins, the main active ingredient of radix notoginseng, have a neuroprotective role in ischemic brain injury, and have been popularized as a maintenance treatment for acute cerebral infarction and its sequelae. We conducted literature searches on the Web of Science, ClinicalTrials.gov, Cochrane Collaboration, CNKI, Wanfang and the China Scientific & Technological Achievements Database and analyzed the experimental and clinical outcomes of studies investigating the use of radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury to improve the understanding of relevant research trends and existing problems. We found that over the past 10 years, China has maintained its interest in Panax notoginseng research, while such studies are scarce on the Web of Science. However, Chinese researchers often focus on the neuroprotective role of radix notoginseng in ischemic brain injury, but there are no large-scale clinical data to con fi rm its ef fi cacy and safety. There remains a need for more rigorous large-sample randomized controlled clinical trials with long-term follow-up, to determine whether radix notoginseng lowers stroke recurrence and improves patient’s quality of life.
nerve regeneration; neuroprotection; Panax notoginseng; cerebral ischemia; stroke; Panax notoginseng saponins; basic; clinical; neural regeneration
Funding:This study was supported by a grant from the Scientific Research Project during the Twelvth Five-Year Period of Jilin Provincial Educational Bureau in China, No. 2013-441; a grant from the Scientific Research Project of Jilin Provincial Health Bureau in China, No. 2012Z102.
Li HP, Qiang L, Zhang CY, Wang CH, Mu ZX, Jiang L. Publication trends in studies examining radix notoginseng as a treatment for ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(17):1635-1642.
Introduction
Radix notoginseng is the dried root ofPanax notoginseng(Araliaceae). It is found in the wild in a narrow zone of southwest China, at 1,500 to 1,800 meters above sea level and at 23.5° north latitude (Jiangxi, Hubei, Guangdong, Guangxi, Sichuan, and Yunnan provinces). However, the majority of radix notoginseng used today is cultivated (Chu et al., 2001; Liu, 2009). According to thePharmacopoeia of the People’s Republicof China, radix notoginseng is used to induce hemostasis, alleviate blood stagnation and relieve pain. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that the main active ingredient of radix notoginseng isPanax notoginsengsaponins. Over 20 active saponins and 17 trace elements, as well as proteins, vitamins, and polysaccharides, have been extracted from high-quality radix notoginseng (Ng, 2006). Notoginsenoside R1, a majorPanax notoginsengsaponin, protects the brain against ischemia and hypoxia (He et al., 2011).
Ischemic stroke or cerebral infarction occurs when local blood circulation in the brain is blocked, resulting in ischemia and hypoxia. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury is considered to be the major pathophysiological process of ischemic cerebrovascular disease (Mergenthaler et al., 2004).
Since 2006,Panax notoginsengsaponins have become one of China’s fastest-growing drugs used in hospitals. Injectable preparations of radix notoginseng, including freeze-driedXueshuantongandXuesetongpowders containing over 60% notoginsenoside R1, have been used in the clinic for maintenance treatment of acute cerebral infarction and its sequelae (CAST, 1997). Fourteen manufacturers producePanax notoginsengsaponins approved by the China Food and Drug Administration, and there are approximately 750 approval documents for radix notoginseng preparations and 77 manufacturers of these drugs (Chu et al., 2001).
Data and Methods
Web of Science data analysis
Data source: Science Citation Index (SCI) Expanded, total of 8,765 journals.
Time span: 2009-2014.
Search terms: ts= (sanqi or “panax notoginseng”) & ts= (stroke or “cerebral infarction” or “brain ischemia”).
Inclusion criteria: Peer-reviewed published articles including original research, reviews, meetings, and conference abstracts.
Analysis method: A bibliometric analysis of articles concerning radix notoginseng preparations listed on the Web of Science was performed on the following data: publicationyear, publication outputs of countries and institutes, document types, and citation frequency.
Wanfang database analysis
Data source: 1,201 medical journals appeared in the Wanfang database (wanfangdata.com.cn).
Time span: 2005-2014.
Keywords [in Chinese]: Radix notoginseng, cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction and neuroprotection.
Inclusion criteria: Journal articles; academic dissertations; conference papers.
Analysis method: All papers retrieved were subjected to duplicate checking and sorting, before being summarized in combination with manual inspection. This was followed by statistical analysis in Excel. The annual data were analyzed to obtain a trend curve. Discipline distribution was confi rmed manually, and the discipline categories were classi fi ed according to the source of study object and academic disciplines of the authors.
Funding analysis based on CNKI
Data source: The CNKI database is the largest searchable database of academic literature in China, comprising abstracts and full texts of articles published in 10,112 journals. We conducted an in-depth analysis of the CNKI database according to discipline, publishing year, funding, research level, authors and agencies.
Time span: 2005-2014.
Keywords [in Chinese]: Radix notoginseng, cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction and neuroprotection.
Inclusion criteria: All articles included in the CNKI.
Analysis method: Funded articles were sorted and summarized in combination with manual inspection followed by statistical analysis in Excel.
Relevant achievement analysis based on the China Scientifc & Technological Achievements Database (CSTAD)
Data source: CSTAD is a database of achievements using new technology, which has become the most authoritative technical achievement database in China because of its level of accuracy and detail. In addition to new achievements and technology transfer, this database also provides technical advice and information sources for use in technical reform, product development and process innovation. There are 815,971 items in various disciplines of natural science, which include national-level scientific and technological achievements, with a scope of new technologies, products, processes, materials, and designs.
Time span: 2009-2014.
Keywords [in Chinese]: Radix notoginseng, cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction and neuroprotection.
ClinicalTrials.gov data analysis
Data source: ClinicalTrials.gov is a website that provides patients, family members, healthcare professionals, and members of the public easy access to information on clinical trials sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, other federal agencies, and the pharmaceutical industry, for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The US National Institutes of Health (NIH) developed the site through its National Library of Medicine in collaboration with the Food and Drug Administration and all NIH institutes. The site was made available to the public in February 2000 and currently contains 173,477 clinical studies conducted in 187 countries.
Time span: 2000-′2014.
Search terms: (sanqi or “panax notoginseng”) and (stroke or“cerebral infarction” or “brain ischemia”).
Inclusion criteria: (1) study participants are not yet being recruited; (2) participants are currently being recruited; (3) participants are being (or will be) selected from a predetermined population; (4) study is ongoing, but participants are not currently being recruited or enrolled; (5) the study has concluded normally and participants are no longer being examined or treated; (6) recruiting or enrolling of participants has halted prematurely but may resume; (7) recruiting or enrolling of participants has halted prematurely and will not resume and participants are no longer being examined or treated; (8) study halted prematurely, prior to enrollment of fi rst participant.
Meta-analysis of the Cochrane Library
The Cochrane Library (http://www.thecochranelibrary. com/) is a collection of databases in medicine and other healthcare specialties provided by the Cochrane Collaboration from 1992. Its aim is to make the results of well-conducted controlled trials readily available and is a key resource in evidence-based medicine. To date, 8,616 systemic reviews have been checked by the Cochrane Collaboration.
Time span: 1993-2014.
Search terms: (sanqi or “panax notoginseng”) and (stroke or“cerebral infarction” or “brain ischemia”).
Results
Web of Science
The Web of Science contains 783 papers addressing radix notoginseng as a treatment for ischemic brain injury, focusing mainly on pharmaceutical and chemical analysis. Only 26 out of the 783 papers are associated with the neuroprotective role of radix notoginseng; these have been cited 166 times in 141 articles (average times cited, 6.38; h-index, 9). These papers are mainly from China (22/26), as well as Korea and Japan.
Table 1 shows the most cited original articles addressing the use of radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury on the Web of Science from 2005 to 2014.
The top cited paper (Chen et al., 2009) is from the National Chung Hsing University, Graduate Institute of Biotechnology, Taiwan, China. The main research focus of the laboratory of Jason T. C. Tzen, the corresponding author, is the active ingredients of radix notoginseng and the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects in the human body.
The second and fi fth most popular papers were both from the Department of Pharmacology, Sun Yat-sen University, China. The relevant studies were funded by the NationalNatural Science Foundation of China (No. 30730105), National Basic Research Program of China (Program 973; No. 2009CB521903), and Science Foundation of Guangzhou in China. The corresponding author, Yongyuan Guan, works in a laboratory that studies the effects of radix notoginseng on ion channels and neuroprotection. In these two papers addressing the purified ingredients ofPanax notoginsengsaponins, the authors propose that ginsenoside Rd can significantly inhibit calcium overload following middle cerebral artery occlusion, prevent Ca2+in fl ux in vascular smooth muscle, dilate the cerebral blood vessels, and improve cerebral circulation; moreover, radix notoginseng can be used against glutamate-induced apoptosis in rat cortical neurons.
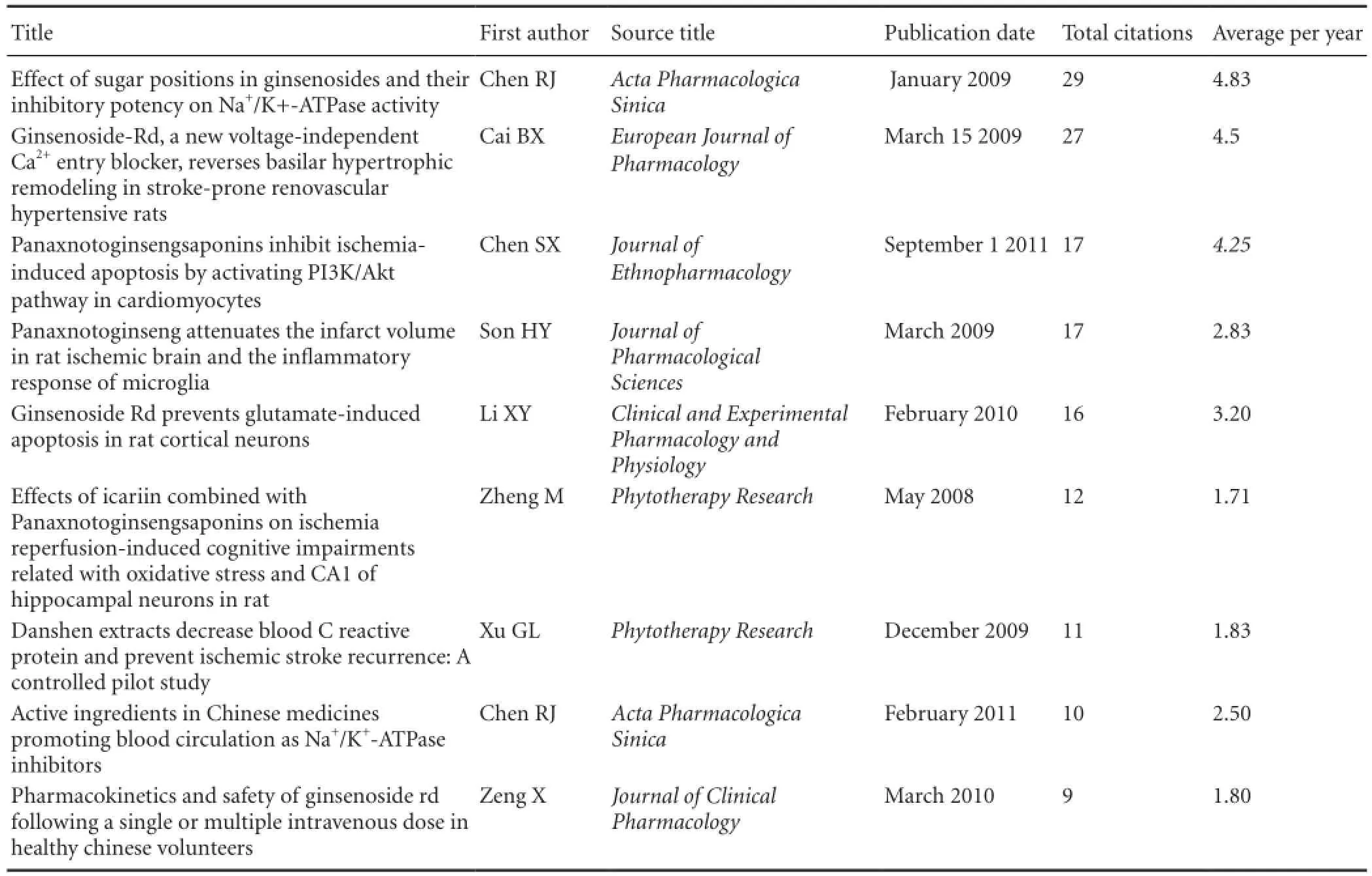
Table 1 Top 10 citations of original articles addressing the use of radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury on the Web of Science, from 2005 to 2014
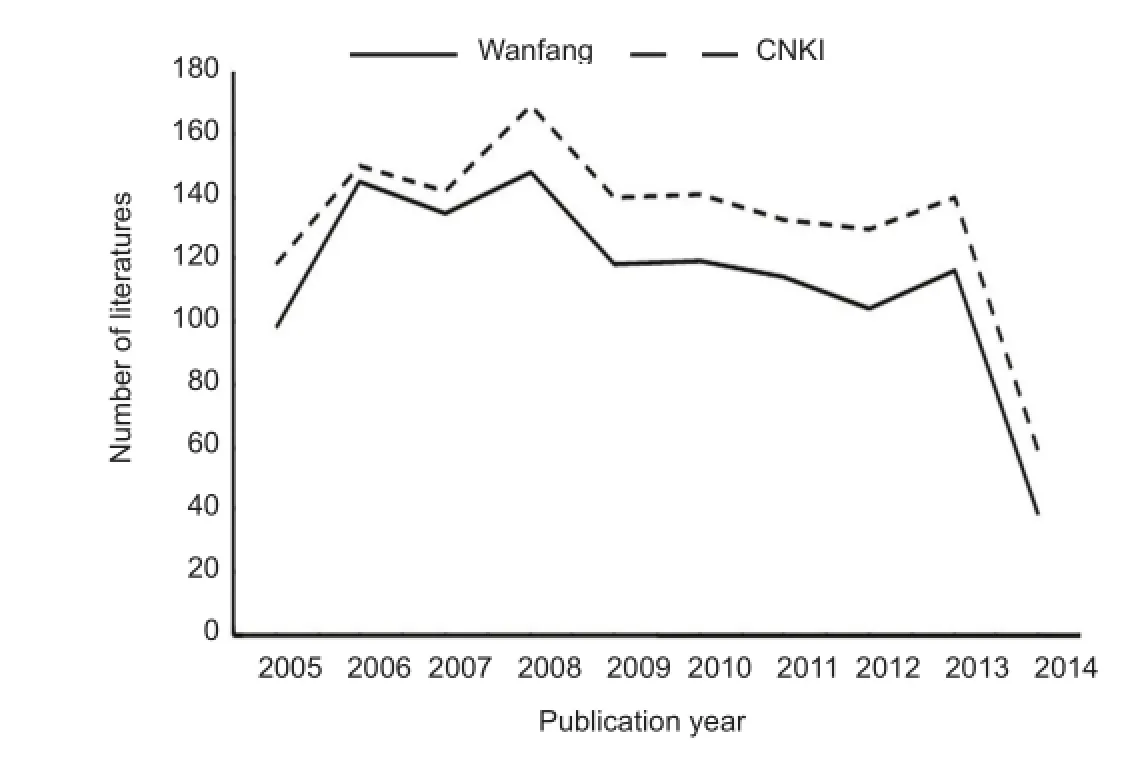
Figure 1 Comparison of the number of articles included in the CNKI and Wanfang databases between 2005 and 2014.
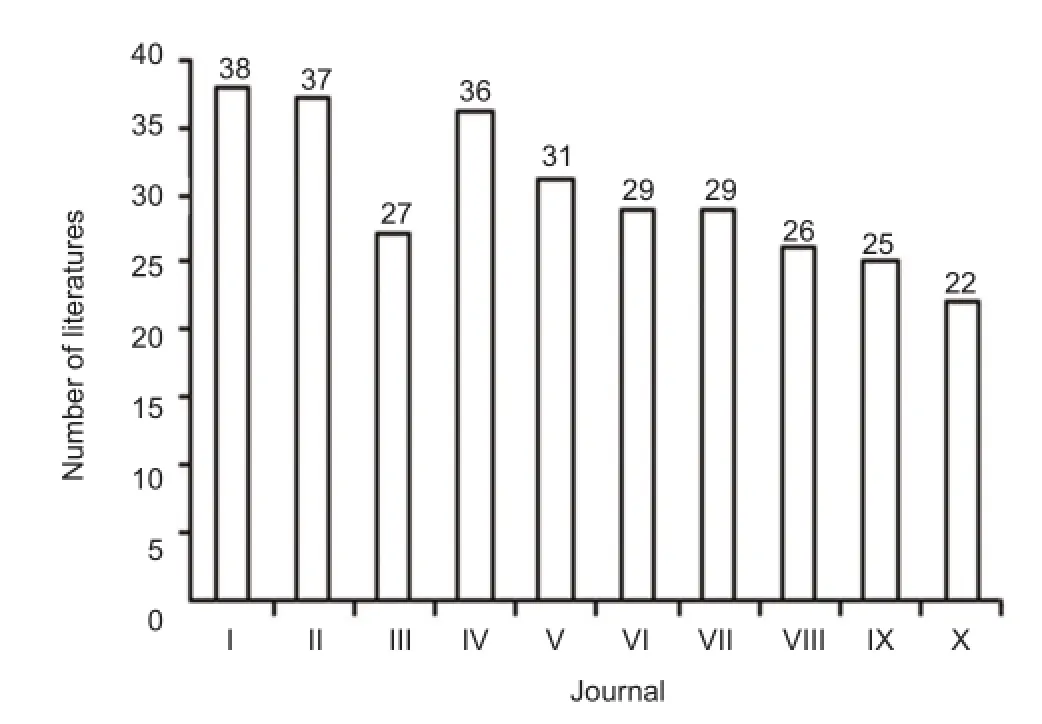
Figure 2 Top 10 journals with the most articles concerning the use of radix notoginseng for ischemic brain injury from 2005 to 2014.
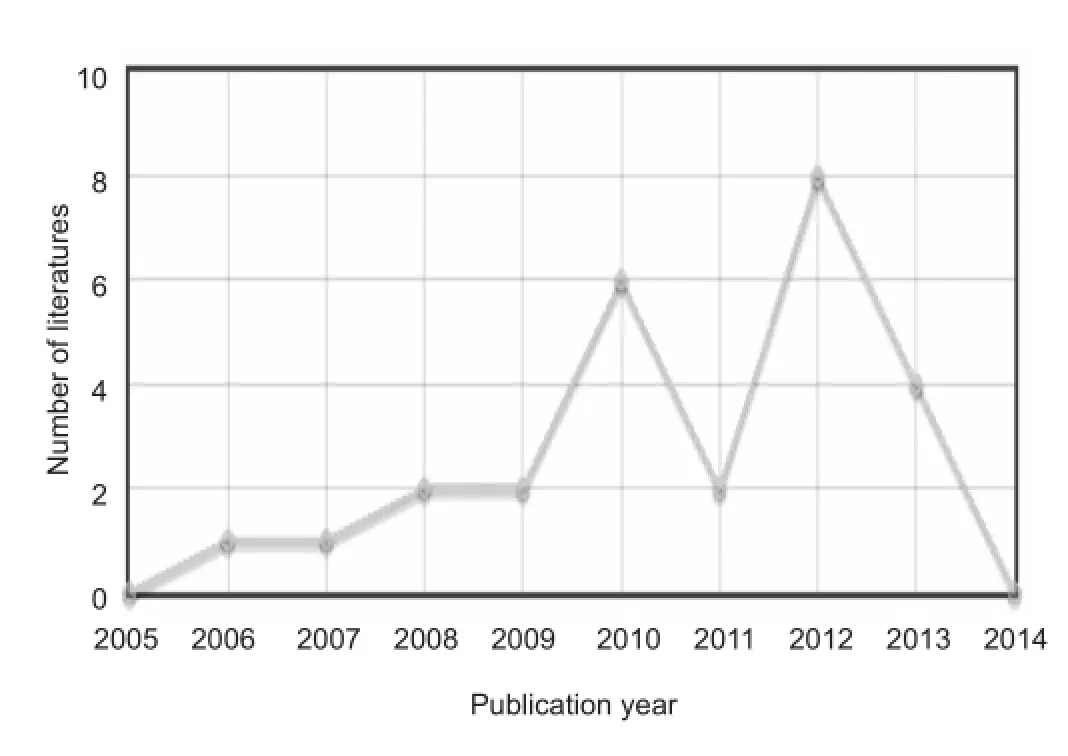
Figure 3 Articles by Changqing Deng in CNKI from 2005 to 2014.
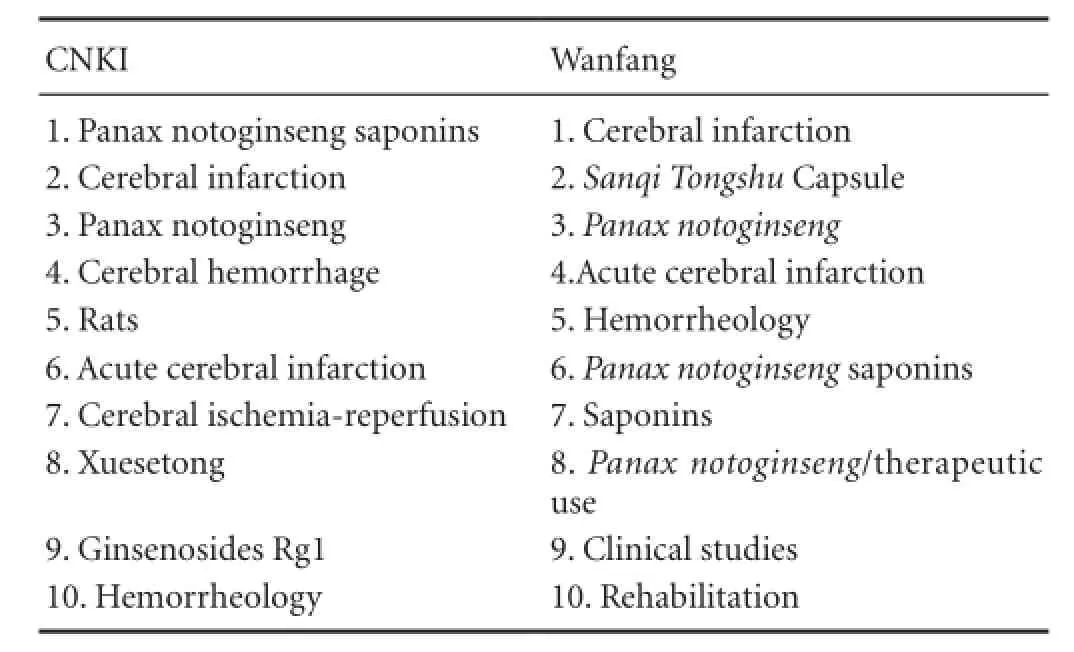
Table 2 Most popular keywords in articles addressing the use of radix notoginseng for ischemic brain injury in the CNKI and Wanfang databases
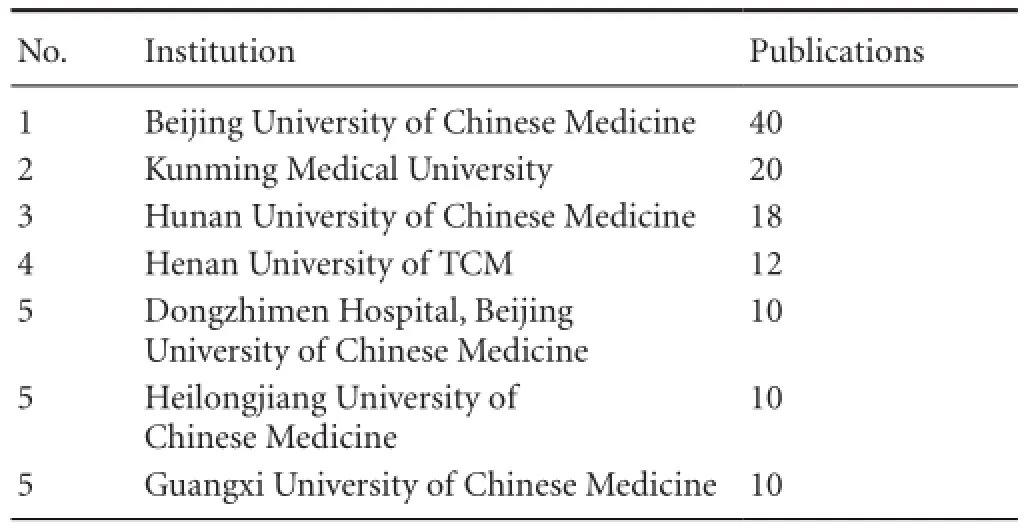
Table 4 Most productive institutions in CNKI from 2005 to 2014
The third most popular paper comes from Guangdong General Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Science, China. In this paper,Panax notoginsengsaponins are shown to protect local ischemia-induced apoptosisin vitroandin vivoby activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2011).
The fourth most popular paper came from Dongguk University, Korea (Son et al., 2009). Park and co-workers found that radix notoginseng eased in fl ammation in the infarcted region and reduced the infarct volume, providing sound evidence thatPanax notoginsengsaponins are effective against in fl ammation.
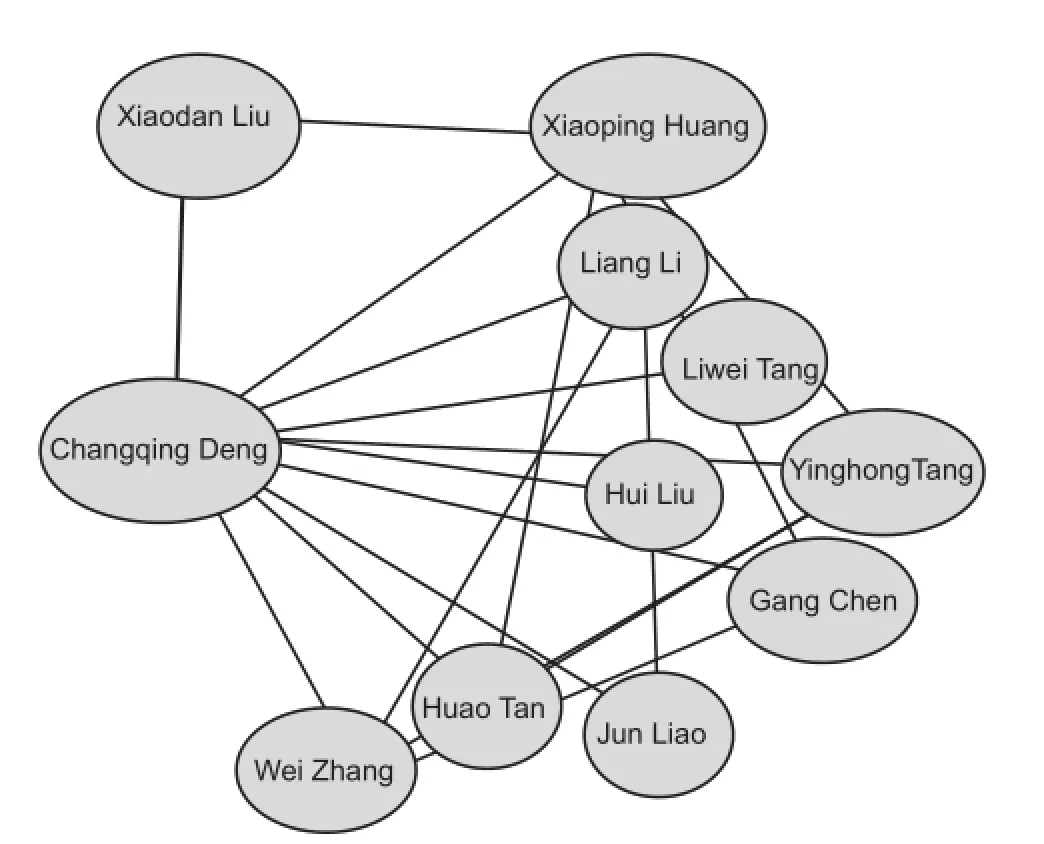
Figure 4 Distribution of authors collaborating with Changqing Deng from 2005 to 2014, according to the CNKI database.
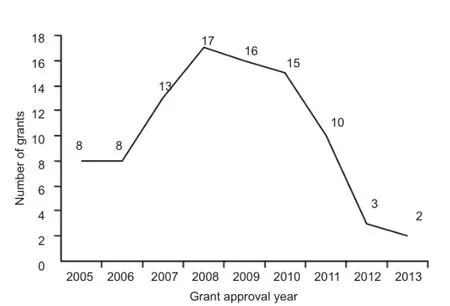
Figure 5 Achievements concerning radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury in CSTAD from 2005 to 2014.
The above papers were mainly published in the following journals listed in the SCI:Journal of Ethnopharmacology;Phytotherapy Research;Neural Regeneration Research;Journal of the Neurological Sciences;Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology.
Comparative analysis of Chinese databases
Research trends
Between 2005 and 2014, 1,320 papers addressing radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury were retrieved from the CNKI database, and 1,134 from the Wanfang database. Research trends are consistent between the two databases. The annual publication output was highest in 2008, with 169 and 148 papers included in CNKI and Wanfang, respectively. The number of publications increased fastest in 2006, with 150 and 145 papers included in CNKI and Wanfang that year, respectively, a growth of 27.12% and 47.96%. Publication volume decreased most in 2009, with only 140 and 118 new articles included in CNKI and Wanfang, respectively, or a decrease of 17.16% and 20.27% (Figure 1).
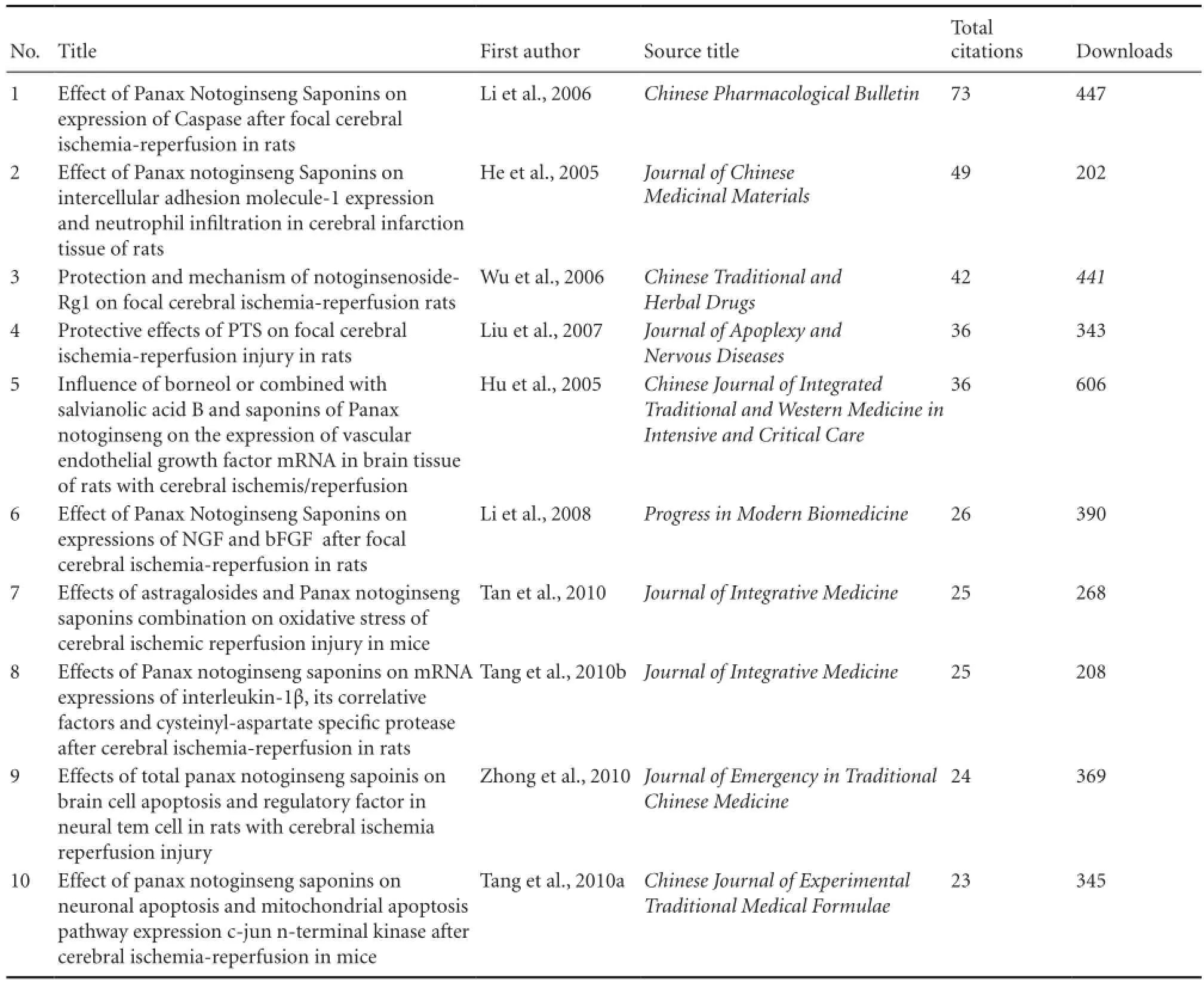
Table 3 The most-cited articles in the CNKI database, from 2005 to 2014, addressing radix notoginseng treatment of ischemic brain injury
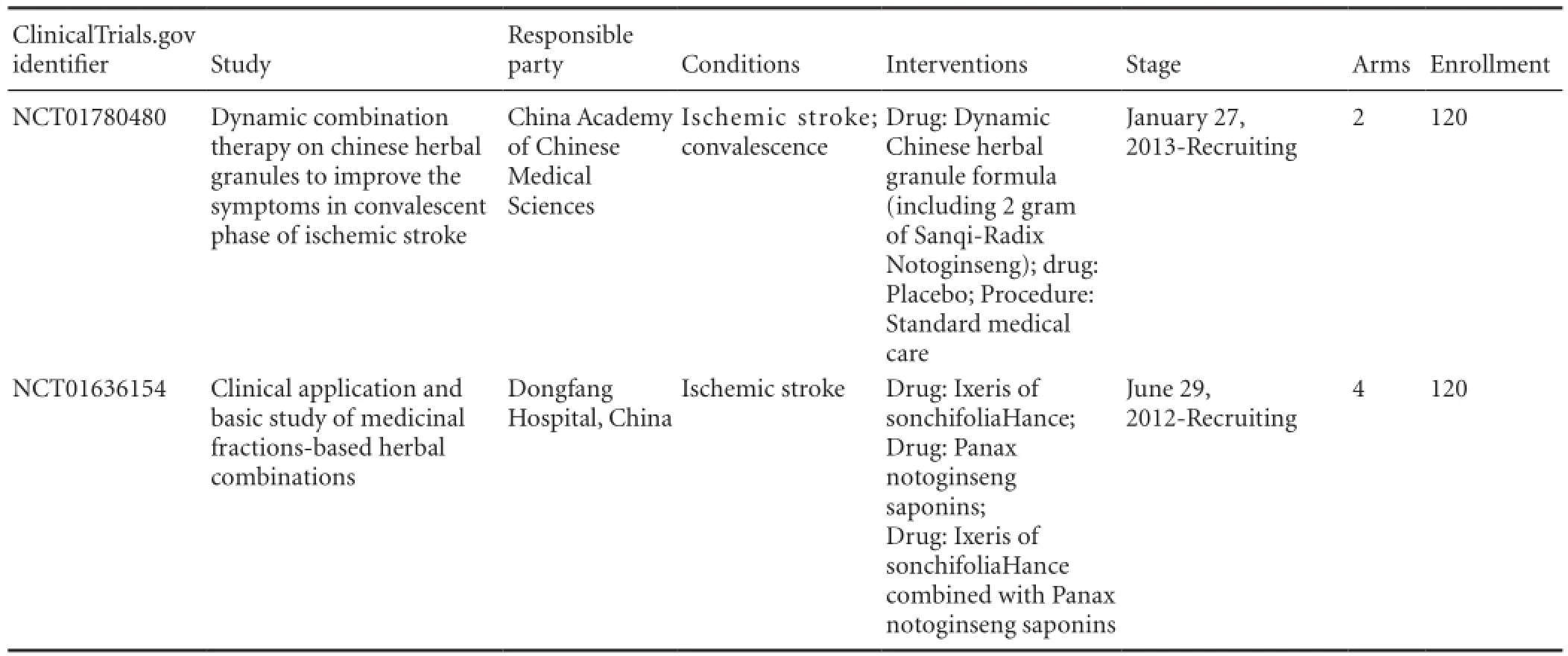
Table 5 Clinical trials of radix notoginseng as a treatment for ischemic brain injury listed in ClinicalTrials.gov.
Main journal output
A total of 1 320 articles concerning the use of radix notoginseng for ischemic brain injury were included in CNKI from 2005 to 2014, published mainly in the journals shown in Figure 2 and discussed below.
In the past 10 years, theChinese Traditional Patent Medicinehas published the most articles (38), among which the three most-cited are “Effect ofPanax notoginsengon cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats” (Jiang et al., 1995; 63 citations), “Effect ofPanax ginseng, Panax pseudoginseng, AcanthopanaxandSchisandraon protein biosynthesis in mouse brain” (Ye et al., 1993; 30 citations), and “Effect of Panax notoginseng saponins on the expression of BNDF in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion” (Zhang et al., 2008; 23 citations). The top three most downloaded articles are“Quantitative determination of notoginsenoside R1 and ginsenoside Rg1, Rb1 contents in Xinnao Guantong Guttate Pill by HPLC gradient elution method” (Liu et al., 2007; 240 downloads), “Effect of Sanqi Tongshu Capsule on Syp and PSD-95 expression of different periods of cerebral infarction” (Cui et al., 2008; 243 downloads), and “Advanced development of new preparation and component of Salvia andPanax notoginseng” (Zhang et al., 2011; 63 downloads).
Additionally, the three most-published journals in the non-TCM field arethe Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio/Cerebrovascular Disease, Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases,andChinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, with about 30 papers on radix notoginseng for ischemic brain injury (Figure 2).
Research hotspots
High-frequency keywords in the databases re fl ect the direction of research and commonly covered subjects, as well as the hot topics and research questions across different time periods. The 10 most popular keywords listed in articles related to the use of radix notoginseng for ischemic brain injury in the CNKI and Wanfang databases over the past 10 years are listed in Table 2.
Research fronts
The most relevant keywords relating to the treatment of ischemic brain injury with radix notoginseng occur in the Wanfang database, reflecting the research direction of cross-sectional studies in this field. The 10 most popular keywords searched by the researchers are: risk factors; hemorrheology; extraction process; ginseng; high performance liquid chromatography; thin layer chromatography; ginsenosides;Salvia mittiorrhiza; chemical composition; content determination. Based on these words, we can conclude that the researchers were more interested on the main active ingredients of radix notoginseng and the quality of its preparation, as well as the mechanisms underlying its effects in the treatment of ischemic brain injury.
Most-cited articles and authors
The most-cited articles in CNKI between 2005 and 2014, which address radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury, are listed in Table 3.
Changqing Deng (Li et al., 2006) is the corresponding author with the most citations and comes from Hunan University of Chinese Medicine in China. He is engaged in basic research onBuyang HuanwuTangandPanax notoginsengsaponins in the treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. His 34 articles are included in the Wanfang database and cited 256 times, with an h-index of 9.
Changqing Deng is a prolific author, publishing every year for the past decade. In 2012, he published eight articles (Figure 3). This author collaborates with the authors shown in Figure 4, who study radix notoginseng and neurological diseases, and has been repeatedly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Most productive institutions
Based on data from the CNKI database (2005-2014), the most productive institutions in this 10-year period are the Beijing University of Chinese Medicine with 40 articles and Kunming Medical University with 20 articles (Table 4).
Main funding projects
There are 39 funds across 1,320 articles in the CNKI database (2005-2014), including five national-level funds, 28 provincial-level and ministerial-level funds, 6 city-level funds. The national-level funds include the National Natural Science Foundation of China (43 items), China Postdoctoral Fund ( fi ve items), National Key Technology R&D Program of China (four items), National Basic Research Program of China, Program 973 (three items), National Key Science and Technology Program of China (one item), Scientific Research Fund of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of China (one item), and Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects (one item). Additionally, a total of 88 projects with published articles are funded by the 28 provincial-level and ministerial-level funds.
Technological achievements
We retrieved 92 rewarded or planned achievements concerning radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury at provincial-, municipal-level, and ministerial-levels from CSTAD between 2009 and 2014. Among these 92 achievements, 70 are related to medicine and health, and 22 to industrial technology. In 2008, the most funded project in China was supported by 17 funds, but this number shows a declining trend since 2008 (Figure 5).
ClinicalTrials.gov database
To date, only two clinical trials concerning radix notoginseng for ischemic brain injury have been registered in ClinicalTrials.gov, both of which come from China (Table 5).
Cochrane Library
Only one study, “Sanchi for acute ischaemic stroke”, classifiable as a randomized or quasi-randomized controlled clinical trial of Panax preparations for the treatment ofacute ischemic stroke, was retrieved in the Cochrane Library (http://www.thecochranelibrary.com/). The study was reported by Chen et al. (2008) from Huaxi Hospital of Sichuan University in China, and the relevant article was included by the Cochrane Stroke Group in 2008. The study focused on the evaluation of the therapeutic effect and safety of radix notoginseng in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, based on data from published literature retrieved from 15 clinical trial registers and bibliographic databases, including the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register, Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Cochrane Complementary Medicine Field Registry, EMBASE, CNKI, VIP, and the Wanfang database.
The authors screened a total of eight randomized controlled trials. A significant difference was found between radix notoginseng and placebo or no treatment in the therapeutic ef fi cacy against acute ischemic stroke within 30 days of treatment. There were 660 participants enrolled in the studies reported in these eight articles. Seven of the articles show poor quality, six of which have a follow-up period of less than 1 month. Only two of the eight articles show that if treatment continues for 28 days, the use of radix notoginseng can signi fi cantly reduce the mortality and disability of patients after acute ischemic stroke. One of these two articles reports a higher Barthel index in the patients undergoing radix notoginseng treatment. Comprehensive analysis of seven studies shows that radix notoginseng can signi fi cantly improve neurological de fi cits. The overall mortality rate is less than 1%, indicating that the participants mostly appear to have mild stroke and fewer adverse reactions. However, there is little information about the quality of life or stroke recurrence. Based on the available evidence, the authors conclude that radix notoginseng may be effective for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. However, the low number and poor quality of the included studies results in considerable bias, so we cannot be certain of the efficacy and safety of radix notoginseng in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
Discussion
The majority of the 1 320 articles from CNKI focus on experimental research to explore the mechanism of radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury, while the 1 134 articles from Wanfang mainly address its clinical use. Researchers are also concerned with the main active ingredients ofPanax notoginseng, the quality ofPanax notoginsengpreparations, and relevant clinical results.
Animal studies have found thatPanax notoginsengsaponins can significantly improve behavior symptoms, relieve brain edema, and reduce infarct size in rat models of cerebral ischemia. Cytological, morphological and lipid oxidation studies have shown thatPanax notoginsengsaponins can reduce serum malondialdehyde content and increase superoxide dismutase activity in the brain, suggesting that they protect against nerve cell damage from energy metabolism disorders, and also function as cerebrovascular regulators.
Literature on the mechanism ofPanax notoginsengsaponins has mainly concentrated on the following subjects: (1) the role ofPanax notoginsengsaponins in mouse global cerebral ischemia and rat focal cerebral ischemia; (2) their protective role in primary rat cerebral cortical neurons; (3) their effect on brain tissue blood supply; (4) their effect on energy metabolism; (5) their effect on intracellular free calcium concentration; (6) their effect on the calcium intake capacity of synaptosomes; (7) their effect on the release of excitatory amino acids and specific binding to the receptor; (8) their inhibitory effect on the oxidation of rat liver and brain homogenates and lipid peroxidation induced by the Fe2+/ascorbic acid system; (9) their effect on platelet function.
Only two trials on the use of radix notoginseng in the treatment of ischemic brain injury have been registered on ClinicalTrials.gov. Both are in the recruitment period and expected to recruit 120 cases, with no results announced yet.
Conclusion
In China,Panax notoginsenghas been used for a long time and is considered to be an effective treatment for ischemic stroke. Relevant articles about its clinical use, however, are lacking in quality. There remains a need for more rigorous large-scale randomized controlled clinical trials with extended follow-up periods to determine the clinical ef fi cacy ofPanax notoginsengin improving the quality of life and reducing stroke recurrence after acute ischemic stroke.
Cai BX, Li XY, Chen JH, Tang YB, Wang GL, Zhou JG, Qui QY, Guan YY (2009) Ginsenoside-Rd, a new voltage-independent Ca2+ entry blocker, reverses basilar hypertrophic remodeling in stroke-prone renovascular hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 606:142-149.
Chen RJ, Chung TY, Li FY, Lin NH, Tzen JT (2009) Effect of sugar positions in ginsenosides and their inhibitory potency on Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:61-69.
Chen RJ, Jinn TR, Chen YC, Chung TY, Yang WH, Tzen JT (2011) Active ingredients in Chinese medicines promoting blood circulation as Na+/K+ -ATPase inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:141-151.
Chen S, Liu J, Liu X, Fu Y, Zhang M, Lin Q, Zhu J, Mai L, Shan Z, Yu X, Yang M, Lin S (2011) Panax notoginseng saponins inhibit ischemia-induced apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt pathway in cardiomyocytes. J Ethnopharmacol 137:263-270.
Chen X, Zhou M, Li Q, Yang J, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Kong S, Zhou D, He L (2008) Sanchi for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev:CD006305.
Chu JJ, Liu L, Hua XG (2001) Overview of Sanchi and Sanchi industry. Dangdai Shengtai Nongye 10:116-121.
Cui FF, Zhai JY, Zou WM, Wang XL, Zou YH, Zhu LQ (2008)Effect of Sanqi Tongshu Capsule on Syp and PSD-95 expression of different periods of cerebral infarction. Zhong Cheng Yao 1:31-34.
CAST (Chinese Acute Stroke Trial) Collaborative Group(1997) CAST: randomised placebo-controlled trial of early aspirin use in 20,000 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet 349:1641-1649.
He L, Chen X, Zhou M, Zhang D, Yang J, Yang M, Zhou D (2011) Radix/rhizoma notoginseng extract (sanchitongtshu) for ischemic stroke. Lancet 349:9.
He W, Zhu ZP (2006) Effect of Panax notoginseng Saponins on intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and neutrophil in fi ltration in cerebral infarction tissue of rats. Zhong Yao Cai 5:403-405.
Hu LM, Zhang YJ, Wang W, Wu Y, Fan X, Gao XM, Zhang BL (2005) In fl uence of borneol or combined with salvianolic acid B and saponins of panax notoginseng on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA in brain tissue of rats with cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Jijiu Zazhi 12:263-266.
Jiang KY, Qian ZN(1995) Effect of panax notoginseng on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Zhong Cheng Yao 7:32-33.
Li H, Deng CQ, Chen BY, Chen RF, Zhang SP, Liang Y (2006) Effects of Panax Notoginseng Saponins on expression of Caspase after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao 2:189-193.
Li H, Deng CQ, Xiong AJ, Chen BY (2008) Effect of Panax Notoginseng Saponins on expressions of NGF and bFGF after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Xiandai Shengwu Yixue Jinzhan 2:219-221.
Li XY, Liang J, Tang YB, Zhou JG, Guan YY (2009) Ginsenoside Rd prevents glutamate-induced apoptosis in rat cortical neurons. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:199-204.
Liu CF, Wen YQ, Wang H, Chen SZ (2008) Quantitive determination of notogin senoside R1 and ginsenoside Rg1, Rb1 contents in Xinnao Guantong Guttate Pill by HPLC gradient elution method. Zhong Cheng Yao 29:1167-1169.
Liu XQ (2009) Clinical application of Sanchi. Linchuang Heli Yongyao Zazhi 2:88-89.
Liu ZC, Zhou GE, Zhao KJ, Rao Ml (2007) Protective effects of PTS on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats J Apoplexy Nerv Dis 1:38-40.
Mergenthaler P, Dirnagl U, Meisel A (2004) Pathophysiology of stroke: lessons from animal models. Metab Brain Dis 19:151-167.
Ng T (2006) Pharmacological activity of sanchi ginseng (Panax notoginseng). J Pharm Pharmacol 58:13.
Son HY, Han HS, Jung HW, Park YK (2009) Panax notoginseng attenuates the infarct volume in rat ischemic brain and the in fl ammatory response of microglia. J Pharmacol Sci 109:368-379.
Tan H, Huang XP, Deng CQ (2010) Effects of astragalosides and Panax notoginseng saponins combination on oxidative stress of cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury in mice. J Chin Integr Med 5:448-452.
Tang YH, Huang XP, Tan Hua, Chen BY, Deng CQ (2010a) Effect of Panax Notoginseng Saponins on neuronal apoptosis and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway expression c-Jun N-terminal kinase after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi 16:129-132.
Tang YH, Zhang SP, Liang Y, Deng CQ (2010b) Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on mRNA expressions of interleukin-1β, its correlative factors and cysteinyl-aspartate speci fi c protease after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. J Chin Integr Med 3:328-332.
Wu LO, Zhan HQ, Yan JL, Cai WF, Wu JP, Yang KK (2006) Protection and mechanism of notoginsenoside-Rg1 on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats. Zhong Cao Yao 37:229-233.
Xu G, Zhao W, Zhou Z, Zhang R, Zhu W, Liu X (2009) Danshen extracts decrease blood C reactive protein and prevent ischemic stroke recurrence: a controlled pilot study. Phytother Res 23:1721-1725.
Ye CY, Liu ZP (1993) Effect of Panax ginseng, Panax pseudoginseng,Acanthopanas and Schisandra on protein biosynthesis in mouse’s brain. Zhong Cheng Yao 16: 30-31.
Zeng X, Deng Y, Feng Y, Liu Y, Yang L, Huang Y, Sun J, Liang W, Guan Y (2010) Pharmacokinetics and safety of ginsenoside Rd following a single or multiple intravenous dose in healthy Chinese volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 50:285-292.
Zhang X, Chen G, Mu L(2011) Advanced development of new preparation and component of Salvia and Panax notoginseng. Zhong Cheng Yao 33:1568-1570.
Zhang YQ, Mo GH , Chen M, Zeng XF , Lu H (2008) Effect of panax notoginseng saponinsa on the expression of BDNF in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Zhong Cheng Yao 7:958-961.
Zheng M, Qu L, Lou Y (2008) Effects of icariin combined with Panax notoginseng saponins on ischemia reperfusion-induced cognitive impairments related with oxidative stress and CA1 of hippocampal neurons in rat. Phytother Res 22:597-604.
Zhong S, Chen WC, Xu YQ, Huang YZ, Yang JY, Zhang XY (2010) Effects of Total Panax Notoginseng Sapoinis on Brain Cell Apoptosis and Regulatory Factor in Neural tem Cell in Rats with Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jizheng 2:279-282.
Copyedited by Jackson C, Li CH, Wang L, Song LP, Zhao M
Ligang Jiang, M.D., Department of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Beihua University, Jilin 132021, Jilin Province, China, Beihua78726@163.com.
10.4103/1673-5374.141792
http://www.nrronline.org/
Accepted: 2014-08-14
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Stem cell transplantation for treating stroke: status, trends and development
- Virtual reality training improves balance function
- Neuroprotective effects of Buyang Huanwu decoction on cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal damage
- Methylmercury chloride damage to the adult rat hippocampus cannot be detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- Damage of hippocampal neurons in rats with chronic alcoholism
- Tooth loss inhibits neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice

